Содержание
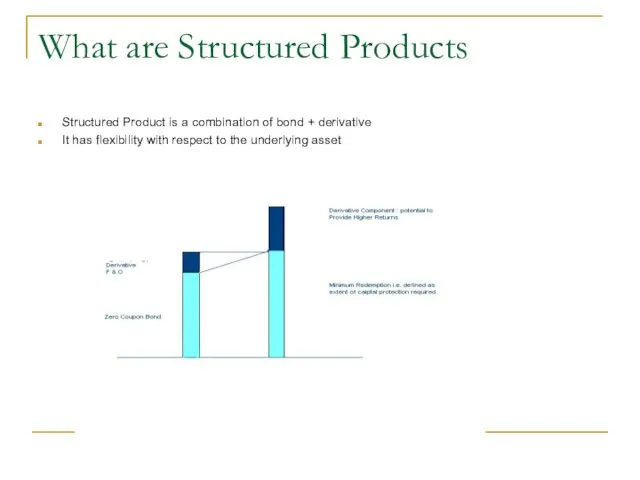
- 2. What are Structured Products Structured Product is a combination of bond + derivative It has flexibility
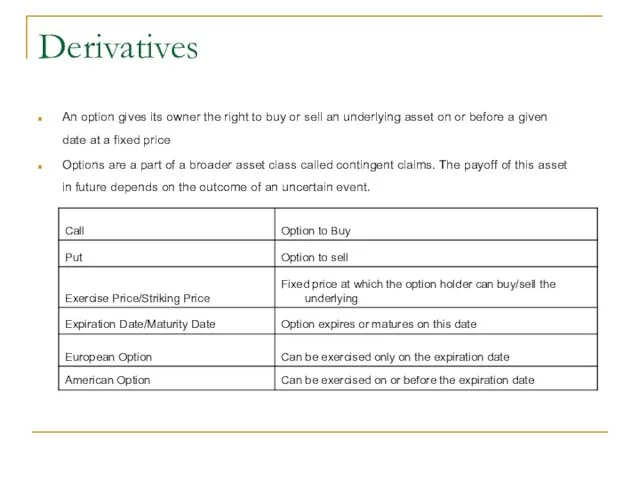
- 3. Derivatives An option gives its owner the right to buy or sell an underlying asset on
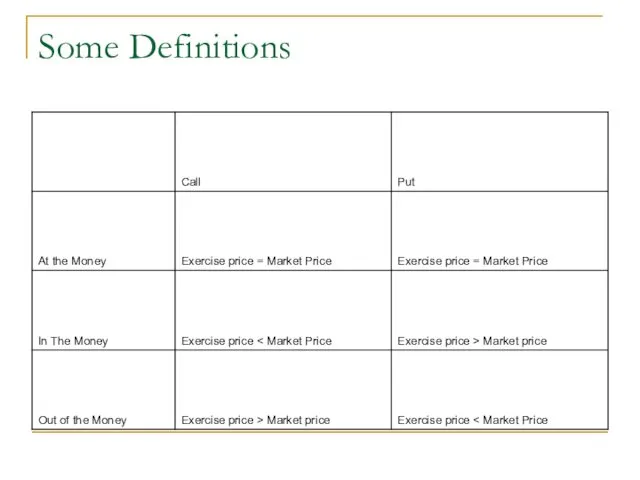
- 4. Some Definitions
- 5. Types of Structured Products CPPI ( Constant Proportion Portfolio Insurance) Based Structures : The client is
- 6. CPPI Constant Proportion Portfolio Insurance (CPPI) is the name given to a trading strategy that is
- 7. CPPI-Jargon Floor : Present Value of desired capital to be preserved at maturity. If the product
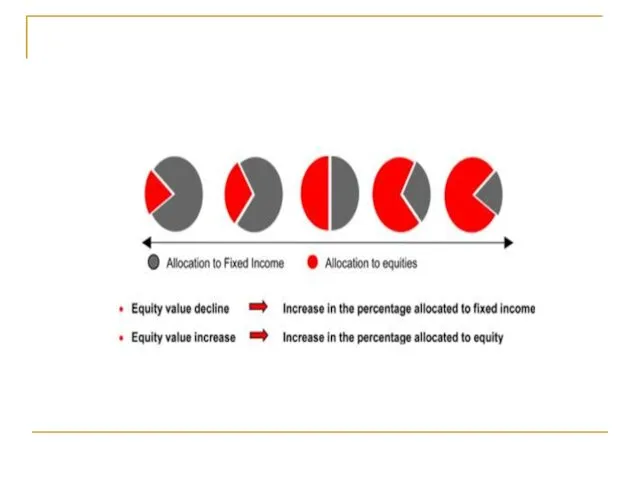
- 8. How CPPI operates Essentially the strategy involves continuously re-balancing the portfolio of investments during the term
- 10. Example of CPPI Initial Investment : 100 Minimum Guarantee : 80 after 5years Investment pattern if
- 11. Example of CPPI Same example if market rises and value of equity goes up from 40
- 12. Risk in CPPI-Cash Locked In the worst case scenario the market trends downwards. Then the risky
- 13. Risk in CPPI-Model Risk Another risk is known as Model risk. This is the risk that
