Содержание
- 2. Water Pollution: Types, Effects, and Sources What is water pollution? Major types of pollutants, sources and
- 3. Major Categories of Water Pollutants Infectious Agents Bacteria, Viruses, Protozoa, Parasitic Worms Source: Human and animal
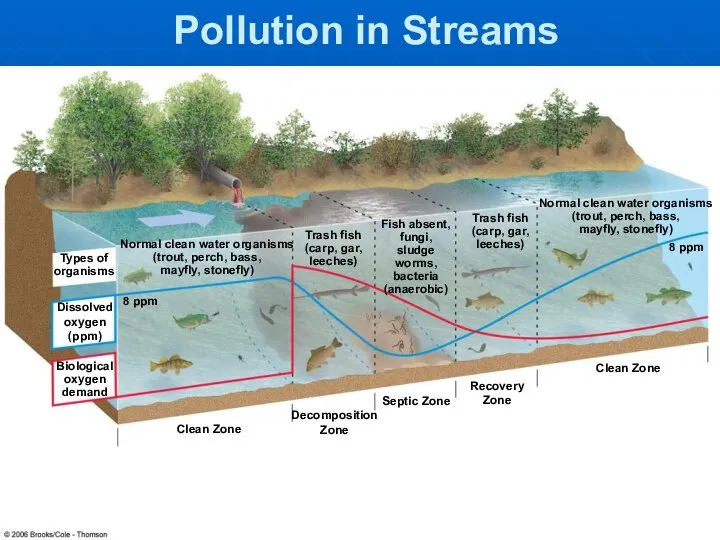
- 4. Pollution in Streams
- 5. Benefits of Floodplains Highly productive wetlands Provide natural flood and erosion control Maintain high water quality
- 6. Dangers of Floodplains and Floods Deadly and destructive Human activities worsen floods Failing dams and water
- 7. Before and During a Flood in St. Louis, Missouri
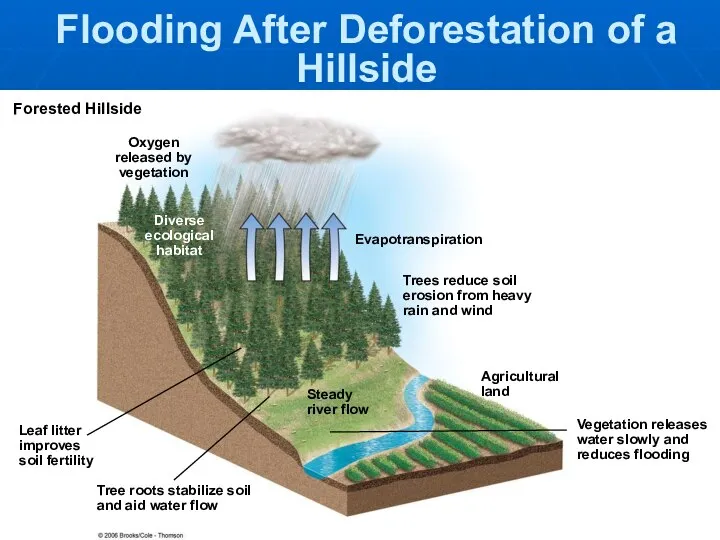
- 8. Oxygen released by vegetation Diverse ecological habitat Evapotranspiration Trees reduce soil erosion from heavy rain and
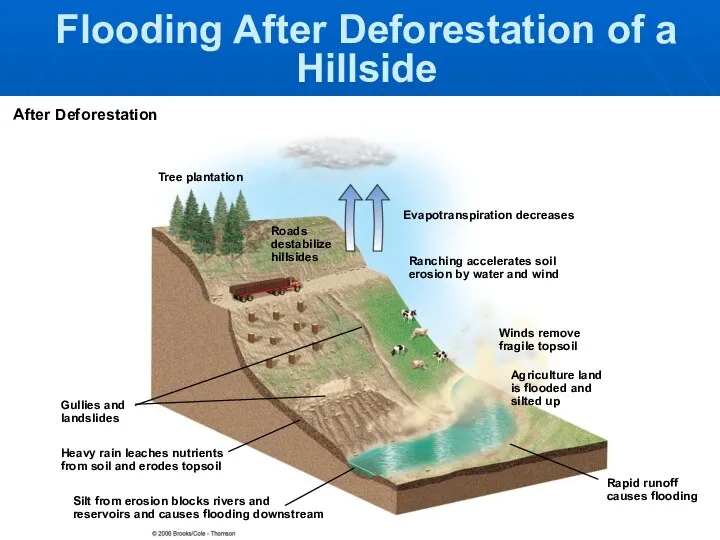
- 9. Tree plantation Evapotranspiration decreases Ranching accelerates soil erosion by water and wind Winds remove fragile topsoil
- 10. Reducing Flood Risks Channelization Levees (floodwalls) Dams Protect and restore wetlands Identify and manage flood-prone areas
