Содержание
- 2. Outline Software Quality Assurance Plan Definition of quality for software products Software Metrics Software Testing, types
- 3. Outcomes Understand the key parts of the Software Testing process Know how to identify the metrics
- 4. Software Quality Assurance Plan The purpose of the Software Quality Assurance Plan (SQAP) is to define
- 5. Software Quality Assurance Plan Set common templates (standards) Define the sequence of actions Ensure that standards
- 6. What is Quality? How do you understand the term Quality of software product? Is it rather
- 7. What is Quality? Verification – The evaluation of whether or not a product, service, or system
- 8. Fault, failure and error Fault/defect – a condition that may cause a failure in a system,
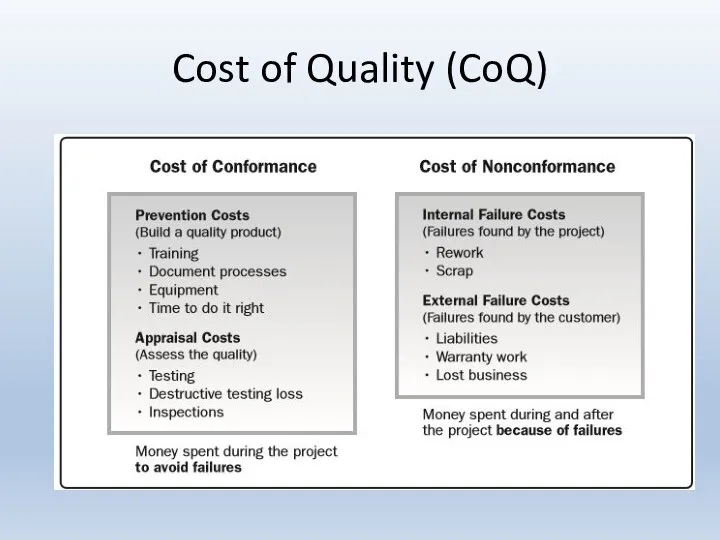
- 9. Cost of Quality (CoQ)
- 10. Software Project Metrics Tools for anyone involved in software engineering to understand varying aspects of the
- 11. Seven basic Quality tools
- 12. Software Metrics: effects of proper usage Reduce cost by 15% - 20% by just measuring Create
- 13. Software Project Metrics: types Life Cycle Step metrics Costs and budget metrics Requirements’ change metrics Development
- 14. Software Project Metrics in Agile An agile version of the Goal Question Metric (GQM) strategy. The
- 15. Software Project Metrics General Project Metrics: Completed activities budget (percentage of completed tasks) Actual budget ratio
- 16. Software Metrics Requirements Metrics: Frequency of change in the total requirements set Rate of introduction of
- 17. Software Metrics Process Metrics:
- 18. Software Metrics Product Metrics: Testing General Testing time Test cases metrics Passed/Failed Test Cases Not Run
- 19. What is Testing of SW? Maintaining a set of techniques for detecting and correcting errors in
- 20. Testing Test Plan - a document describing the scope, approach, resources and schedule of intended test
- 21. Testing Master Test Plan: A single high-level test plan for a project/product that unifies all other
- 22. Testing of SW? Who does the testing Programmers (developers) Testers Users (Alpha testing & Beta testing)
- 24. Testing of SW? Testing purposes: Acceptance testing Conformance testing Configuration testing; Performance testing; Stress testing; User
- 25. Requirements Traceability Matrix Requirement Traceability Matrix – Parameters include Requirement ID Risks Requirement Type and Description
- 26. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 27. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 28. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 29. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 30. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 31. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 32. Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 33. Product Complexity Metrics Source lines of code. Cyclomatic complexity, is used to measure code complexity. Function
- 35. Скачать презентацию































 Федеральный закон РФ о наркотических средствах и психотропных веществах
Федеральный закон РФ о наркотических средствах и психотропных веществах Закономерности диффузии дыхательных газов
Закономерности диффузии дыхательных газов Вспомогательное оборудование печатных машин
Вспомогательное оборудование печатных машин Двухэтажный каттедж с мансардой в блокированной застройке
Двухэтажный каттедж с мансардой в блокированной застройке Корпоративные производственные системы. Лекция 4
Корпоративные производственные системы. Лекция 4 Органическая химия – это наука, изучающая соединения углерода, или её ещё называют химией соединений углерода. Название «органиче
Органическая химия – это наука, изучающая соединения углерода, или её ещё называют химией соединений углерода. Название «органиче Наше Отечество - презентация для начальной школы
Наше Отечество - презентация для начальной школы Основные разделы правовой статистики
Основные разделы правовой статистики По математической сказке… МОУ «Сорская СОШ №3 с УИОП» Учитель: Канаева Татьяна Анатольевна
По математической сказке… МОУ «Сорская СОШ №3 с УИОП» Учитель: Канаева Татьяна Анатольевна Зацветёт, зазеленеет наш весёлый огород.
Зацветёт, зазеленеет наш весёлый огород. Новый Титаник
Новый Титаник FK Barcelona
FK Barcelona Библейские притчи. Притча о добром самарянине
Библейские притчи. Притча о добром самарянине Боевые искусства Древней Руси
Боевые искусства Древней Руси Структурные типы данных (Delphi / Pascal, глава 3)
Структурные типы данных (Delphi / Pascal, глава 3) Рукводство по заполнению отчета по практике
Рукводство по заполнению отчета по практике Леонардо Да Винчи: гениальная личность
Леонардо Да Винчи: гениальная личность Как люди ныряют в воду
Как люди ныряют в воду Гражданское общество: понятие, подсистемы, функции. Подготовила: Мишина Дарья
Гражданское общество: понятие, подсистемы, функции. Подготовила: Мишина Дарья Гигиеническое стоматологическое обучение и воспитание детей в организованных коллективах Санитарное просвещение – составн
Гигиеническое стоматологическое обучение и воспитание детей в организованных коллективах Санитарное просвещение – составн Словообразование и словоизменение. Обобщение. Учитель начальных классов МАОУ «Лицей №62» г. Саратова Лукьянова Ольга Анатоль
Словообразование и словоизменение. Обобщение. Учитель начальных классов МАОУ «Лицей №62» г. Саратова Лукьянова Ольга Анатоль Phraseologie
Phraseologie Туберкулез и сахарный диабет
Туберкулез и сахарный диабет Волейбол
Волейбол  Болонский процесс
Болонский процесс конференция отцов Гораздо легче стать отцом, чем остаться им В.Ключевский
конференция отцов Гораздо легче стать отцом, чем остаться им В.Ключевский Презентация "А.С.Пушкин на портретах художников О.Кипренского и В.Тропинина" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "А.С.Пушкин на портретах художников О.Кипренского и В.Тропинина" - скачать презентации по МХК Тестирование программного обеспечения. История и основные понятия
Тестирование программного обеспечения. История и основные понятия