Содержание
- 2. Why is Photosynthesis important? Makes organic molecules (glucose) out of inorganic materials (carbon dioxide and water).
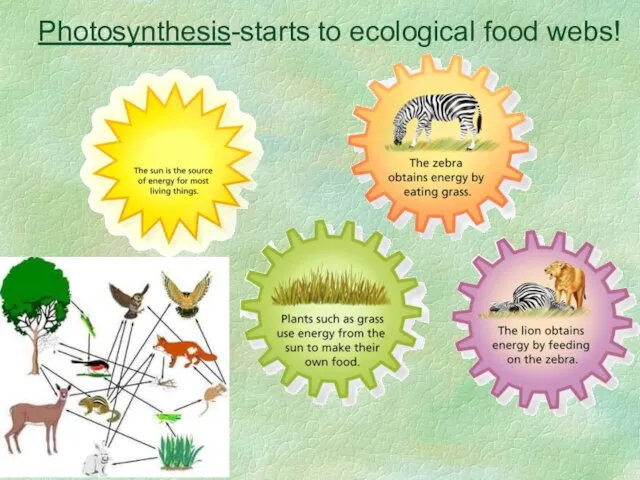
- 3. Photosynthesis-starts to ecological food webs!
- 4. Plants use sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide into glucose. Glucose is a kind of
- 5. How do we know that plants make carbohydrates from just carbon dioxide water and light energy?
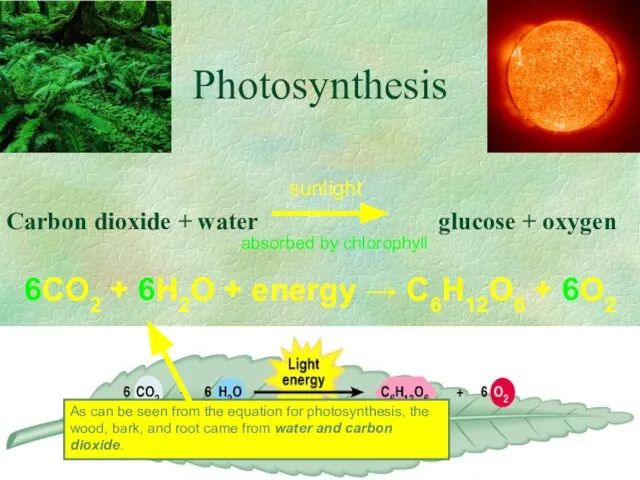
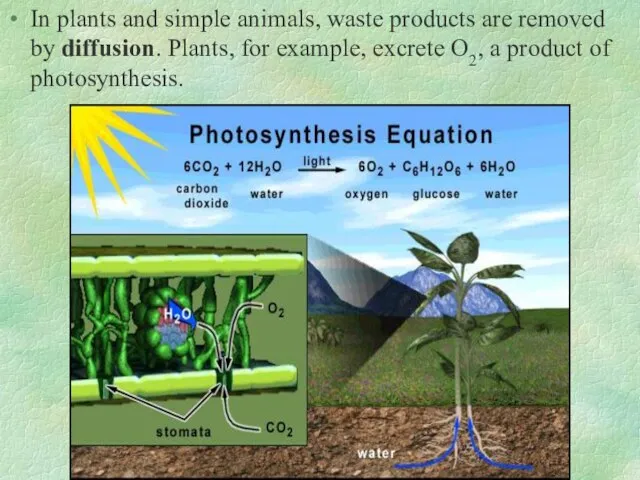
- 6. Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen sunlight absorbed by chlorophyll 6CO2 + 6H2O +
- 7. Check it! Plants in Action What is the process that uses the sun’s energy to make
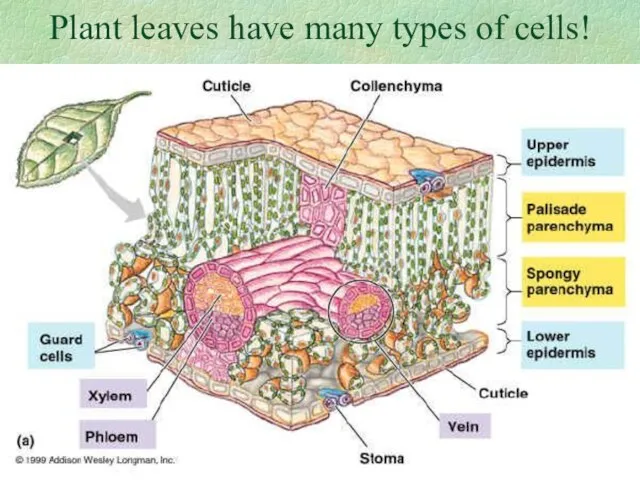
- 8. Plant leaves have many types of cells!