- 14. Risk in CPPI-Trading Band Width According to the CPPI methodology, risky assets are being bought in
- 15. Gap Protection Banks that provide CPPI underwrite this so-called ‘Gap Risk’ and guarantee to stand by
- 16. The difference between CPPI and standard fixed participation methodology Unlike a standard structured product which places
- 17. Some Indian Structured Products
- 18. HSBC Capital Guard Portfolio The key features of this product are: * 100% Capital Protection Guaranteed
- 19. JM Financial’s Triple AAAce Scheme JM Financial’s Triple AAAce Scheme, will invest in equity funds for
- 20. Structured Products in Global Markets Some Examples
- 21. Exotics Exotics are exotic options which are different from the plain vanilla European and American Options.
- 22. Structured Products-Growth Protected Note Turbo Note Digital Plus Lock-in Accumulator Delta One Certificate Outperformer Sprint Best
- 23. Structured Products-Income Callable Corridor Scoop Reverse Convertible Reverse Discount FX Target Callable Stability Note Phoenix Note
- 24. Protected Note A Protected Note is a structured procuct,100% Capital Guaranteed at maturity, which allows the
- 25. Example of Protected Note Example 1: Increase of the underlying on the final observation date If
- 26. Turbo Note A Turbo Note is a structured product,100% Capital Guaranteed at maturity, which allows the
