Содержание
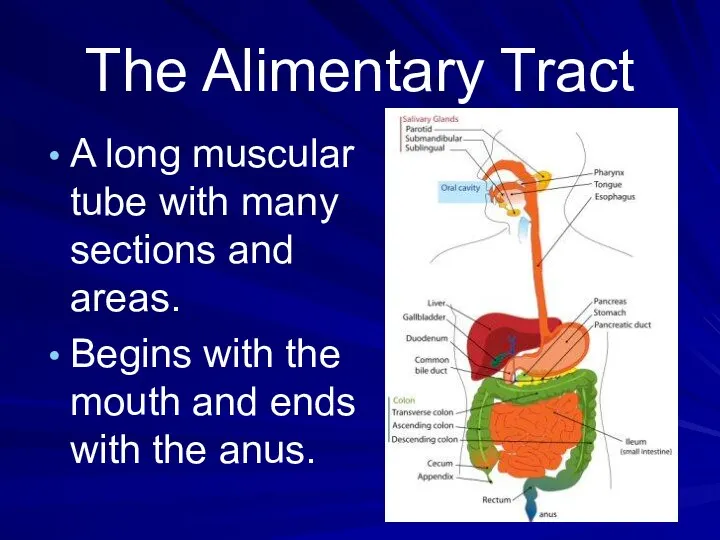
- 2. The Alimentary Tract A long muscular tube with many sections and areas. Begins with the mouth
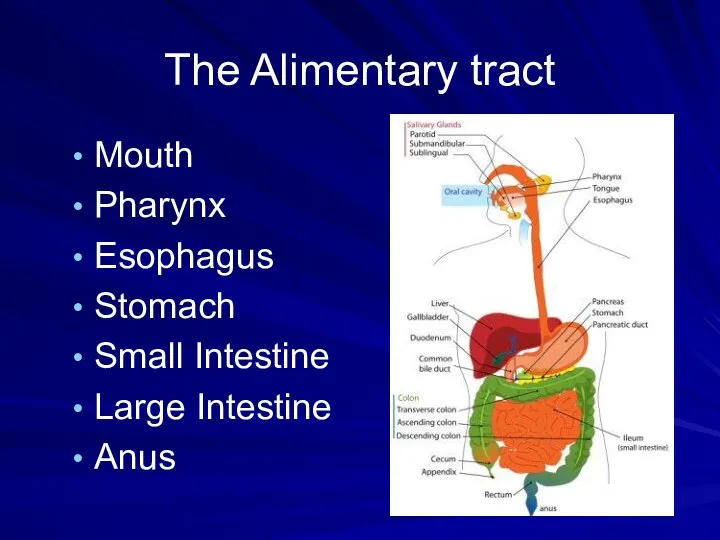
- 3. The Alimentary tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Anus
- 4. Accessory Parts Organs that are not in the Alimentary tract but helps in the digestion Teeth
- 5. Mouth Functions: Food enters in the mouth or oral cavity Tasting Mechanical breakdown of food Secretion
- 6. Mouth Structures in the mouth that aids digestion: Teeth – cut, tear, crush and grind food.
- 7. Mouth Tongue Mixes and rolls food into tiny mashed up bits (Bolus) Pushes the bolus toward
