Содержание
- 2. WHICH ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MODALS AND VERBS?
- 3. MODAL VERBS Can Be able to Can’t Could May Might Would *** Be able to and
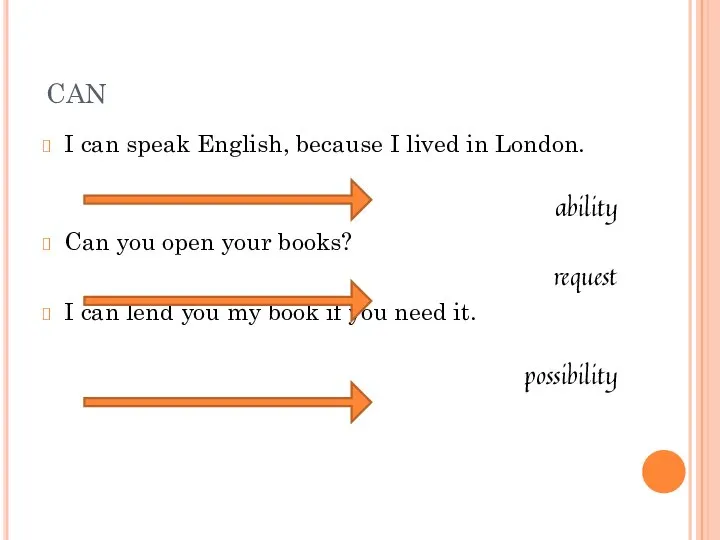
- 4. CAN I can speak English, because I lived in London. ability Can you open your books?
- 5. My brother is able to play football very well ability BE ABLE TO
- 6. COULD I could run very fast when I was a child. past ability Could you help
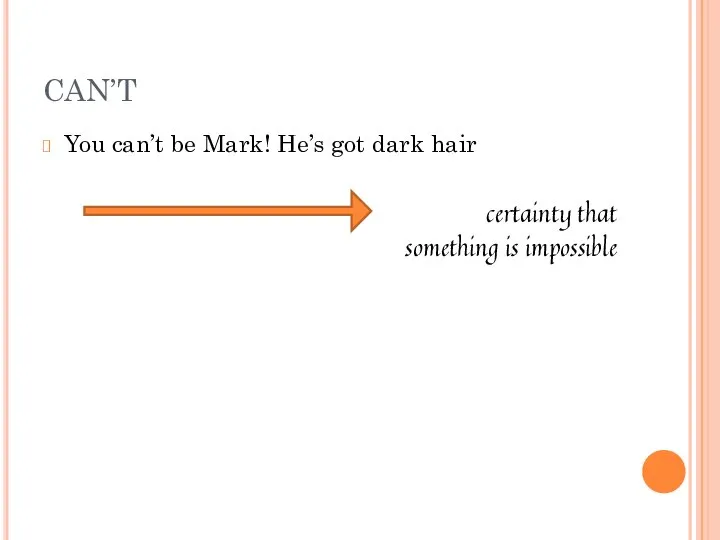
- 7. You can’t be Mark! He’s got dark hair certainty that something is impossible CAN’T
- 8. MAY It may rain next week possibility May I pay with a credit card? polite request
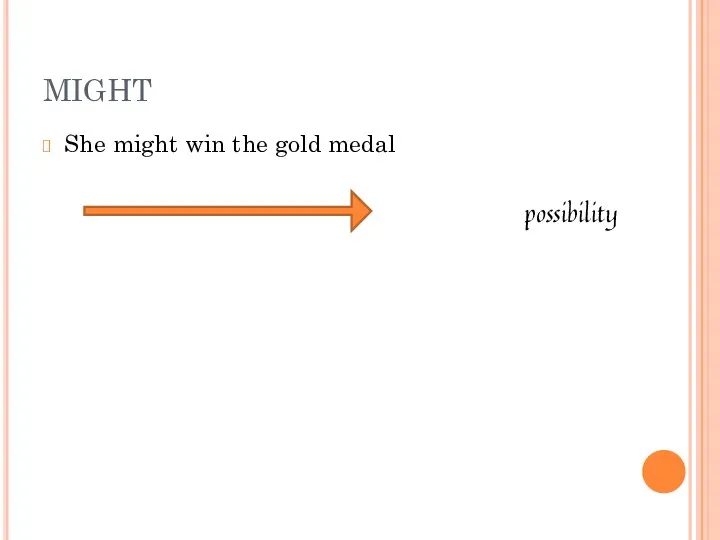
- 9. She might win the gold medal possibility MIGHT
- 10. WOULD Would you open the door, please? formal request Would you like some coffee? offer
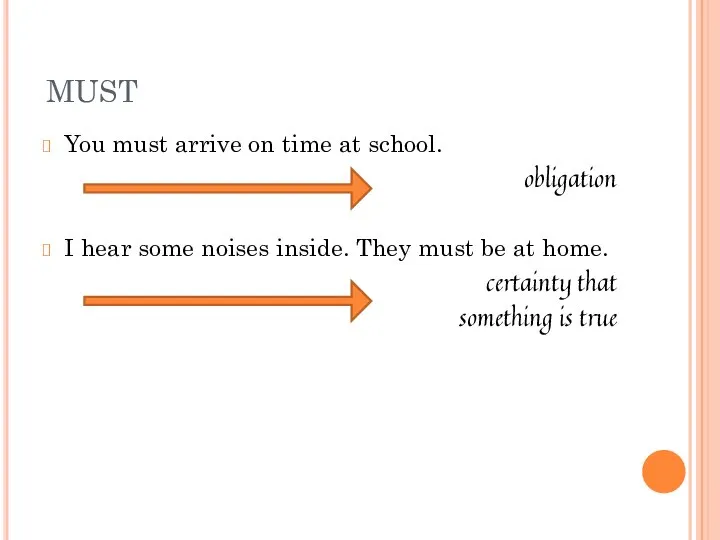
- 11. MUST You must arrive on time at school. obligation I hear some noises inside. They must
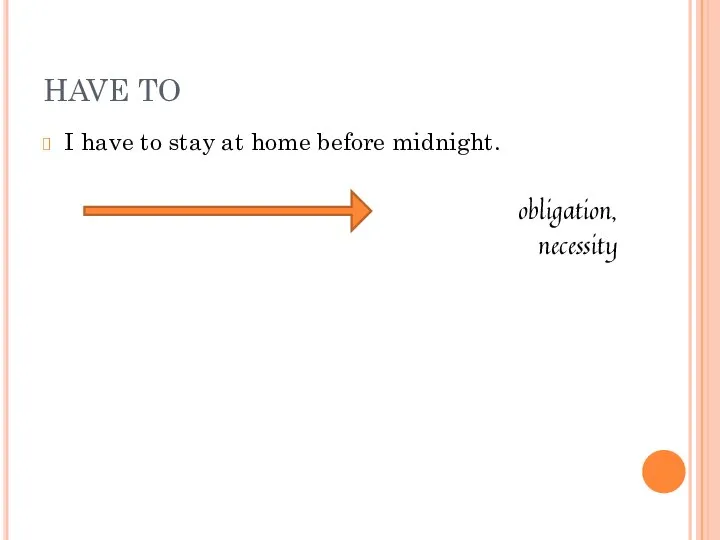
- 12. I have to stay at home before midnight. obligation, necessity HAVE TO
- 13. I need to go to the market because I’ve anything to eat. obligation, necessity NEED TO
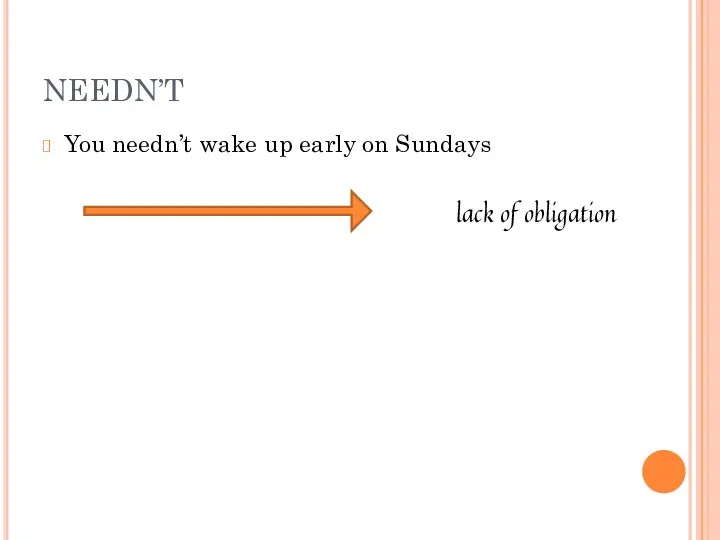
- 14. You needn’t wake up early on Sundays lack of obligation NEEDN’T
- 15. You dont’ have to bring anything to the party lack of obligation DON’T HAVE TO
- 16. You mustn’t smoke in this area. prohibition MUSTN’T