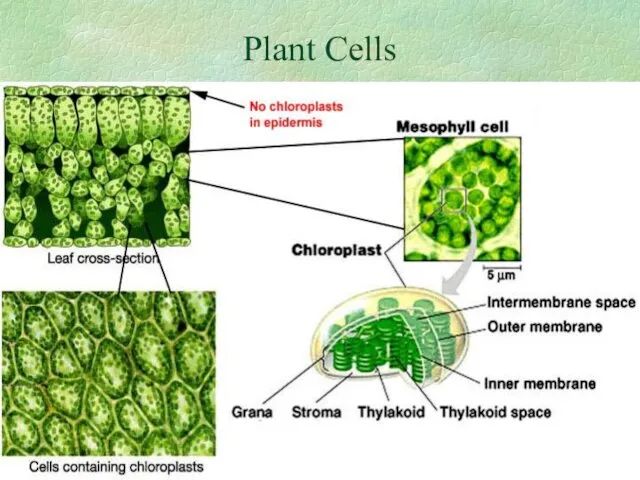
- 9. Plant Cells
- 10. The photograph below is an elodea leaf X 400. Individual cells are clearly visible. The tiny
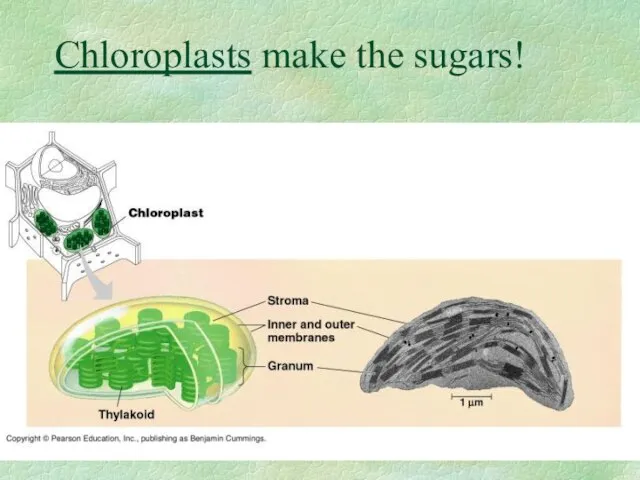
- 11. Chloroplasts make the sugars!
- 12. Plants Leaves are green because they contain the pigment: chlorophyll Leaves have a large surface area
- 13. Chloroplasts make the oxygen too!
