Содержание
- 2. Ecology Ecology is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment Put
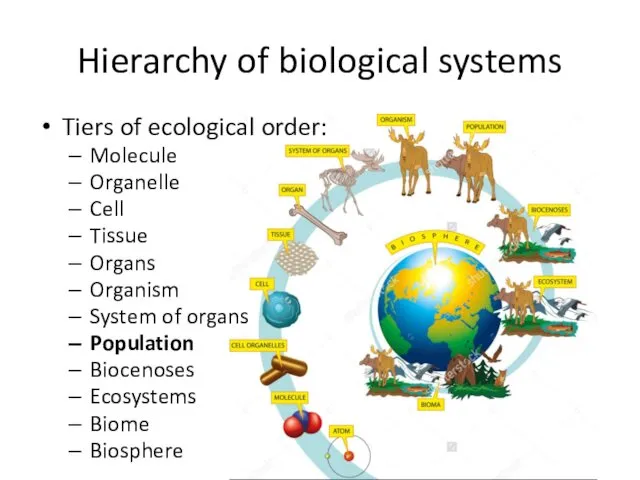
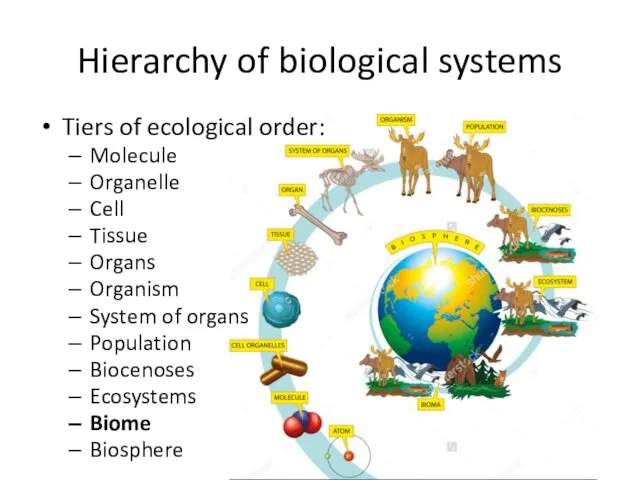
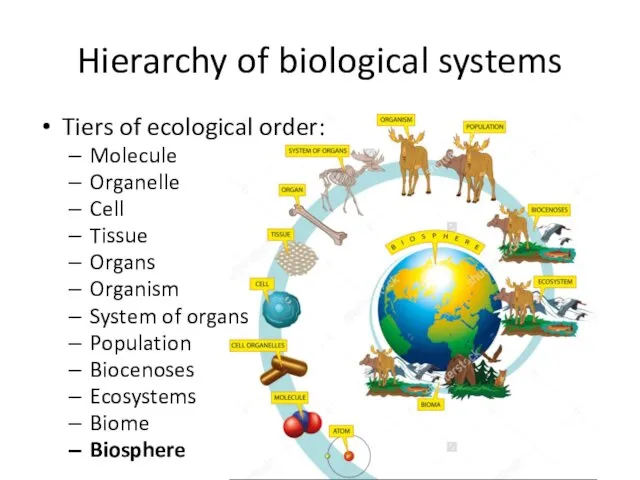
- 3. Hierarchy of biological systems Tiers of ecological order: Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organs Organism System of
- 4. Population Population is a summation of all the organisms of the same group or species, which
- 5. Population growth Limiting factors of population growth: food temperature mates space Limiting factors: density-dependent density-independent
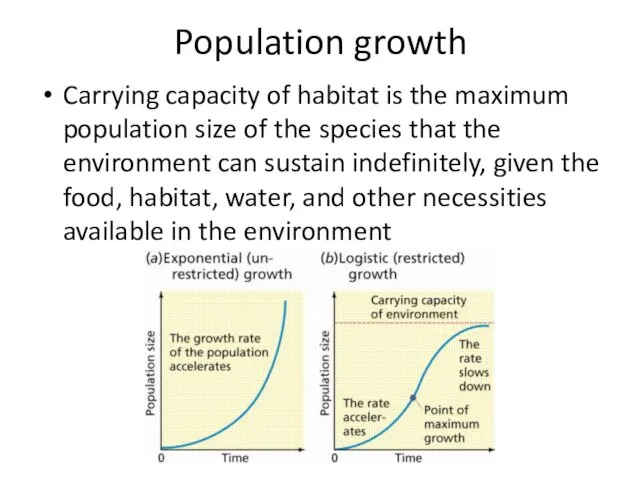
- 6. Population growth Carrying capacity of habitat is the maximum population size of the species that the
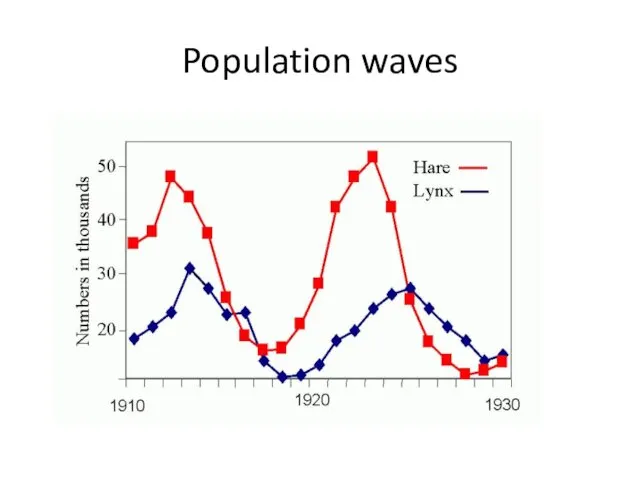
- 7. Population waves
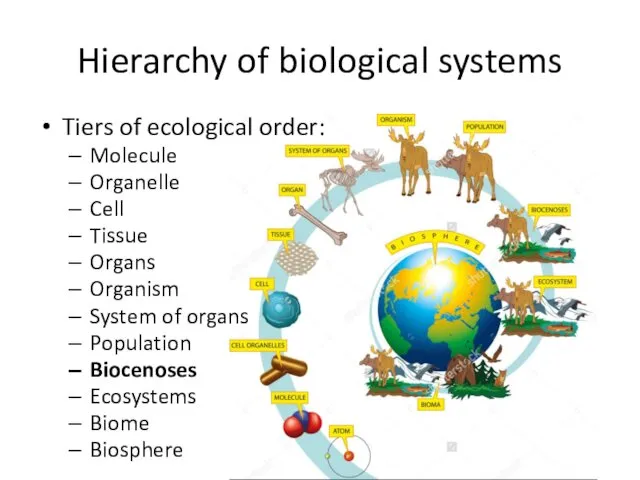
- 8. Hierarchy of biological systems Tiers of ecological order: Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organs Organism System of
- 9. Community Community (biocenosis) is an assemblage or association of populations of two or more different species
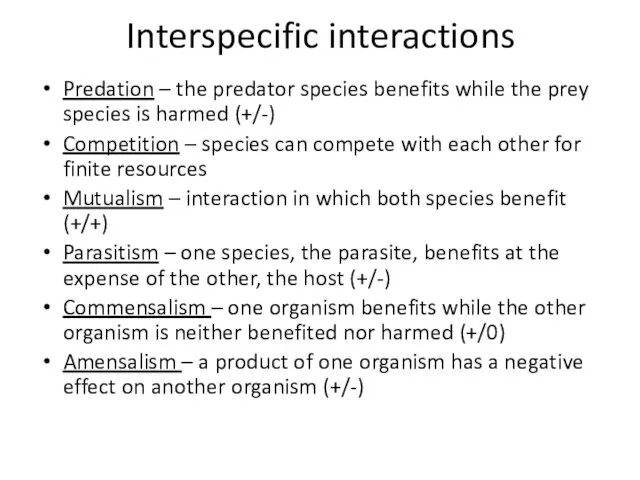
- 10. Interspecific interactions Predation – the predator species benefits while the prey species is harmed (+/-) Competition
- 11. 1 2 4 3 5
