Содержание
- 2. VERBALS (неличные формы глагола) The Infinitive The Gerund The Participle
- 3. VERBALS (неличные формы глагола) The Infinitive “To be or not to be, that is the question”.
- 4. VERBALS (неличные формы глагола) The Infinitive e.g. Alison likes to read. The Gerund e.g. Alison likes
- 5. Герундий The Gerund Герундий – это неличная форма глагола, имеющая грамматические особенности как глагола, так и
- 6. The Gerund is used: As a noun e.g. Swimming keeps you fit.
- 7. The Gerund is used: After: love, like, enjoy, dislike, hate, prefer to express general preference. e.g.
- 8. The Gerund is used: After go for activities: e.g. They often go climbing at the weekends.
- 9. The Gerund is used: After prepositions: e.g. He left without saying goodbye.
- 10. The Gerund is used: The Gerund is used: After certain verbs: admit, avoid, consider, deny, fancy,
- 11. The Gerund is used: The Gerund is used: After: be busy, it’s no use/good, it’s (not)
- 12. The Gerund is used: After the verbs: see, hear, feel, watch, listen to, notice to describe
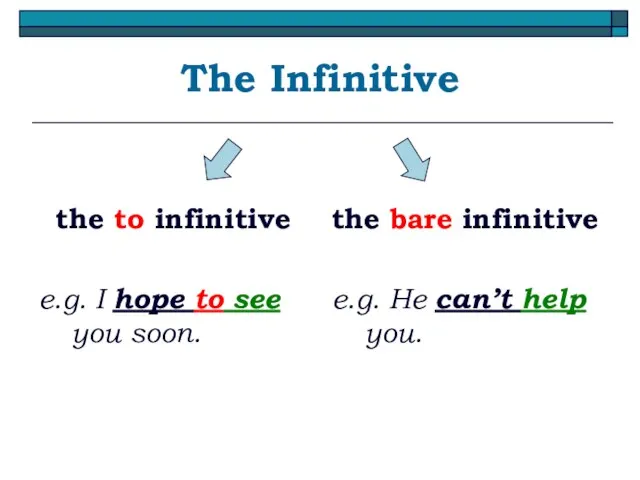
- 13. The Infinitive the to infinitive e.g. I hope to see you soon. the bare infinitive e.g.
- 14. The to infinitive is used: To express purpose – e.g. She went to the bank to
- 15. The to infinitive is used: after verbs such as know, decide, ask, learn, want to know,
- 16. The to infinitive is used: After adjectives: nice, sorry, glad, happy, willing, afraid, ashamed, etc. e.g.
- 17. The to infinitive is used: After: it + be + adjective (+of +noun/pronoun) e.g. It was
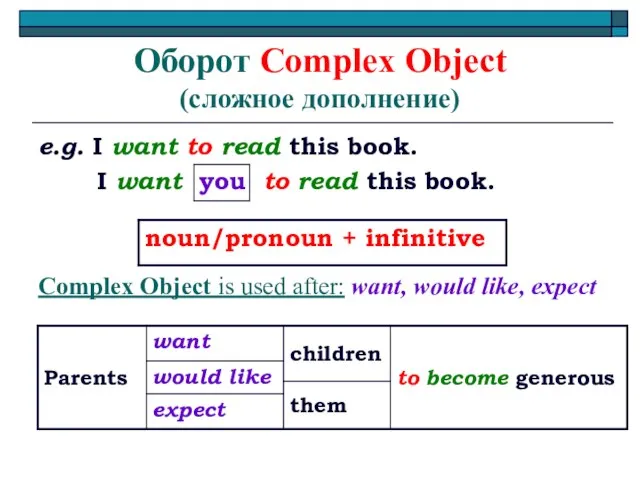
- 18. Оборот Complex Object (сложное дополнение) e.g. I want to read this book. I want you to
- 19. The bare infinitive is used: After modal verbs (may, should, can, must, etc.) e.g. You must
- 21. Скачать презентацию
















 Spotlight 9. English in use
Spotlight 9. English in use Тема урока:Цветик-семицветик Проведение конкурсов
Тема урока:Цветик-семицветик Проведение конкурсов  Happy Easter
Happy Easter Relationships. Vocabulary
Relationships. Vocabulary Business plan template
Business plan template What do we do at school?
What do we do at school? Прошедшее продолженное время
Прошедшее продолженное время Настоящее простое время
Настоящее простое время Фрукты. Английский язык
Фрукты. Английский язык Урок английского языка в 10 классе по теме «Земля – тревога! Вымирающие животные» Учитель : Гладкова О.И. МОУ СОШ № 24 г Кострома.
Урок английского языка в 10 классе по теме «Земля – тревога! Вымирающие животные» Учитель : Гладкова О.И. МОУ СОШ № 24 г Кострома. What is questionnaire. Types of questionnaires
What is questionnaire. Types of questionnaires Film Review
Film Review  Literary Britain Reading is a vital form of communication with all of mankind, and wisdom of many ages Olzhas Suleymenov
Literary Britain Reading is a vital form of communication with all of mankind, and wisdom of many ages Olzhas Suleymenov Forget to V. Forget Ving
Forget to V. Forget Ving He wakes up
He wakes up My family. Лексико-грамматический материал в устной и письменной речи
My family. Лексико-грамматический материал в устной и письменной речи Who is in the lift?
Who is in the lift? Презентация к уроку английского языка "Александр Невский" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Александр Невский" - скачать  B1-intermediate relationships. Lesson 1
B1-intermediate relationships. Lesson 1 Суффиксы прилагательных
Суффиксы прилагательных Welkom to Belarus
Welkom to Belarus Обобщающий урок по теме «Еда» Серебрякова Е.А учитель английского языка МОУ «Усть-Кубинская СОШ»
Обобщающий урок по теме «Еда» Серебрякова Е.А учитель английского языка МОУ «Усть-Кубинская СОШ» Модуль. Практическое занятие № 1
Модуль. Практическое занятие № 1 I like food
I like food The Passive Voice
The Passive Voice My favorite writers
My favorite writers  ACID RAIN
ACID RAIN