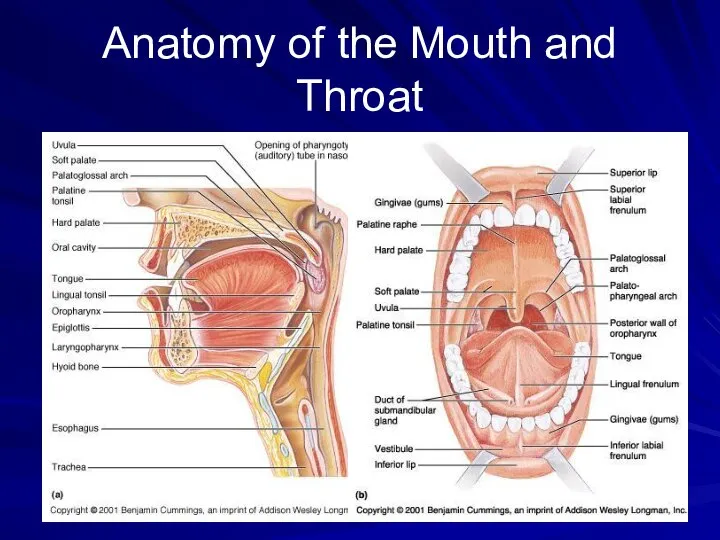
- 8. Anatomy of the Mouth and Throat
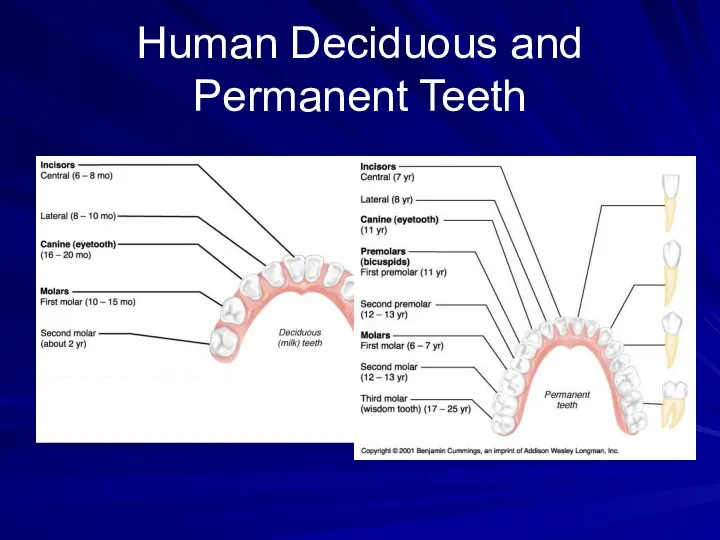
- 9. Human Deciduous and Permanent Teeth
- 10. Mechanism of Swallowing Swallowing is a coordinated activity of the tongue, soft palate, pharynx and esophagus.
- 12. Esophagus A straight muscular tube that is about 10 inches (25 cm) long which connects the
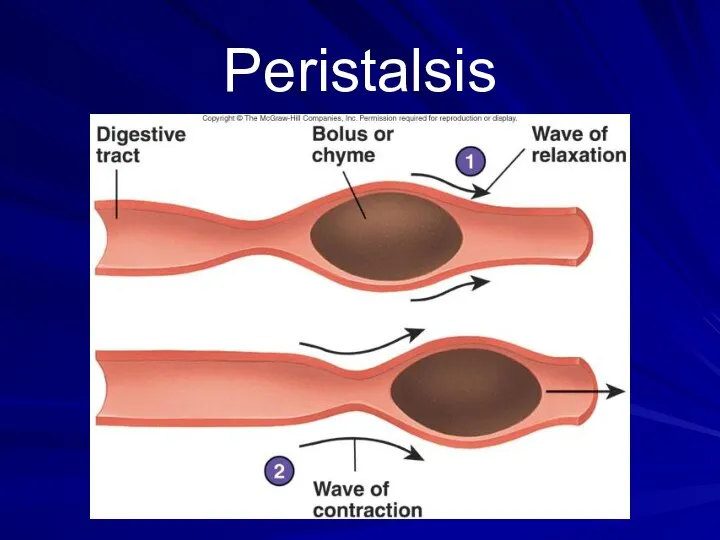
- 13. Peristalsis
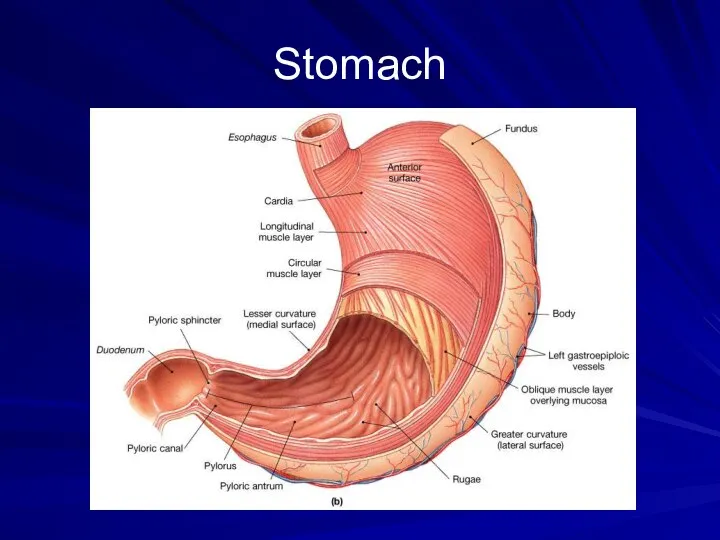
- 14. Stomach J-shaped muscular sac Has inner folds (rugae) that increases the surface area of the stomach.