- 12. Community ecology Community ecology studies how the interactions between community members and their environment affect how
- 13. Hierarchy of biological systems Tiers of ecological order: Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organs Organism System of
- 14. Ecosystem An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of
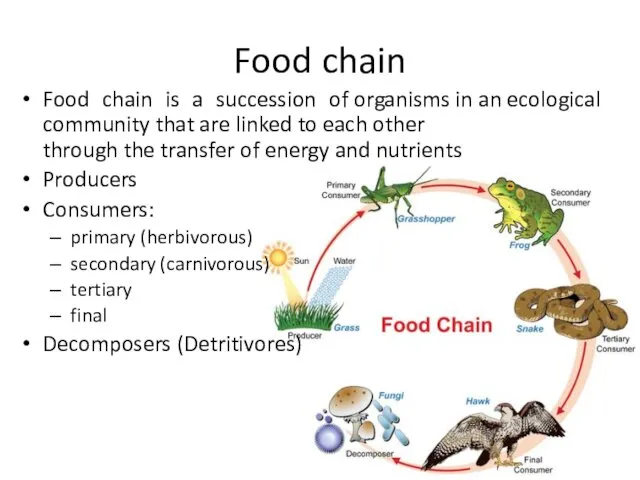
- 15. Food chain Food chain is a succession of organisms in an ecological community that are linked
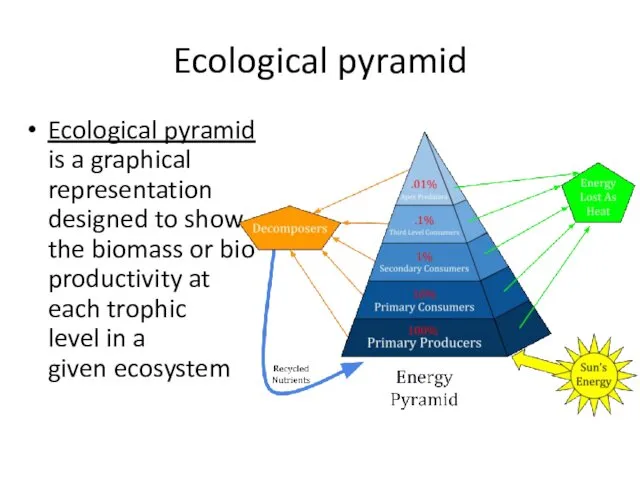
- 19. Ecological pyramid Biomass is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem
- 20. Ecological pyramid Ecological pyramid is a graphical representation designed to show the biomass or bio productivity
- 21. Hierarchy of biological systems Tiers of ecological order: Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organs Organism System of
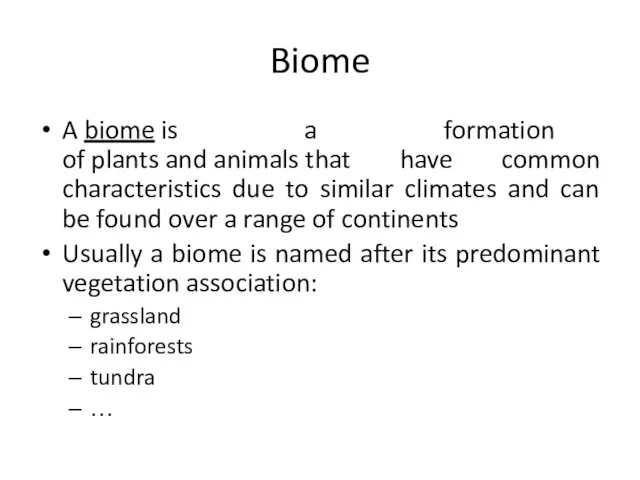
- 22. Biome A biome is a formation of plants and animals that have common characteristics due to
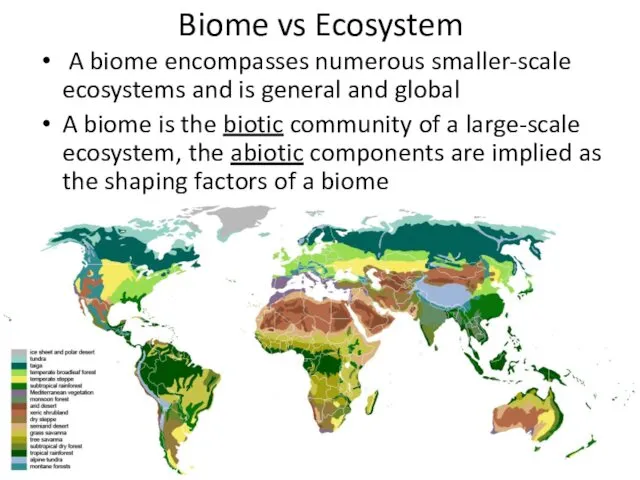
- 23. Biome vs Ecosystem A biome encompasses numerous smaller-scale ecosystems and is general and global A biome
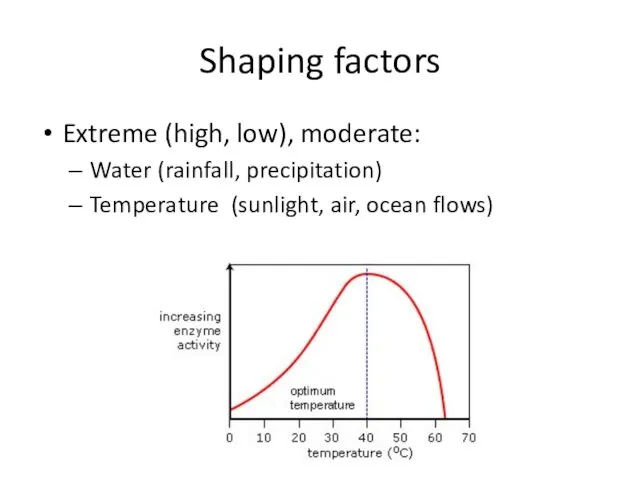
- 24. Shaping factors Extreme (high, low), moderate: Water (rainfall, precipitation) Temperature (sunlight, air, ocean flows)