- 11. Lake Pollution Dilution less effective than with streams Stratification in lakes and relatively little flow hinder
- 12. Oligotrophic and Eutrophic Lakes
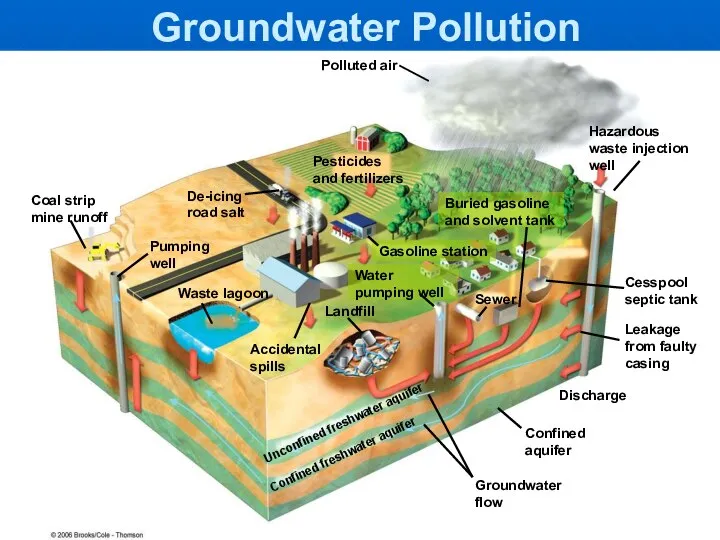
- 13. Groundwater Pollution: Causes and Persistence Sources of groundwater pollution Slow flowing: slow dilution and dispersion Consequences
- 14. Coal strip mine runoff Pumping well Waste lagoon Accidental spills Groundwater flow Confined aquifer Discharge Leakage
- 15. Extent of Groundwater Pollution Not much is known about groundwater pollution Organic contaminants, including fuel leaks
- 16. Pump nanoparticles of inorganic compounds to remove pollutants (may be the cheapest, easiest, and most effective
- 17. Ocean Pollution How much pollution can oceans tolerate? Some pollutants degrade and dilute in oceans Ocean
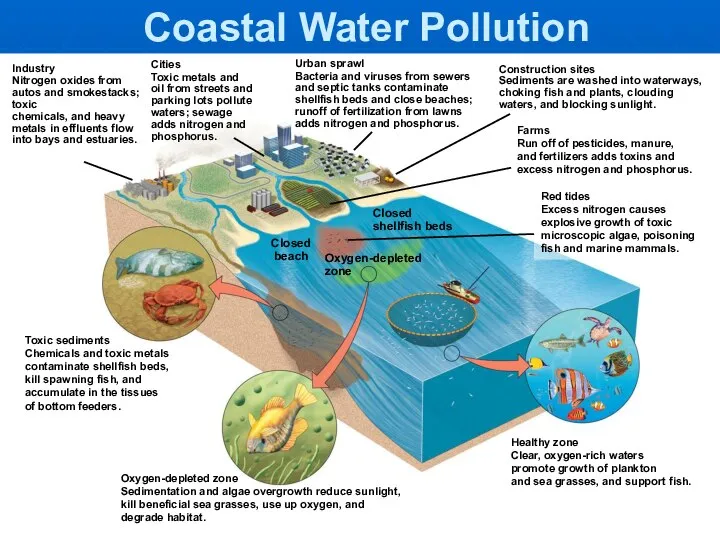
- 18. Industry Nitrogen oxides from autos and smokestacks; toxic chemicals, and heavy metals in effluents flow into