- 14. Stoma This opening how plants exchange gases! Check it! Can you name the two important gases
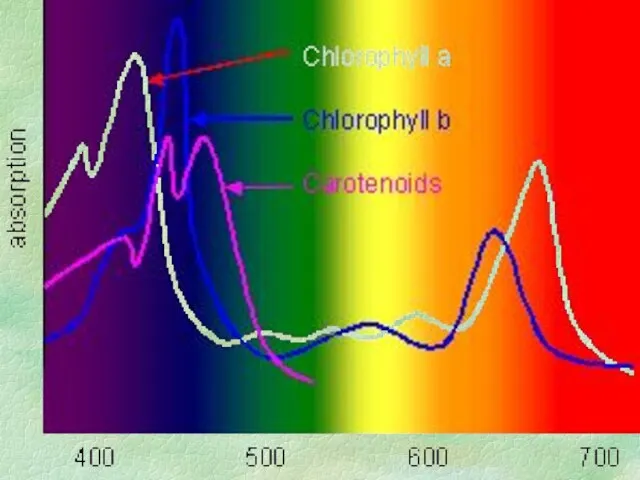
- 15. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Absorbing Light Energy to make chemical energy: glucose! Pigments: Absorb different colors of white light
- 16. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Why do we see green? Green color from white light reflected NOT absorbed Chloroplast: organelle
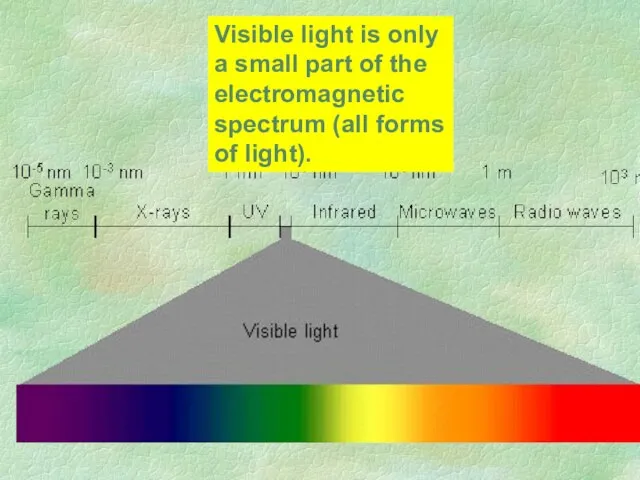
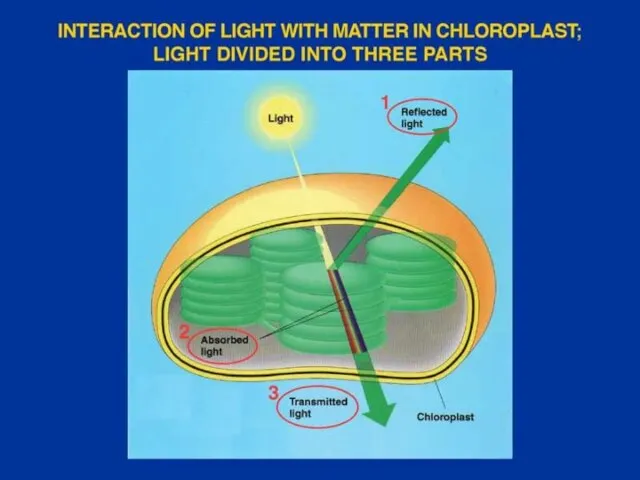
- 17. Visible light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum (all forms of light).
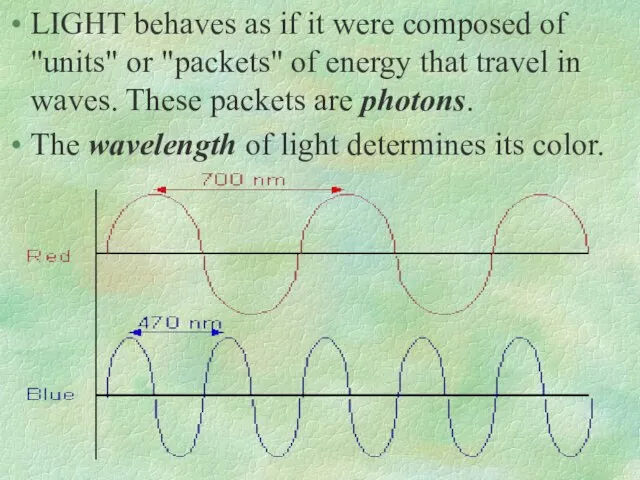
- 18. LIGHT behaves as if it were composed of "units" or "packets" of energy that travel in
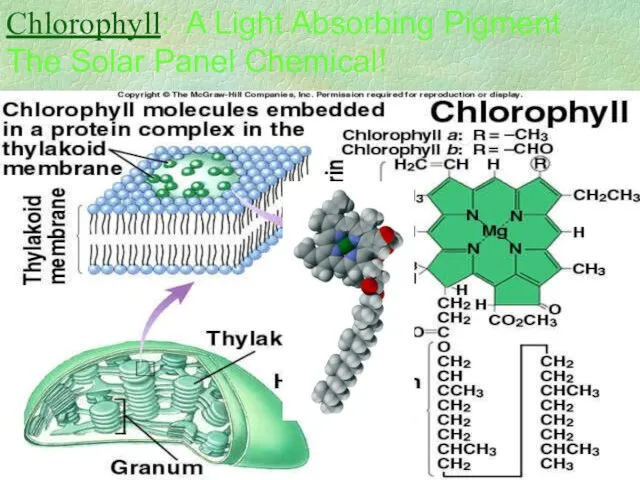
- 20. Chlorophyll: A Light Absorbing Pigment The Solar Panel Chemical!