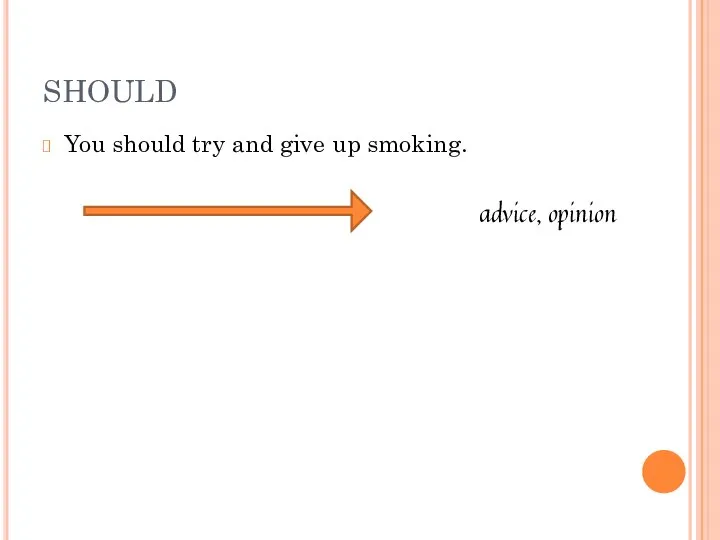
- 17. You should try and give up smoking. advice, opinion SHOULD
- 18. You ought to go to the doctor if you don’t feel well. advice, opinion OUGHT TO
- 19. Modal Pefects refer to PAST or COMPLETED ACTIONS: You should go to the doctor to feel
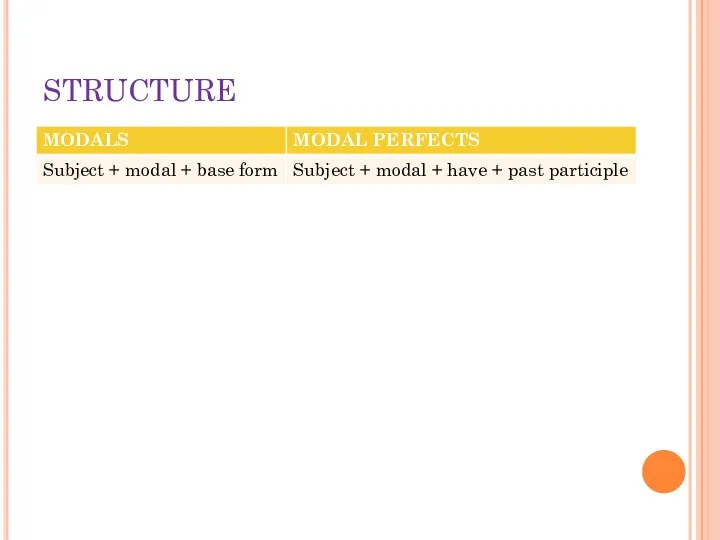
- 20. STRUCTURE
- 21. MODAL PERFECTS Must have May have / might have Could have Couldn’t have Would have Should
- 22. MUST HAVE She hasn’t arrived yet. She must have been in a traffic jam. certainty that
- 23. MAY HAVE / MIGHT HAVE She may / might have missed the bus a guess about
- 24. COULD HAVE You could have studied more for this exam. ability to have done something but
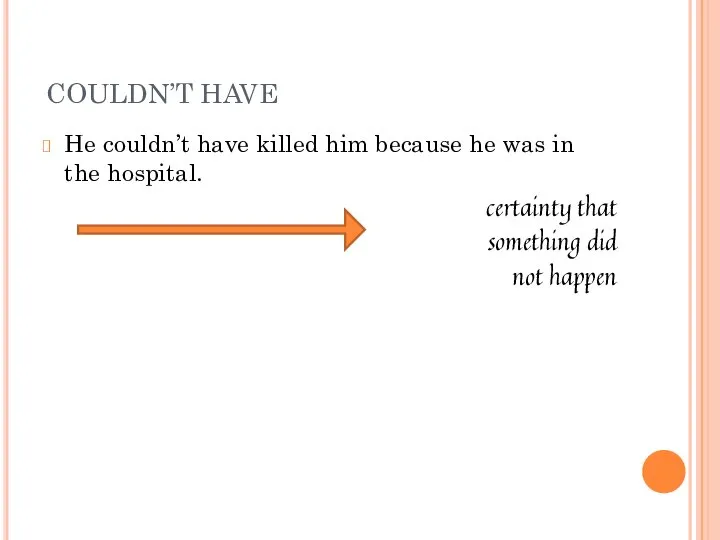
- 25. COULDN’T HAVE He couldn’t have killed him because he was in the hospital. certainty that something
- 26. WOULD HAVE I would have gone to the beach, but I didn’t feel very well willingness
- 27. SHOULD HAVE / OUGHT TO HAVE You should have told me that they splitted up. criticism
- 28. SHOULDN’T HAVE You shouldn’t have insulted her! criticism after an event
- 30. Скачать презентацию


















 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Anglo – American youth slang" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Anglo – American youth slang" - скачать  Подготовка учащихся к ЕГЭ Подготовка учащихся к ЕГЭ Задания С1, С2 Васецкая Наталья Владимировна, МОУ СОШ №6