- 27. Turbo Note Advantages 100% capital protection The product provides higher participation in the increase of an
- 28. Example of Turbo Note Participation : 100% of increase of the underlying Barrier : 130% Example
- 29. Digital Plus A Digital Plus is a structured product ,100% capital guaranteed at maturity, which allows
- 30. Digital Plus Advantages The investor can benefit from the entire positive performance of the underlying A
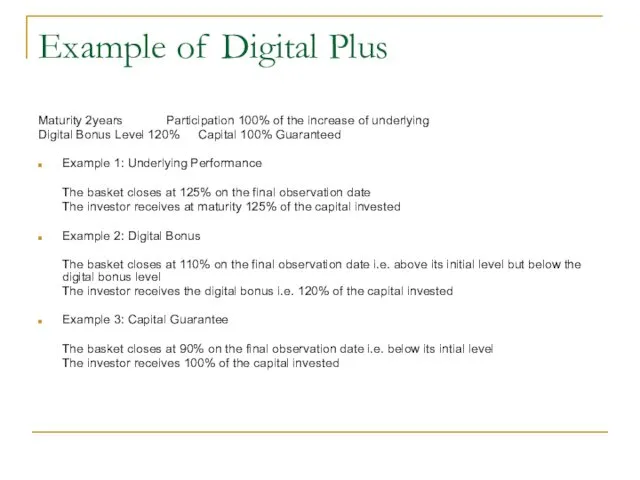
- 31. Example of Digital Plus Maturity 2years Participation 100% of the increase of underlying Digital Bonus Level
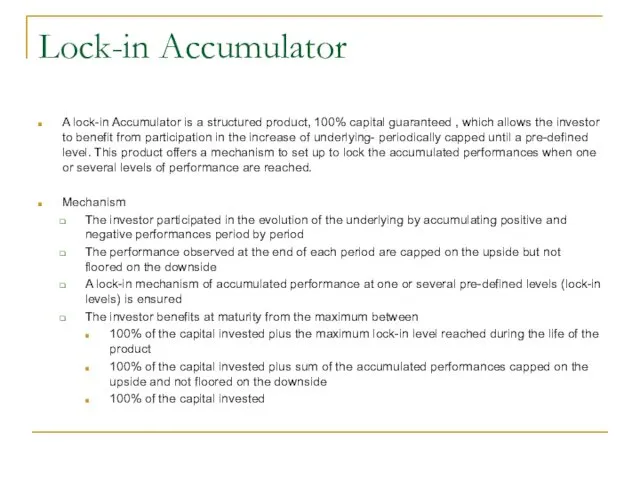
- 32. Lock-in Accumulator A lock-in Accumulator is a structured product, 100% capital guaranteed , which allows the
- 33. Lock-in Accumulator Advantages The capital is 100% guaranteed at maturity The investor can benefit from a
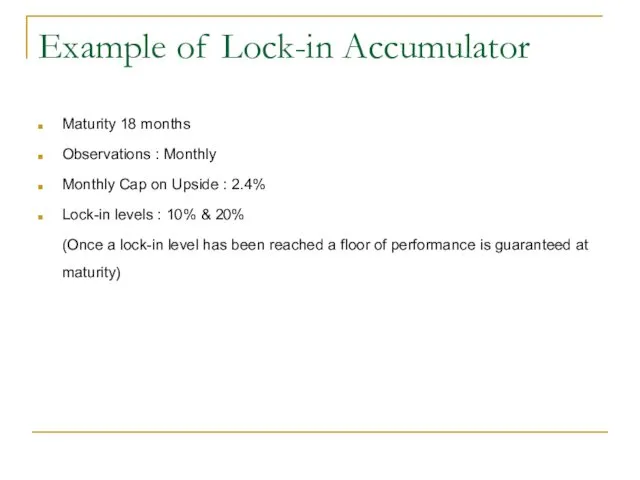
- 34. Example of Lock-in Accumulator Maturity 18 months Observations : Monthly Monthly Cap on Upside : 2.4%
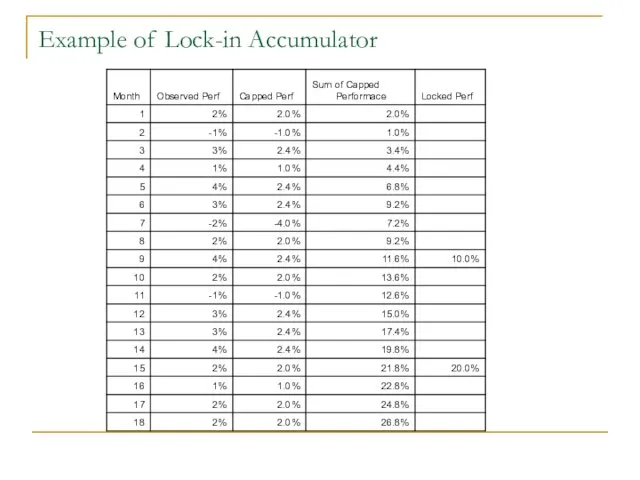
- 35. Example of Lock-in Accumulator
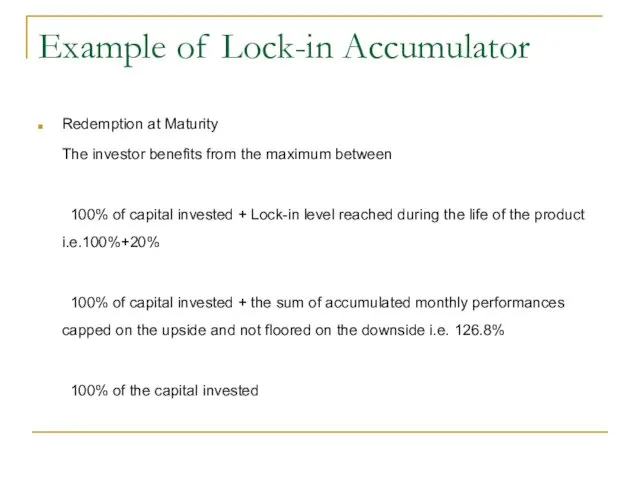
- 36. Example of Lock-in Accumulator Redemption at Maturity The investor benefits from the maximum between 100% of