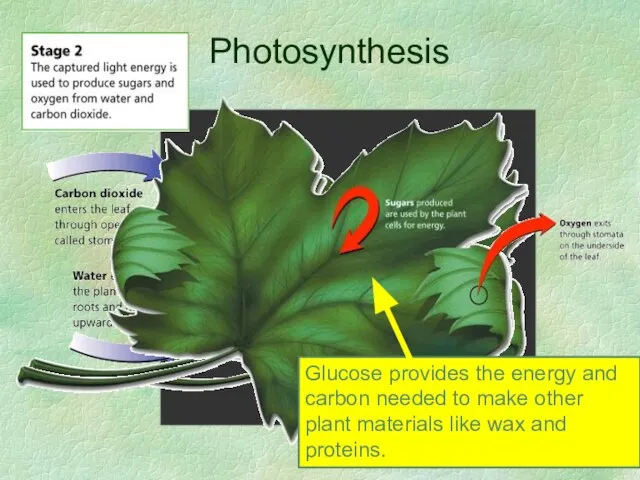
- 22. Photosynthesis
- 23. Oxygen and Sugar!
- 24. In plants and simple animals, waste products are removed by diffusion. Plants, for example, excrete O2,
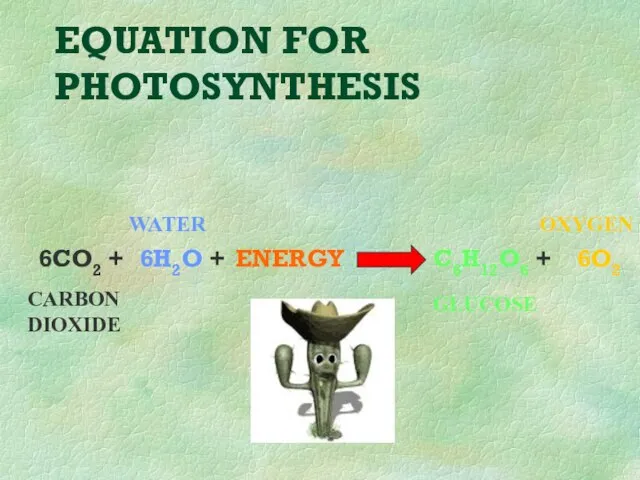
- 25. EQUATION FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY C6H12O6 + 6O2 CARBON DIOXIDE WATER GLUCOSE OXYGEN
- 26. The end!
