Содержание
- 2. Integumentary System Only 1.5 to 4 mm thick but is body’s largest organ 7% of body
- 3. Integument Composition Two basic layers Epidermis External Stratified squamous epithelium Dermis Deeper Mostly dense irregular connective
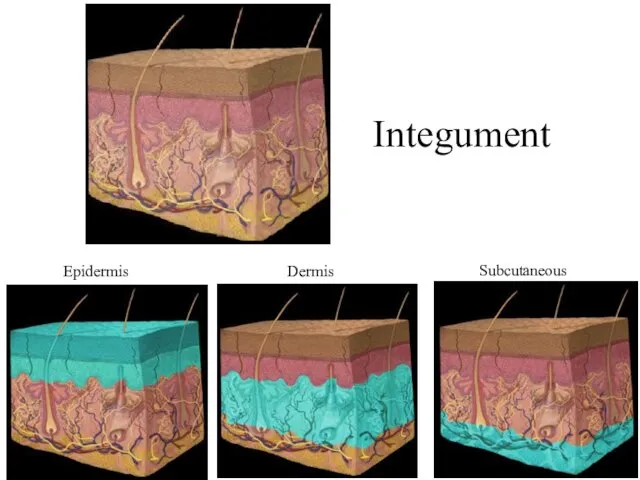
- 4. Integument Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer
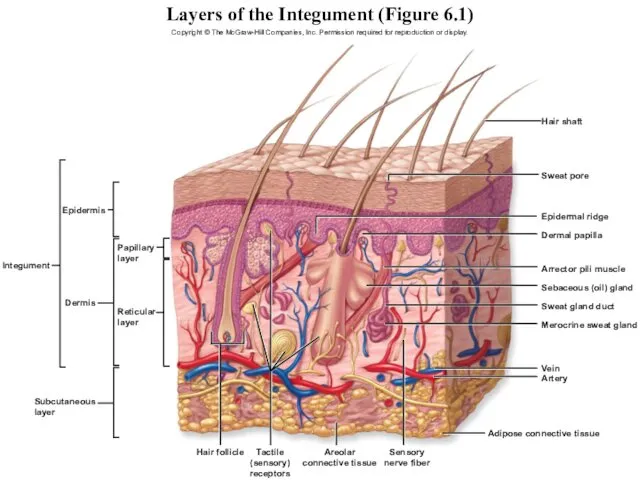
- 5. Layers of the Integument (Figure 6.1) Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
- 6. Epidermis Epithelial tissue arranged in 5 layers or strata Cells divide in only in base layer
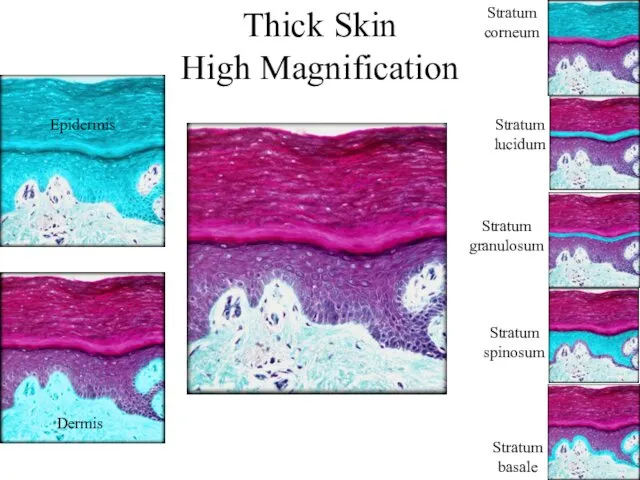
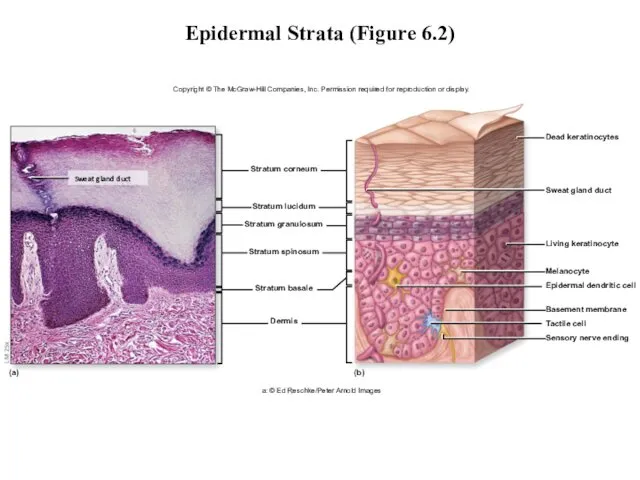
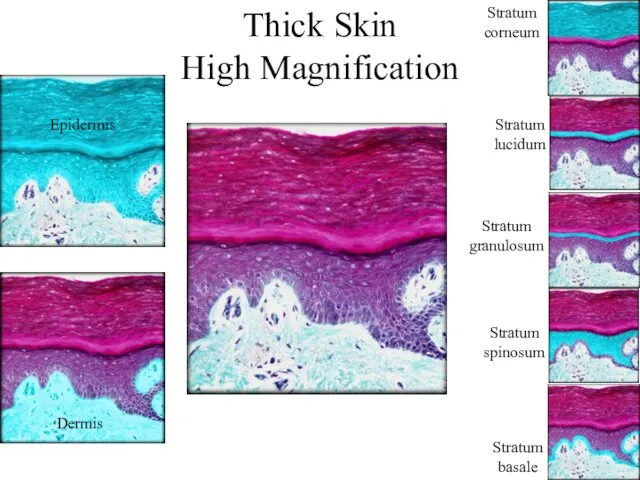
- 7. Epidermal Strata From deep to superficial Stratum basale (base layer) Stratum spinosum (spiny layer) Stratum granulosum
- 8. Thick Skin High Magnification Epidermis Dermis Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum
- 9. Stratum Basale Single layer of cuboidal to low columnar cells attached to a basement membrane Include
- 10. Stratum Spinosum Cells are pushed up from below and become “squished” and look spiny on cross
- 11. Stratum Granulosum Cells in this layer start to keratinize (fill with keratin) and look grainy Keratohyalin-
- 12. Stratum Lucidum Keratinocytes with transforming keratohyaline Keratohyaline transforms to clear substance eleidin Found only in thick
- 13. Stratum Corneum 20-30 layers of dead keratinocytes Keratin now fully formed Cells are dead Keratinized stratified