- 37. Delta One Certificate A Delta One Certificate I a structured product which allows the investor to
- 38. Example of Delta One Certificate Example 1: Increase of Underlying The basket closes at 120% on
- 39. Outperformer An outperformer is a structured product which allows the investor to benefit from a high
- 40. Outperformer Structure Buy a Call Zero (in order to arbitrate the dividends) Buy x% of a
- 41. Example of Outperformer Underlying XYZ Stock Maturity : 12 months Capital : Not Guaranteed Participation 130%
- 42. Sprint A sprint is is a structured product which allows the investor to benefit from a
- 43. Sprint Structure Buy a Call Zero ( In order to arbitrate the dividends) Buy 100% of
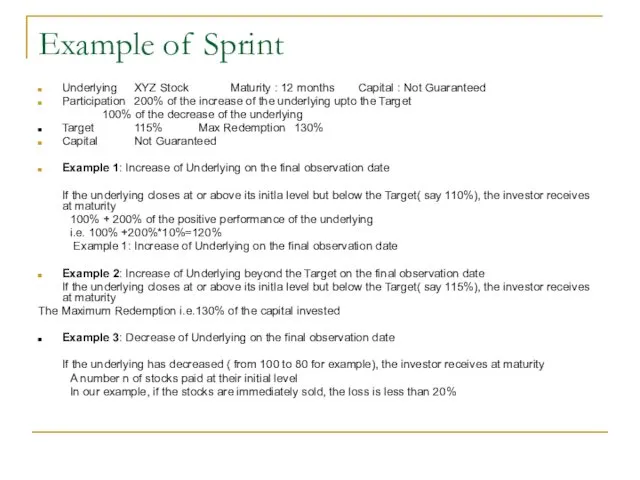
- 44. Example of Sprint Underlying XYZ Stock Maturity : 12 months Capital : Not Guaranteed Participation 200%
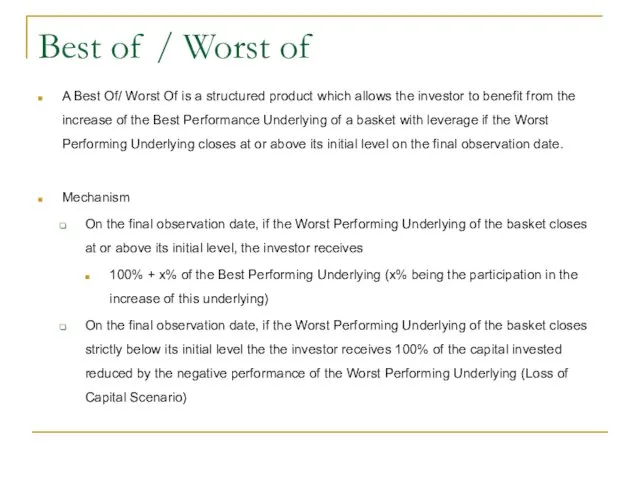
- 45. Best of / Worst of A Best Of/ Worst Of is a structured product which allows
- 46. Best of / Worst of Advantages The investor benefits from a high leveraged participation in the
- 47. Example of Best Of/Worst Of Underlying: ABC Stock and XYZ Stock Maturity : 12months Participation :
- 48. Callable Corridor A Callable Corridor is a structured product , 100% capital protected at maturity, which