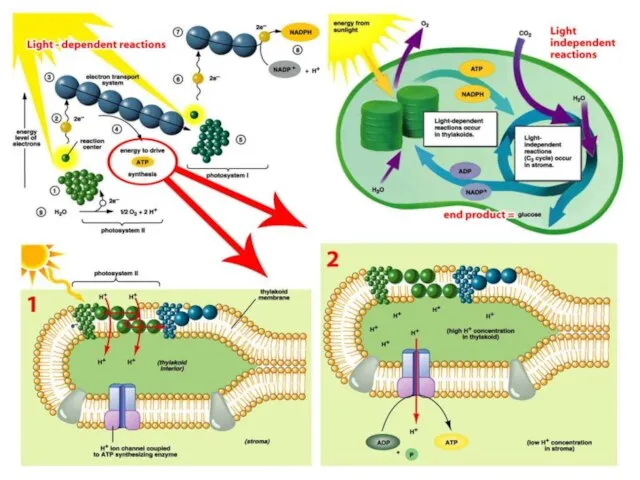
- 27. PHOTOSYNTHESIS 2 Phases Light-dependent reaction Light-independent reaction Light-dependent: converts light energy into chemical energy; produces ATP
- 28. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Light-dependent reaction (LIGHT Reaction) Requires light Occurs in chloroplast (in thylakoids) Chlorophyll (thylakoid) traps energy
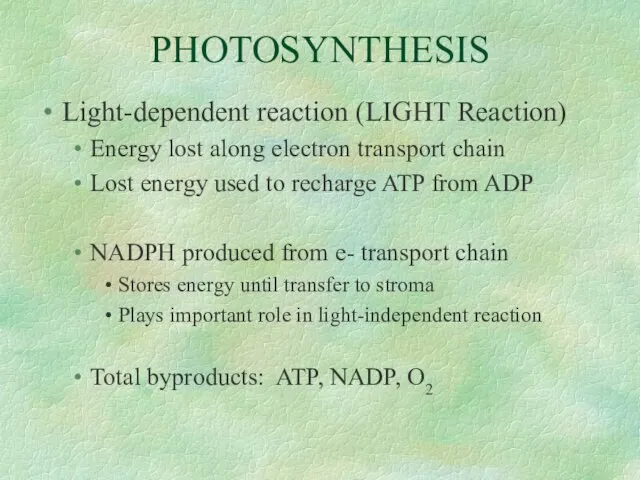
- 29. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Light-dependent reaction (LIGHT Reaction) Energy lost along electron transport chain Lost energy used to recharge
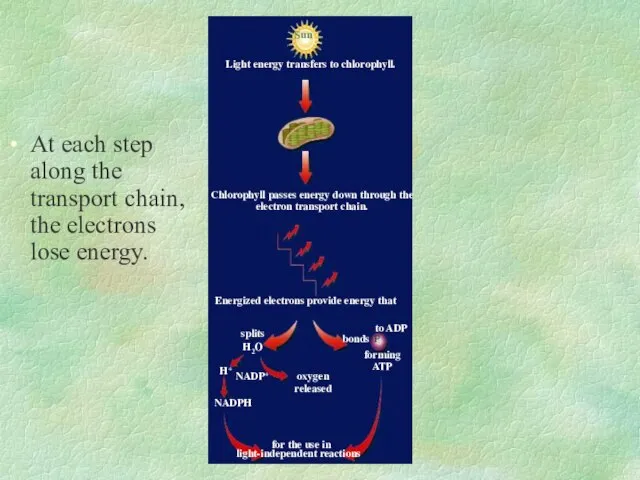
- 30. PHOTOSYNTHESIS How did we get O2 as a byproduct?! Photolysis: replaces lost electrons by splitting water
- 31. Sun Chlorophyll passes energy down through the electron transport chain. for the use in light-independent reactions
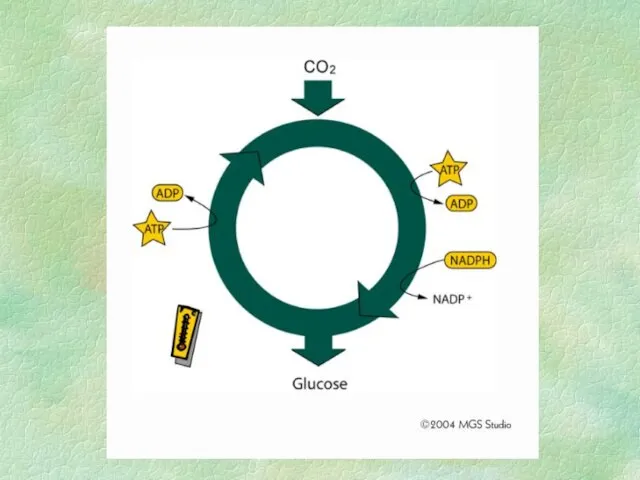
- 32. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Light-independent reaction (Dark Reaction) Does not require light Calvin Cycle Occurs in stroma of chloroplast
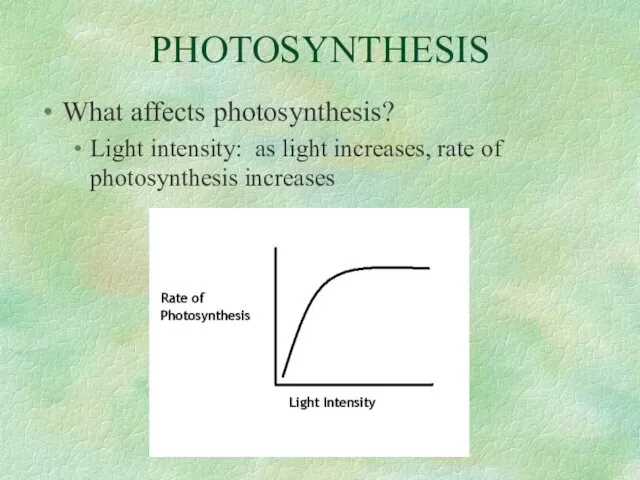
- 34. PHOTOSYNTHESIS What affects photosynthesis? Light intensity: as light increases, rate of photosynthesis increases
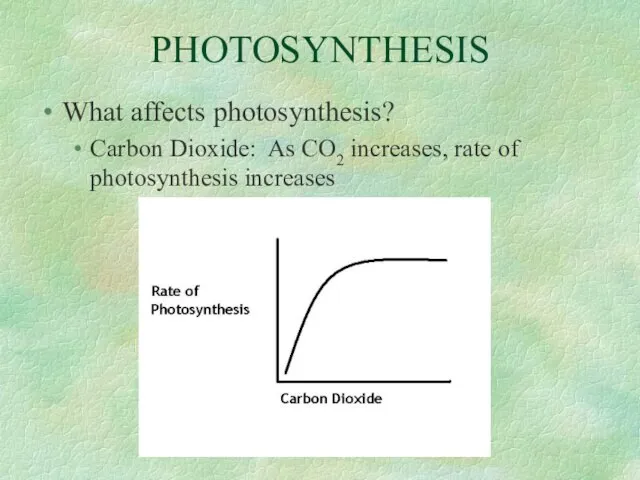
- 35. PHOTOSYNTHESIS What affects photosynthesis? Carbon Dioxide: As CO2 increases, rate of photosynthesis increases
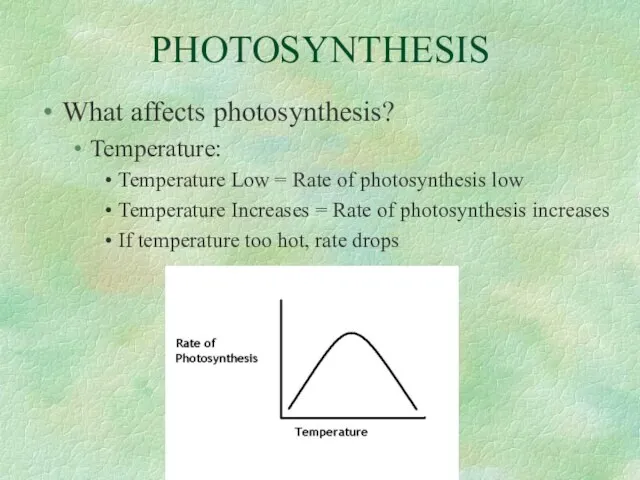
- 36. PHOTOSYNTHESIS What affects photosynthesis? Temperature: Temperature Low = Rate of photosynthesis low Temperature Increases = Rate
- 37. Check it! The process that uses the sun’s energy to make simple sugars is _____________. Cellular