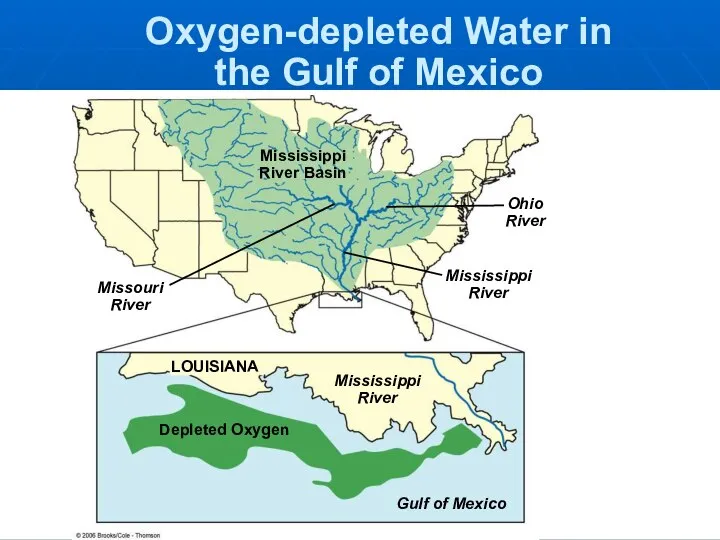
- 19. Mississippi River Basin Missouri River Ohio River Mississippi River LOUISIANA Mississippi River Depleted Oxygen Gulf of
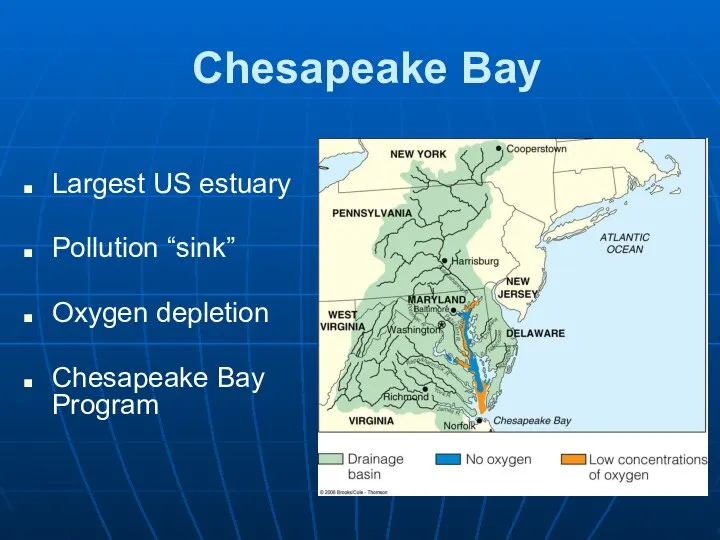
- 20. Chesapeake Bay Largest US estuary Pollution “sink” Oxygen depletion Chesapeake Bay Program
- 21. Effects of Oil on Ocean Life Crude and refined petroleum Tanker accidents and blowouts Exxon Valdez
- 22. Prevention Cleanup Ban dumping of wastes and sewage by maritime and cruise ships in coastal waters
- 23. Preventing Nonpoint Source Pollution Mostly agricultural wastes Use vegetation to reduce soil erosion Reduce fertilizer use
- 24. Laws for Reducing Point Source Pollution Clean Water Act Water Quality Act
- 25. Sewage Treatment Systems Sewage treatment in rural and suburban areas Septic tanks Primary (physical) sewage treatment
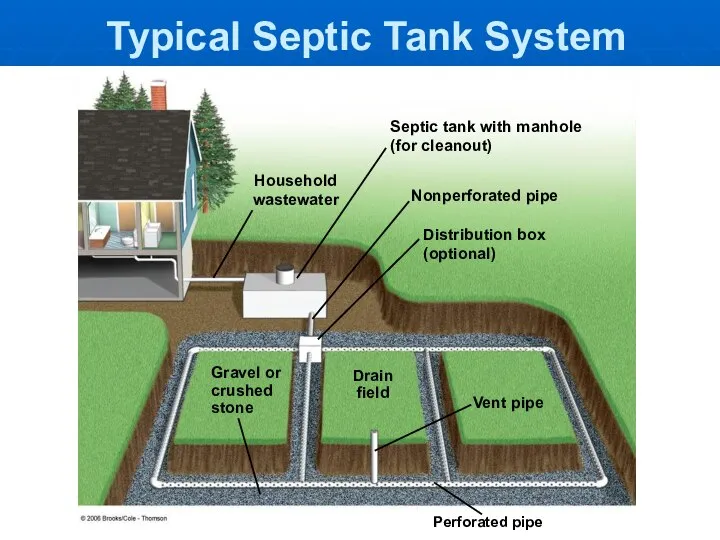
- 26. Typical Septic Tank System Household wastewater Perforated pipe Distribution box (optional) Septic tank with manhole (for