- 49. Callable Corridor Structure Buy a strip of daily binary European Options Buy a zero coupon Sella
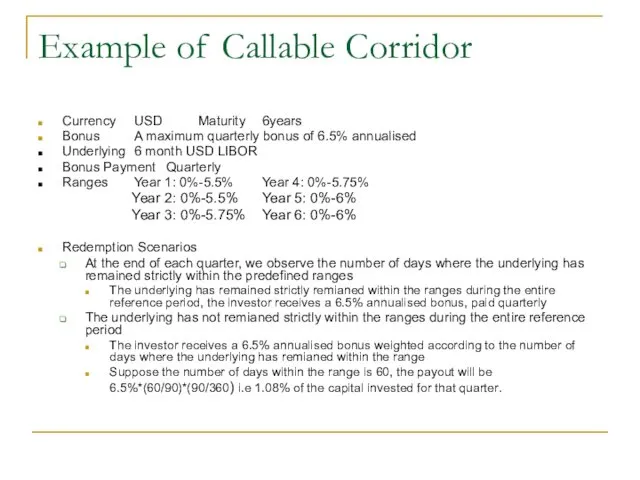
- 50. Example of Callable Corridor Currency USD Maturity 6years Bonus A maximum quarterly bonus of 6.5% annualised
- 51. Hw to Create Your Own Structured Product Strategy A1 Using Fixed Deposits and Equity Strategy A2
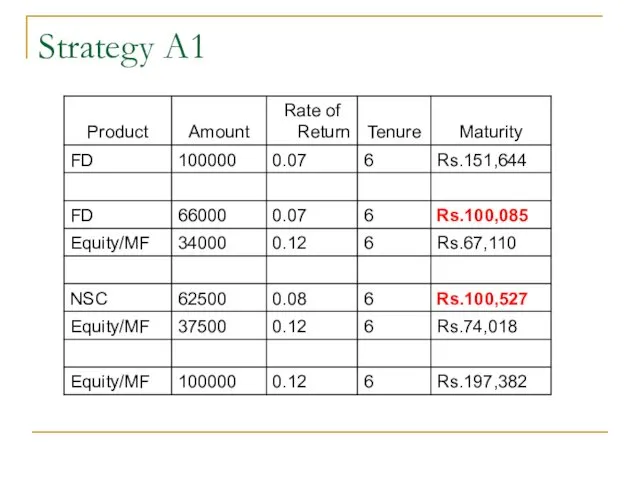
- 52. Strategy A1
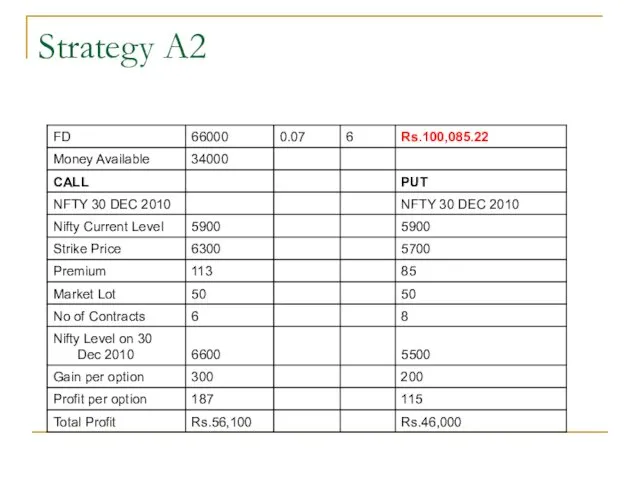
- 53. Strategy A2
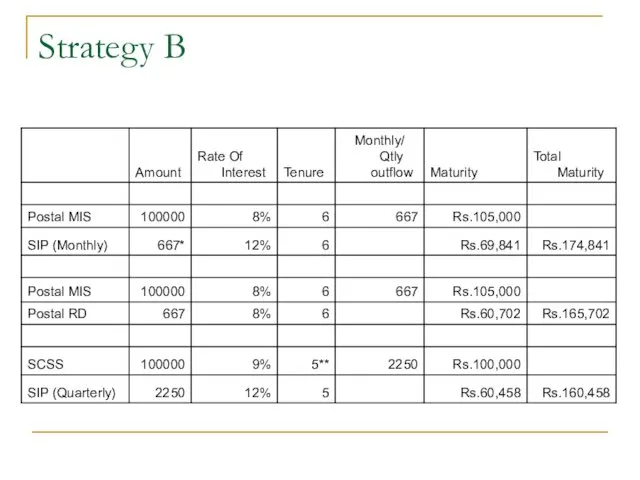
- 54. Strategy B
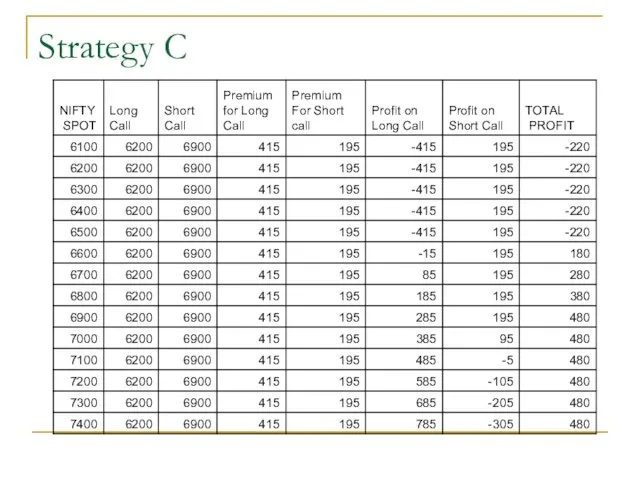
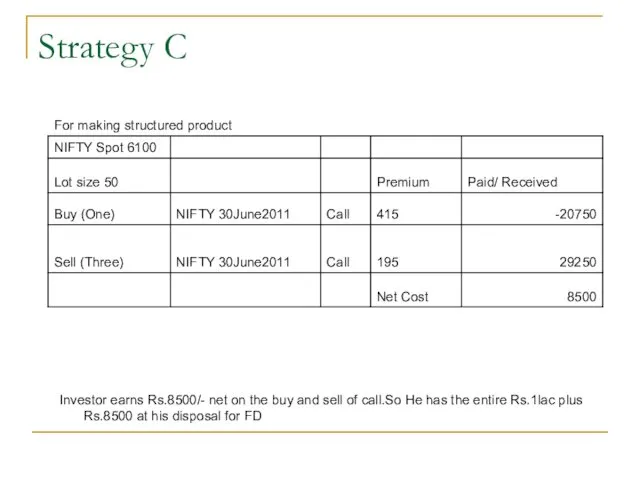
- 55. Strategy C
- 56. Strategy C Maximum Loss = Difference in the premium of Long and Short Call =415-195 =220
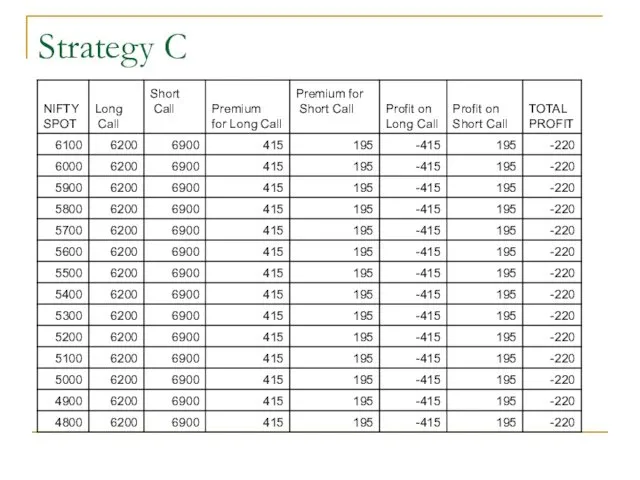
- 57. Strategy C
- 58. Strategy C
- 59. Strategy C Maximum Loss = Difference in the premium of Long and Short Call =415-195 =220
- 60. Risk in Structured Products Issuers Credit Risk Market Risk : The value of investment changes with
- 61. Distribution Platforms in India PMS : FMP/Insurance Direct Distribution Issuers are NBFC’s Platform providers are MF’s,
- 63. Скачать презентацию










































 Економічний зріст
Економічний зріст Игорный бизнес в ЮАР