- 38. Check it! The function accomplished by the light-dependent reactions is ______________. Energy storage Sugar production Carbon
- 40. Скачать презентацию

















 Презентация на тему "Высшие споровые растения. Зеленые мхи" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Высшие споровые растения. Зеленые мхи" - скачать презентации по Биологии ЦАРСТВО ПРОКАРИОТЫ ПОДЦАРСТВО БАКТЕРИИ
ЦАРСТВО ПРОКАРИОТЫ ПОДЦАРСТВО БАКТЕРИИ  Віруси рослин
Віруси рослин Презентация на тему Нервная система. Рефлекс. Инстинкт
Презентация на тему Нервная система. Рефлекс. Инстинкт Лекция
Лекция Основы физиологии растений. Дыхание растений
Основы физиологии растений. Дыхание растений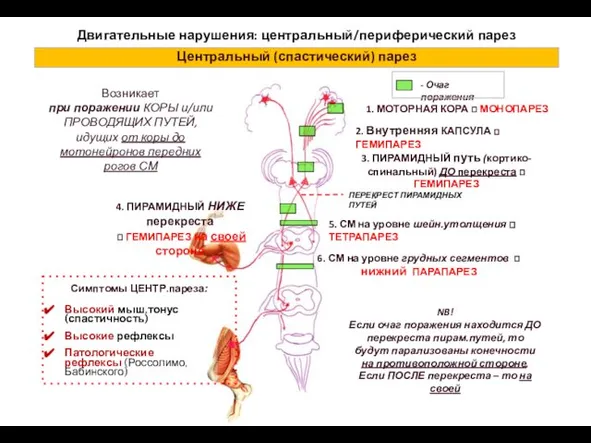 Двигательные нарушения: центральный/периферический парез
Двигательные нарушения: центральный/периферический парез Многообразие червей
Многообразие червей Среда обитания
Среда обитания Интеллектуальная игра-викторина Цветы в легендах и преданиях
Интеллектуальная игра-викторина Цветы в легендах и преданиях Тип Мшанки
Тип Мшанки Тема «Вселенная» Урок 1: «Звёзды на небе» Подготовила учитель биологии и химии МАОУ «СОШ №13 Великого Новгорода» Мариничева Лариса
Тема «Вселенная» Урок 1: «Звёзды на небе» Подготовила учитель биологии и химии МАОУ «СОШ №13 Великого Новгорода» Мариничева Лариса Тема: Философское учение о человеке. Природа человека Особенности философского исследования человека. Гуманизм и его историческ
Тема: Философское учение о человеке. Природа человека Особенности философского исследования человека. Гуманизм и его историческ Введение в эстезиологию. Органы чувств в свете учения И.П. Павлова об анализаторах. Орган зрения