- 25. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Temperature Water ------------------- Biodiversity
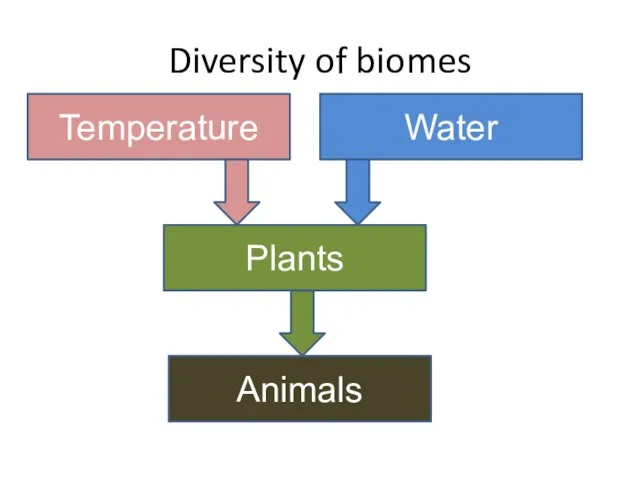
- 26. Diversity of biomes Temperature Water Plants Animals
- 27. Hierarchy of biological systems Tiers of ecological order: Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organs Organism System of
- 28. Biosphere The biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems The living organisms are affected by
- 29. Ecological problems
- 31. Скачать презентацию














 Phrasal verb (фразовый глагол)
Phrasal verb (фразовый глагол) The outstanding people of Russia
The outstanding people of Russia Презентация к уроку английского языка "Eden project" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Eden project" - скачать  Adverbs
Adverbs why British guardsmen such caps?
why British guardsmen such caps? Оборот There is/are. Особый вид сказуемого есть, находится
Оборот There is/are. Особый вид сказуемого есть, находится Royal family Quiz
Royal family Quiz Link to your listener’s concerns
Link to your listener’s concerns The Present, Past and Future Simple tenses
The Present, Past and Future Simple tenses Electricity
Electricity Student of the year
Student of the year Be polite! Say…
