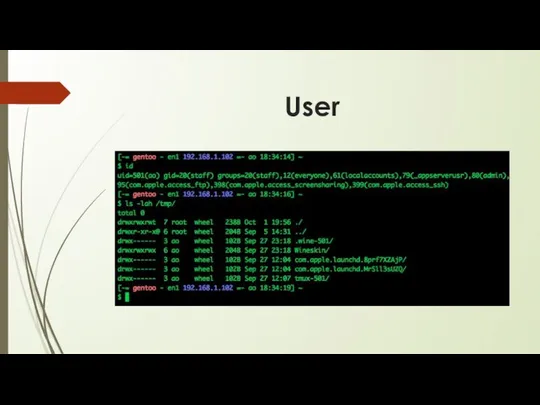
/etc/shadow file
root:$6$EA9l7lWI$1KXpR1dYwKe0icL0ohivqdyPdwzcxn0FuH.:16856:0:99999:7:::
Username, up to 8 characters. Case-sensitive, usually all lowercase. A
direct match to the username in the /etc/passwd file.
Password, encrypted.
The number of days since January 1, 1970 since the password was last changed.
The number of days before password may be changed (0 indicates it may be changed at any time)
The number of days after which password must be changed (99999 indicates user can keep his or her password unchanged for many, many years)
The number of days to warn user of an expiring password (7 for a full week)
The number of days after password expires, but can be used. Account will be disabled if pwd is not changed.
The number of days since January 1, 1970 when an account will be disabled
A reserved field for possible future use








 Средства массовой информации в политической системе
Средства массовой информации в политической системе УмкНАЧАЛЬНАЯ ШКОЛА 21 ВЕКА
УмкНАЧАЛЬНАЯ ШКОЛА 21 ВЕКА Activité#1. Тренажер
Activité#1. Тренажер Основы законодательства, регламентирующего обращения граждан в органы государственной власти и местного самоуправления
Основы законодательства, регламентирующего обращения граждан в органы государственной власти и местного самоуправления Игра для 4-6 классов
Игра для 4-6 классов От норм ГТО – к олимпийским медалям
От норм ГТО – к олимпийским медалям Программирование (Паскаль)
Программирование (Паскаль) Миграция рабочей силы США
Миграция рабочей силы США Виды рабочей одежды. Снятие мерок.
Виды рабочей одежды. Снятие мерок. Si-ФЭУ с улучшенными характеристиками
Si-ФЭУ с улучшенными характеристиками Общая характеристика экономических районов РФ
Общая характеристика экономических районов РФ Политология в системе социо-гуманитарного знания
Политология в системе социо-гуманитарного знания Stori'r Pasg
Stori'r Pasg Понятие власти
Понятие власти Презентация Назначение уложённой комиссии
Презентация Назначение уложённой комиссии  Таможенный тариф 1724 года. Принятие морского пошлинного тарифа 1731. Выполнил студент 1-го курса Т-102 Гулый Максим
Таможенный тариф 1724 года. Принятие морского пошлинного тарифа 1731. Выполнил студент 1-го курса Т-102 Гулый Максим Казаки на Кубани
Казаки на Кубани Электроснабжение объектов агропромышленного комплекса
Электроснабжение объектов агропромышленного комплекса Prostor. Телефония и комплексные услуги
Prostor. Телефония и комплексные услуги Особенности планирования и организации уроков рисования. Основы цветоведения. Методика ознакомления с живописью
Особенности планирования и организации уроков рисования. Основы цветоведения. Методика ознакомления с живописью ТЕМА 16. Бизнес-планирование Подготовка молодёжи к предпринимательской деятельности. Начальные шаги в бизнесе. Финансирование
ТЕМА 16. Бизнес-планирование Подготовка молодёжи к предпринимательской деятельности. Начальные шаги в бизнесе. Финансирование  Деятельность в социально-гуманитарной сфере и профессиональный выбор
Деятельность в социально-гуманитарной сфере и профессиональный выбор Терроризм и экстремизм как социальные опасные явления
Терроризм и экстремизм как социальные опасные явления Игра для потписчиков
Игра для потписчиков Причины государственного вмешательства в экономику.
Причины государственного вмешательства в экономику. Введение в объекты Java
Введение в объекты Java Техническая эксплуатация автомобилей в особых условиях
Техническая эксплуатация автомобилей в особых условиях Многоквартирные жилые дома
Многоквартирные жилые дома