Игорный бизнес в ЮАР Классификация условий трудовой деятельности
Классификация условий трудовой деятельности Экономикалық өсу
Экономикалық өсу Проблемы развития малого бизнеса в республике Хакасия
Проблемы развития малого бизнеса в республике Хакасия Методы очистки питьевой воды, 68 Редок Полина, э122б
Методы очистки питьевой воды, 68 Редок Полина, э122б Электромеханический завод Пегас. Кабельная продукция
Электромеханический завод Пегас. Кабельная продукция Контрольная работа по экономике
Контрольная работа по экономике Експорт та імпорт Великої Британії
Експорт та імпорт Великої Британії Предложение и спрос на рынке труда Республики Башкортостан
Предложение и спрос на рынке труда Республики Башкортостан Система национальных счетов. Основные макроэкономические показатели. (Тема 2)
Система национальных счетов. Основные макроэкономические показатели. (Тема 2) Регулювання торгівлі фінансовими активами. (Тема 4)
Регулювання торгівлі фінансовими активами. (Тема 4) Manufacturing Statistics Current trends and challenges
Manufacturing Statistics Current trends and challenges Экономика. Своя игра
Экономика. Своя игра Экономика, экономическая теория. Тестовые задания
Экономика, экономическая теория. Тестовые задания Нематериальные активы предприятия