Be polite! Say… At school
At school Презентация к уроку английского языка "Culture shock" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Culture shock" - скачать  The traditions of Ukrainians Student made 7-a-class Pysarenko Yulia Shebalkova Elizabeth Oleinikova Helena
The traditions of Ukrainians Student made 7-a-class Pysarenko Yulia Shebalkova Elizabeth Oleinikova Helena  The Zero Conditional (100%)
The Zero Conditional (100%) Употребление артикля с существительными, обозначающими части суток, времена года
Употребление артикля с существительными, обозначающими части суток, времена года Долгосрочные тенденции в движении финансового капитала. Подготовили: Сичкаренко Анна, Яценко Яна Т-105
Долгосрочные тенденции в движении финансового капитала. Подготовили: Сичкаренко Анна, Яценко Яна Т-105 Ecology In Russia
Ecology In Russia Times
Times American society
American society My city Petropavlovsk
My city Petropavlovsk Madame Tussauds Waxworks Museums Around the World
Madame Tussauds Waxworks Museums Around the World Animals
Animals Презентация к уроку английского языка "Funny animals" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Funny animals" - скачать  Tom and Jerry
Tom and Jerry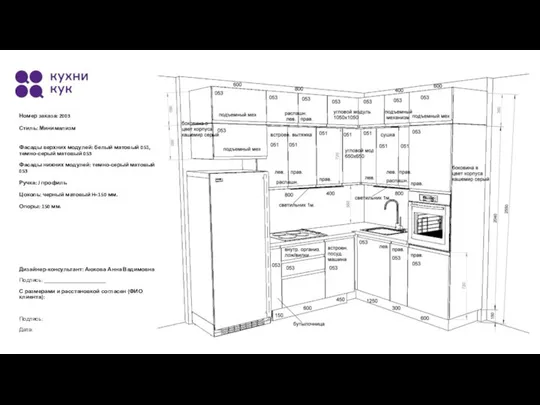 Кухня под заказ
Кухня под заказ Guess the Season
Guess the Season