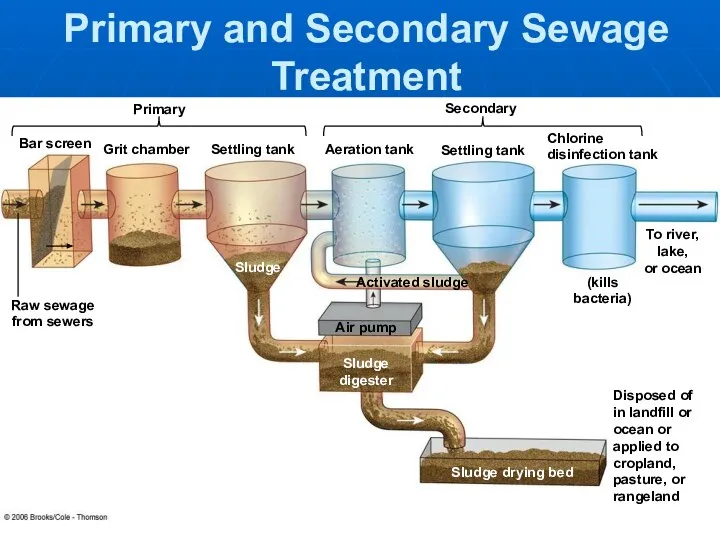
- 27. Primary and Secondary Sewage Treatment Raw sewage from sewers Bar screen Grit chamber Settling tank Aeration
- 28. Improving Sewage Treatment Systems that exclude hazardous wastes Non-hazardous substitutes Composting toilet systems Working with nature
- 29. Ecological Wastewater Treatment Burlington, VT University of Vermont
- 30. Should the Clean Water Act be Strengthened? Yes: environmentalists No: farmers, libertarians, manufacturers, and developers State
- 31. Drinking Water Quality Purification of urban drinking water Purification of drinking water in developing countries Bottled
- 33. Скачать презентацию





















 Организация розничной торговли. Розничный товарооборот
Организация розничной торговли. Розничный товарооборот Применение линейного программирования в математических моделях
Применение линейного программирования в математических моделях Права человека классный час в 3-4классах Педагог-организатор МОУ «СОШ №19» г. Энгельса Бумарскова Е.Н.