Введение в эстезиологию. Органы чувств в свете учения И.П. Павлова об анализаторах. Орган зрения Презентация на тему "Спинной мозг: строение, функции" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Спинной мозг: строение, функции" - скачать презентации по Биологии Психофизиология мотиваций и эмоций
Психофизиология мотиваций и эмоций Физиология высшей нервной деятельности (ВНД)
Физиология высшей нервной деятельности (ВНД) Экосистемы. Структура
Экосистемы. Структура Соединительная ткань
Соединительная ткань Процесс кровообращения. Сосуды малого и коронарного кругов кровообращения. Артерии большого круга кровообращения
Процесс кровообращения. Сосуды малого и коронарного кругов кровообращения. Артерии большого круга кровообращения Многообразие паукообразных
Многообразие паукообразных Презентация на тему "Виды вирусных заболеваний человека, животных и растений" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Виды вирусных заболеваний человека, животных и растений" - скачать презентации по Биологии Презентация на тему "Структура бактериальной клетки. Основные формы бактерий. Особенности химического состава микробной клетк
Презентация на тему "Структура бактериальной клетки. Основные формы бактерий. Особенности химического состава микробной клетк Грибы
Грибы Пищевые вещества
Пищевые вещества Генетика мікроорганізмів. Мінливість бактерій. Мікробіологічні основи генної інженерії і біотехнології
Генетика мікроорганізмів. Мінливість бактерій. Мікробіологічні основи генної інженерії і біотехнології Угадай цветок
Угадай цветок Влияние сна на человека
Влияние сна на человека