- 14. Epidermal Strata (Figure 6.2) Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
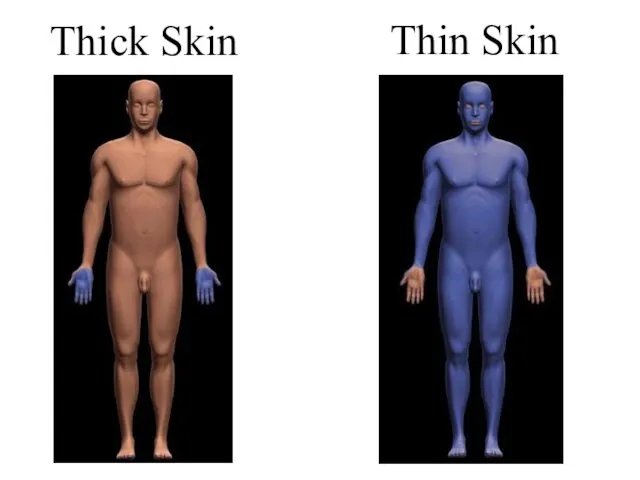
- 15. Variations in the Epidermis Epidermis is not the same over all portions of the body or
- 16. Thick Skin Thin Skin
- 17. Thick Skin High Magnification Epidermis Dermis Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum
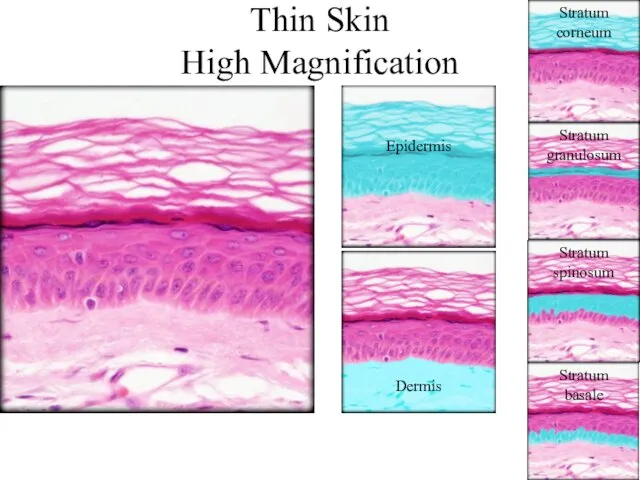
- 18. Thin Skin High Magnification Epidermis Dermis Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum corneum
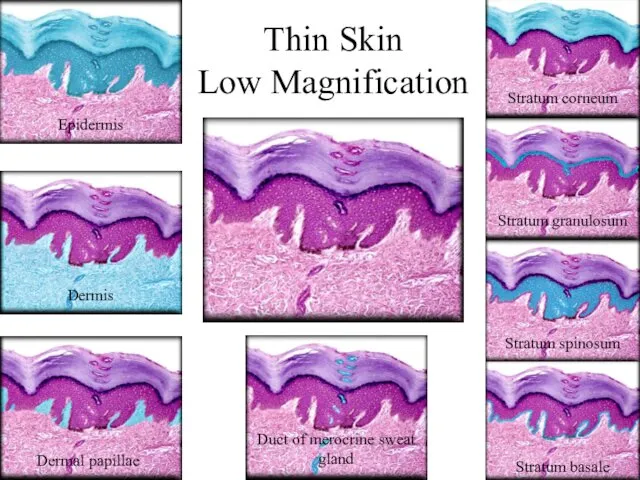
- 19. Thin Skin Low Magnification Epidermis Dermis Dermal papillae Duct of merocrine sweat gland Stratum corneum Stratum
- 21. Скачать презентацию








 Презентация Цветок
Презентация Цветок  Биоэкология растений
Биоэкология растений Презентация на тему Неправильное питание
Презентация на тему Неправильное питание  Гипотеза происхождения жизни
Гипотеза происхождения жизни Дыхательная система человека
Дыхательная система человека Обитатели Тайги
Обитатели Тайги Видовое разнообразие флоры в Казахстане
Видовое разнообразие флоры в Казахстане Презентация на тему О птицах зимой
Презентация на тему О птицах зимой Ученица 9 «Б» класса Нежинского лицея КИЛЯЗОВА ЕКАТЕРИНА
Ученица 9 «Б» класса Нежинского лицея КИЛЯЗОВА ЕКАТЕРИНА  Тигровая викторина
Тигровая викторина Тупорылая Акула
Тупорылая Акула День моржа
День моржа Биохимия, как наука. Элементарный и молекулярный состав живых организмов
Биохимия, как наука. Элементарный и молекулярный состав живых организмов Тест по гистологии. Практика №1
