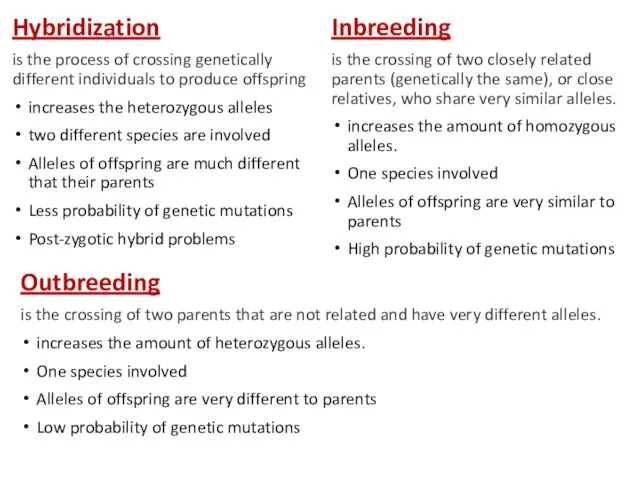
Hybridization
is the process of crossing genetically different individuals to produce
offspring
increases the heterozygous alleles
two different species are involved
Alleles of offspring are much different that their parents
Less probability of genetic mutations
Post-zygotic hybrid problems
Inbreeding
is the crossing of two closely related parents (genetically the same), or close relatives, who share very similar alleles.
increases the amount of homozygous alleles.
One species involved
Alleles of offspring are very similar to parents
High probability of genetic mutations
Outbreeding
is the crossing of two parents that are not related and have very different alleles.
increases the amount of heterozygous alleles.
One species involved
Alleles of offspring are very different to parents
Low probability of genetic mutations


















 Биосинтез белка. Трансляция
Биосинтез белка. Трансляция Любимова М.Ф., учитель биологии, ГОУ 48 2008
Любимова М.Ф., учитель биологии, ГОУ 48 2008  Покрытосеменные растения 6 класс Обучающий тест
Покрытосеменные растения 6 класс Обучающий тест Подцарство Многоклеточные животные. Тип Кишечнополостные
Подцарство Многоклеточные животные. Тип Кишечнополостные Презентация на тему ВОДА И ЗДОРОВЬЕ ЧЕЛОВЕКА
Презентация на тему ВОДА И ЗДОРОВЬЕ ЧЕЛОВЕКА Презентация к уроку на тему «Многообразие насекомых» Подготовлена учителем биологии Русиной Е.В. МАОУ гимназия № 111 г.Уфа, Кали
Презентация к уроку на тему «Многообразие насекомых» Подготовлена учителем биологии Русиной Е.В. МАОУ гимназия № 111 г.Уфа, Кали Влияние половых гормонов на отдаленные эффекты курения
Влияние половых гормонов на отдаленные эффекты курения Презентация на тему "Вегетативное размножение растений" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Вегетативное размножение растений" - скачать презентации по Биологии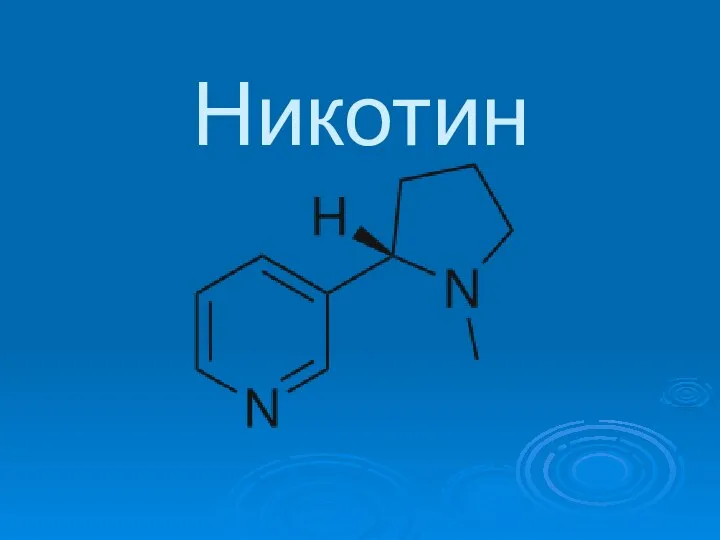 Никотин
Никотин  Биологические особенности роста и плодоношения земляники
Биологические особенности роста и плодоношения земляники Жизненные формы растений
Жизненные формы растений Вирусы
Вирусы Организм человека Теcт 3 класс УМК «Школа России»
Организм человека Теcт 3 класс УМК «Школа России» Необычные домашние питомцы
Необычные домашние питомцы Факультет биотехнологии и биологии 2022
Факультет биотехнологии и биологии 2022 Предмет и задачи микробиологии
Предмет и задачи микробиологии Презентация « Роль воды в жизни растений» « Проращивание семян»
Презентация « Роль воды в жизни растений» « Проращивание семян»  Проект Лапа помощи по защите амурских тигров
Проект Лапа помощи по защите амурских тигров Презентация на тему "Ген долголетия" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Ген долголетия" - скачать презентации по Биологии Медицинская биохимия Раздел биохимии, изучающий нарушения метаболизма, лежащие в основе различных заболеваний
Медицинская биохимия Раздел биохимии, изучающий нарушения метаболизма, лежащие в основе различных заболеваний  Растительные ткани
Растительные ткани Тема: «Животные. Брачные обряды» (Внеклассное мероприятие по биологии)
Тема: «Животные. Брачные обряды» (Внеклассное мероприятие по биологии)  Признаки семейств двудольных растений
Признаки семейств двудольных растений Минеральная вода Презентация для потребителей минеральной воды_
Минеральная вода Презентация для потребителей минеральной воды_ Таблица генетического кода иРНК
Таблица генетического кода иРНК Введение в курс спортивной физиологии. Физиологическая характеристика различных видов мышечной деятельности
Введение в курс спортивной физиологии. Физиологическая характеристика различных видов мышечной деятельности Плоды. Образование плода
Плоды. Образование плода Самые лучшие сторожевые и охранные собаки Сторожевые собаки – лучшие охранники дома и территории. Сторожевыми называют собак,
Самые лучшие сторожевые и охранные собаки Сторожевые собаки – лучшие охранники дома и территории. Сторожевыми называют собак,