- 15. Stomach
- 16. Stomach Pepsin – major enzyme; converts proteins into peptides in the presence of HCL. Mucus –
- 17. Movements in Stomach
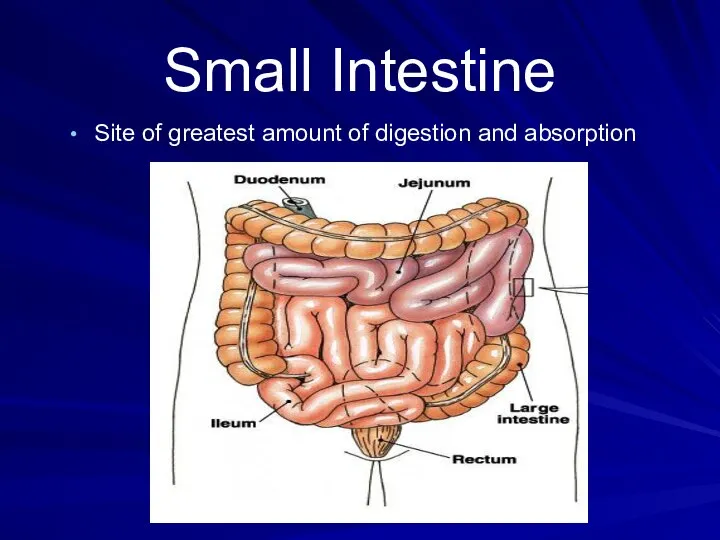
- 18. Small Intestine Long (20 ft), coiled tube beneath the stomach. Has three parts: Duodenum – upper
- 19. Small Intestine Site of greatest amount of digestion and absorption
- 20. Small Intestine Takes about 4 – 8 hrs to complete its journey. Mucosa (inner wall) –
- 21. Small Intestine Has folded inner walls covered with fingerlike projections (villi; sing. – villus) Each villus
- 22. Movement in small intestine: Mixing: Segmental contraction that occurs in small intestine Secretion: Lubricate, liquefy, digest
- 23. Large Intestine a.k.a. Colon larger diameter, but shorter (5 ft) Water is absorbed from the undigested
- 24. Large Intestine
- 25. Large Intestine Waste is pushed into the expanded portion (rectum) of the large intestine. Solid waste
- 26. Accessory Organs Produce or store enzymes that helps in digestion. Liver Largest gland of the body
- 27. Accessory Organs Gall bladder Stores bile in between meals Secretes bile to the duodenum through the
- 28. Accessory Organs Pancreas Produces a juice that contains enzymes (amylase and insulin) to break down carbohydrates,
- 30. Скачать презентацию




















 Игра: страны
Игра: страны Modal Verbs
Modal Verbs Flashcards. Things I can do
Flashcards. Things I can do Королевская семья Великобритании Отношения, семейное древо, тайны и многое другое...
Королевская семья Великобритании Отношения, семейное древо, тайны и многое другое...  My perfect day
My perfect day Hotel “Golden Crown”
Hotel “Golden Crown” Алгоритм перевода
Алгоритм перевода Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs
Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs Презентация к уроку английского языка "День святого патрика" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "День святого патрика" - скачать бесплатно Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense Песни и стихи на уроках английского языка Гончаренко Анна 2338-2А, 303А
Песни и стихи на уроках английского языка Гончаренко Анна 2338-2А, 303А Ket. Speaking. (Рart 2)
Ket. Speaking. (Рart 2) Have you re-gifted presents?
Have you re-gifted presents? Скачать Going to the Doctor
Скачать Going to the Doctor My university KazNU
My university KazNU Ecological problems. What you can do to protect our planet
Ecological problems. What you can do to protect our planet Borad or how the film can affect the flow of tourists
Borad or how the film can affect the flow of tourists Есть два друга - he и it. Кто из них и где стоит?!
Есть два друга - he и it. Кто из них и где стоит?! Benjamin Franklin 1706-1790
Benjamin Franklin 1706-1790  Презентация по английскому языку Особенности фразеологии современного английского языка
Презентация по английскому языку Особенности фразеологии современного английского языка Australia
Australia Игрушки. Toys
Игрушки. Toys Cuba officially the Republic of Cuba
Cuba officially the Republic of Cuba Russian holidays It is a tradition to give greeting cards on these holidays. Here you can see some of them. Работу подготовила Игнатьева Е.Т. Учитель английского языка
Russian holidays It is a tradition to give greeting cards on these holidays. Here you can see some of them. Работу подготовила Игнатьева Е.Т. Учитель английского языка Make a sentence
Make a sentence Скачать Exercise for eyes
Скачать Exercise for eyes TRUE FRIENDS…
TRUE FRIENDS… Student recognition at BCC
Student recognition at BCC