Тест по гистологии. Практика №1 Кровь и остальные компоненты внутренней среды организма
Кровь и остальные компоненты внутренней среды организма Задачи по семеноводству
Задачи по семеноводству Концепции организации живых систем. Популяционно-видовой уровень живого. (Лекция 15)
Концепции организации живых систем. Популяционно-видовой уровень живого. (Лекция 15) Органы чувств
Органы чувств Теории возникновения жизни Теории возникновения жизни на Земле.
Теории возникновения жизни Теории возникновения жизни на Земле. Передача наследственной информации от ДНК к и-РНК и к белку
Передача наследственной информации от ДНК к и-РНК и к белку Экологическое загрязнение Брянской области _
Экологическое загрязнение Брянской области _ Понятие о микроорганизмах. Тема № 7/1
Понятие о микроорганизмах. Тема № 7/1 СТРУКТУРА И ФУНКЦИИ ХРОМОСОМ Автор Долгорукова С.В., учитель высшей категории МОУ гимназия № 2 Г.Екатеринбурга
СТРУКТУРА И ФУНКЦИИ ХРОМОСОМ Автор Долгорукова С.В., учитель высшей категории МОУ гимназия № 2 Г.Екатеринбурга  Презентация на тему Решение проблем с отходами
Презентация на тему Решение проблем с отходами  Томаты
Томаты Основные виды питательных веществ и их значение в питании человека
Основные виды питательных веществ и их значение в питании человека Клеточный цикл. Митоз. Стволовые клетки. Понятие о детерминации и дифференцировке
Клеточный цикл. Митоз. Стволовые клетки. Понятие о детерминации и дифференцировке Иерархия в табуне!
Иерархия в табуне!