Нематериальные активы предприятия Общее экономическое равновесие. Построение кривой IS (сбережения – инвестиции)
Общее экономическое равновесие. Построение кривой IS (сбережения – инвестиции) Глобальні світові проблеми. Сировинна та енергетична проблема світу
Глобальні світові проблеми. Сировинна та енергетична проблема світу Инвестиционный паспорт региона. Брянская область
Инвестиционный паспорт региона. Брянская область Всемирные экономические отношения
Всемирные экономические отношения Инфляция и безработица. Тема 10
Инфляция и безработица. Тема 10 Влияние социально-экономического кризиса на здоровье населения как условия трудового потенциала Южно-Казахстанской области
Влияние социально-экономического кризиса на здоровье населения как условия трудового потенциала Южно-Казахстанской области Макроекономічний огляд. Січень, 2016
Макроекономічний огляд. Січень, 2016 Совершенствование условий труда на предприятии на примере ООО «ПФ «Глас»
Совершенствование условий труда на предприятии на примере ООО «ПФ «Глас» Теоретические основы муниципального хозяйства
Теоретические основы муниципального хозяйства Теория производства фирмы
Теория производства фирмы Стандарт GMP
Стандарт GMP Национальная экономика и результаты ее функционирования
Национальная экономика и результаты ее функционирования