Содержание
- 2. Traditional Scientific Method But it doesn’t describe reality of how science works
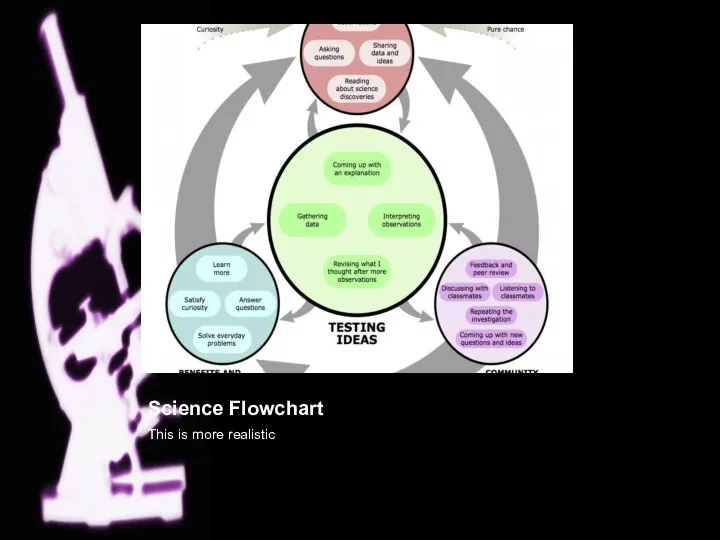
- 3. Science Flowchart This is more realistic
- 4. The Cultural Side The scientific community and the educational institution can rightly be considered ‘subcultures’ each
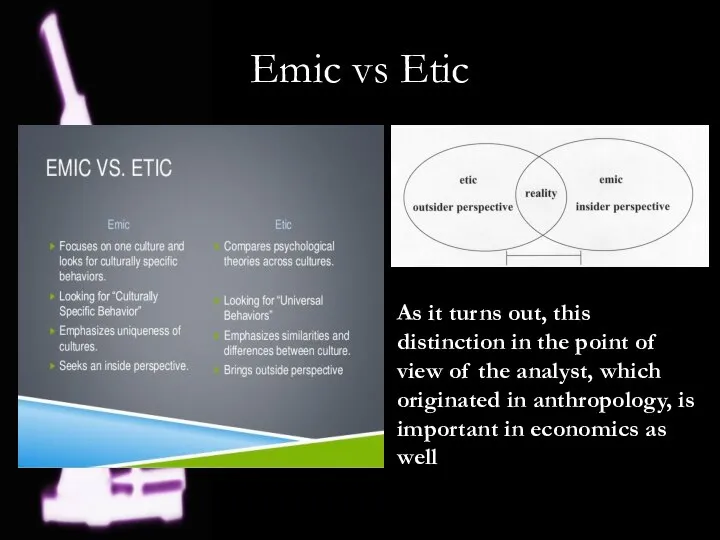
- 5. Emic vs Etic As it turns out, this distinction in the point of view of the
- 6. Philosophy of Science: Karl Popper, 1902-1994 Falsification: a theory is scientific when it is capable of
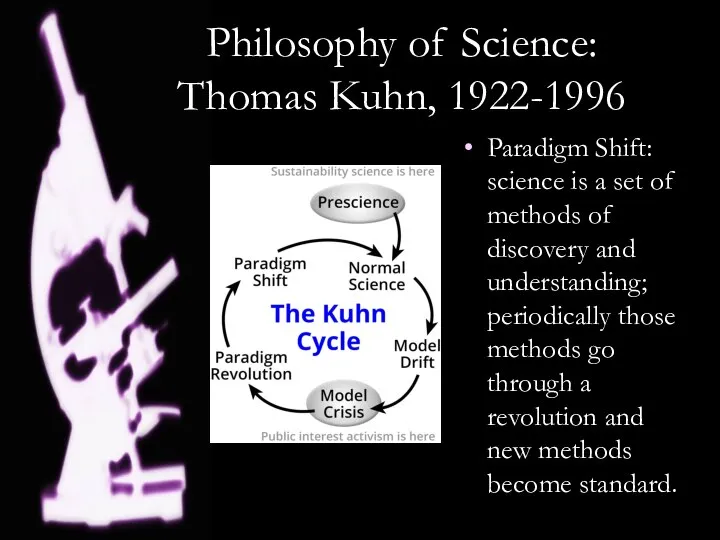
- 7. Philosophy of Science: Thomas Kuhn, 1922-1996 Paradigm Shift: science is a set of methods of discovery
- 8. Economics Paradigms 1: Mainstream US & UK -Classical Economics: Adam Smith to Alfred Marshall. Focus on
- 9. Econ Paradigms 2: Socialism Marxist: revolution by the working class displaces capitalists, so that workers own
- 10. Economics Paradigms 3 -Monetarism: Milton Friedman. Focus on the ability of the Central Bank to mange
- 11. Economics Paradigms 4: Libertarianism -“Capitalism is a social system based on the recognition of individual rights,
- 13. Скачать презентацию







 Макроэкономическое равновесие
Макроэкономическое равновесие Планирование и проектирование организаций
Планирование и проектирование организаций Сільське господарство Миколаівщини
Сільське господарство Миколаівщини Глобализация в конце XX - начале XXI века
Глобализация в конце XX - начале XXI века Управление проектами. Начало проекта, прединвестиционная фаза
Управление проектами. Начало проекта, прединвестиционная фаза Презентация Таможенная политика в период складывания единого централизованного государства.
Презентация Таможенная политика в период складывания единого централизованного государства. Анализ конкурентной среды
Анализ конкурентной среды Антология экономической мысли
Антология экономической мысли Система международных отношений
Система международных отношений ВВП и способы его измерения. Индекс цен
ВВП и способы его измерения. Индекс цен Презентация Теории экономических систем и их практическое значение. Эволюция и основные типы экономических систем