Права человека классный час в 3-4классах Педагог-организатор МОУ «СОШ №19» г. Энгельса Бумарскова Е.Н. Компоненты визуальных сред для работы с базами данных, через источники данных ODBC
Компоненты визуальных сред для работы с базами данных, через источники данных ODBC Эволюция подходов и принципов к управлению персоналом
Эволюция подходов и принципов к управлению персоналом Лыжная подготовка (5-9 классы)
Лыжная подготовка (5-9 классы) Электронные деньги vs Реальные деньги Битва 2012 Сергей Олейник Генеральный директор группы компаний «Аналитический Центр»
Электронные деньги vs Реальные деньги Битва 2012 Сергей Олейник Генеральный директор группы компаний «Аналитический Центр» Физическое воспитание, как социальное явление
Физическое воспитание, как социальное явление Изменение политической системы Российской Империи
Изменение политической системы Российской Империи Взрывчатые вещества и средства их взрывания. Действия правоохранительных органов при обнаружении взрывных устройств
Взрывчатые вещества и средства их взрывания. Действия правоохранительных органов при обнаружении взрывных устройств Итоговое тестирование. ИЗО. 4 класс
Итоговое тестирование. ИЗО. 4 класс Хронический панкреатит
Хронический панкреатит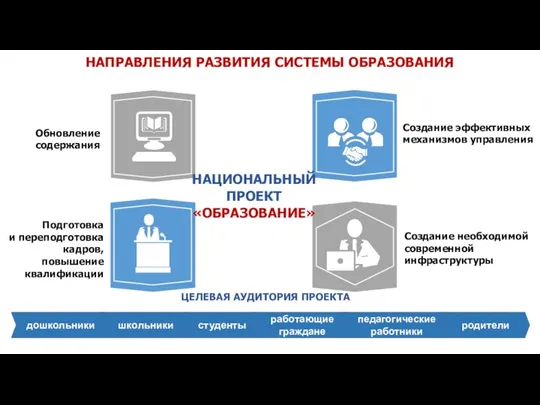 Направления развития системы образования
Направления развития системы образования Разработка методических рекомендаций по изучению FMS BOEING 767
Разработка методических рекомендаций по изучению FMS BOEING 767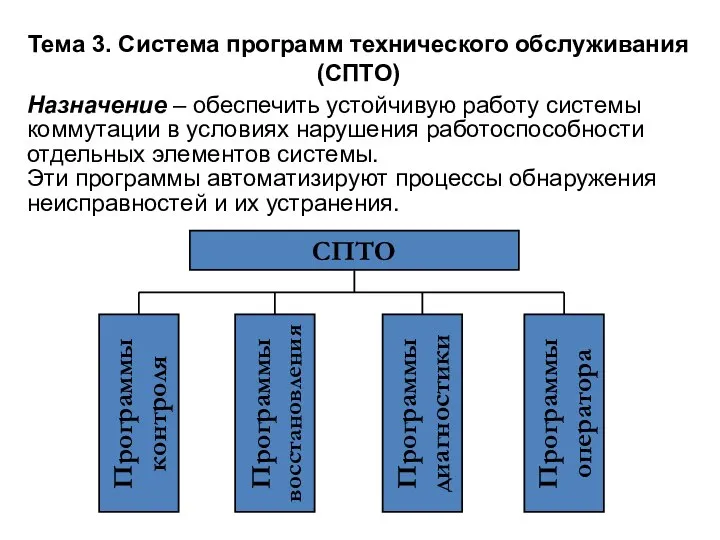 Ch10(СПТО)
Ch10(СПТО) Програмне забезпечення для Peer-To-Peer Lending платформи
Програмне забезпечення для Peer-To-Peer Lending платформи Теоремы сложения и умножения вероятностей. Формула ПВ, формула Байеса
Теоремы сложения и умножения вероятностей. Формула ПВ, формула Байеса Artikel. Noun
Artikel. Noun Government of the Russian Federation
Government of the Russian Federation Словарная работа. Декабрь, январь, февраль.
Словарная работа. Декабрь, январь, февраль. ссылки на интернет ресурсы
ссылки на интернет ресурсы  Христианство как мировая религия
Христианство как мировая религия Правила безопасного поведения при угрозе и во время наводнений 7 класс
Правила безопасного поведения при угрозе и во время наводнений 7 класс 10 шагов к успешному маркетингу через социальные медиа
10 шагов к успешному маркетингу через социальные медиа  Лондон и Париж
Лондон и Париж  История средних веков. Христианская церковь в раннее средневековье
История средних веков. Христианская церковь в раннее средневековье Нестандартно мыслим. Применение теоремы о среднем арифметическом и среднем геометрическом при доказательстве неравенств.
Нестандартно мыслим. Применение теоремы о среднем арифметическом и среднем геометрическом при доказательстве неравенств. Экскурсия по Ясной поляне
Экскурсия по Ясной поляне