Подготовка учащихся к ЕГЭ Подготовка учащихся к ЕГЭ Задания С1, С2 Васецкая Наталья Владимировна, МОУ СОШ №6 Презентация к уроку английского языка "IRELAND" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "IRELAND" - скачать бесплатно Abc – letters of the alphabet
Abc – letters of the alphabet Edward William Cooke 27 March 1811 – 4 January 1880
Edward William Cooke 27 March 1811 – 4 January 1880  Celebrations sn Britain
Celebrations sn Britain Использование мнемотехник при изучении лексики и грамматики в младших классах общеобразовательной школы
Использование мнемотехник при изучении лексики и грамматики в младших классах общеобразовательной школы Research Methods and Field Work. Literature Review
Research Methods and Field Work. Literature Review Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности клуба We Enjoy English
Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности клуба We Enjoy English What is law? A body of rules, imposed and enforced, among the members of a given state.
What is law? A body of rules, imposed and enforced, among the members of a given state.  Writing a story “An unusual gallery”
Writing a story “An unusual gallery” October, 24. History & Mystery of the English language.
October, 24. History & Mystery of the English language. The Reported Speech (general information)
The Reported Speech (general information) Summer Holidays
Summer Holidays Портфолио преподавателя английского языка
Портфолио преподавателя английского языка Презентация к уроку английского языка "Internet as a modern way of communication" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Internet as a modern way of communication" - скачать  Furniture
Furniture Animals
Animals My family, my history, my everything…
My family, my history, my everything… Презентация к уроку английского языка "9 things you need to know about the French author..." - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "9 things you need to know about the French author..." - скачать бесплатно Мои увлечения УЧЕНИЦЫ 5В КЛАССА МОРАЛИШВИЛИ МАРИАМ
Мои увлечения УЧЕНИЦЫ 5В КЛАССА МОРАЛИШВИЛИ МАРИАМ Тишакова Валентина Федоровна Учитель английского языка Тема: ALL SORTS OF FUN FOR YOU, FRIENDS!
Тишакова Валентина Федоровна Учитель английского языка Тема: ALL SORTS OF FUN FOR YOU, FRIENDS! My family
My family The UK. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The UK. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Презентация к уроку английского языка "Madame Tussauds" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Madame Tussauds" - скачать бесплатно The universities of Great Britain
The universities of Great Britain William Shakespeare “The Merchant of Venice”
William Shakespeare “The Merchant of Venice” Пишем письма друзьям. Урок английского языка в 3 классе
Пишем письма друзьям. Урок английского языка в 3 классе