Презентация Теории экономических систем и их практическое значение. Эволюция и основные типы экономических систем Ekonomi̇k bi̇r mal olarak eği̇ti̇m
Ekonomi̇k bi̇r mal olarak eği̇ti̇m Анализ состояния банковской системы Республики Беларусь
Анализ состояния банковской системы Республики Беларусь Глобализация и регионализация как факторы современного мироустройства
Глобализация и регионализация как факторы современного мироустройства Теория поведения фирмы
Теория поведения фирмы Макроэкономический анализ открытой экономики. (Тема 8)
Макроэкономический анализ открытой экономики. (Тема 8) Планирование и политика развития туризма
Планирование и политика развития туризма Хозяйство Северного экономического района
Хозяйство Северного экономического района Планирование и прогнозирование темпов экономического роста и объема ВНП
Планирование и прогнозирование темпов экономического роста и объема ВНП Отчёт директора производственного отделения Челябинские городские электрические сети филиала «Челябэнерго»
Отчёт директора производственного отделения Челябинские городские электрические сети филиала «Челябэнерго» Brasserie Verdus. Инвестиционный проект во Франции
Brasserie Verdus. Инвестиционный проект во Франции Затраты при международных автомобильных перевозках. Дорожные налоги и сборы при выполнении автомобильных перевозок
Затраты при международных автомобильных перевозках. Дорожные налоги и сборы при выполнении автомобильных перевозок Международная торговая политика и организации
Международная торговая политика и организации Консультация. Экономика предприятия
Консультация. Экономика предприятия Безработица. Причины и виды безработицы. Уровень безработицы. Последствия
Безработица. Причины и виды безработицы. Уровень безработицы. Последствия Занятость и безработица. Социальная политика
Занятость и безработица. Социальная политика Несовершенство рынка. Роль государства в современной рыночной экономике
Несовершенство рынка. Роль государства в современной рыночной экономике Аналіз методик оцінки ймовірності банкрутства
Аналіз методик оцінки ймовірності банкрутства