Содержание
- 2. 1.11.2004 Training program General introduction Process recap SAP main structures FI and CO structures General ledger
- 3. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 4. 1.11.2004 Introduction This training will cover the following areas: General ledger Accounts payable Accounts receivable Cash
- 5. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 6. 1.11.2004 Process re-cap Key process 15 consists of: 15a Financial management and accounting 15b Business controlling
- 7. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 8. 1.11.2004 Overview of Financial accounting in SAP In Financial accounting you generate financial reports like the
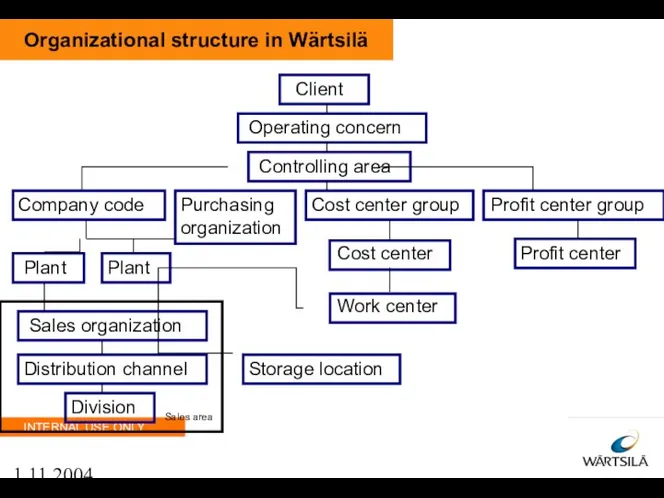
- 9. 1.11.2004 Organizational structure in Wärtsilä Client Operating concern Controlling area Company code Plant Plant Cost center
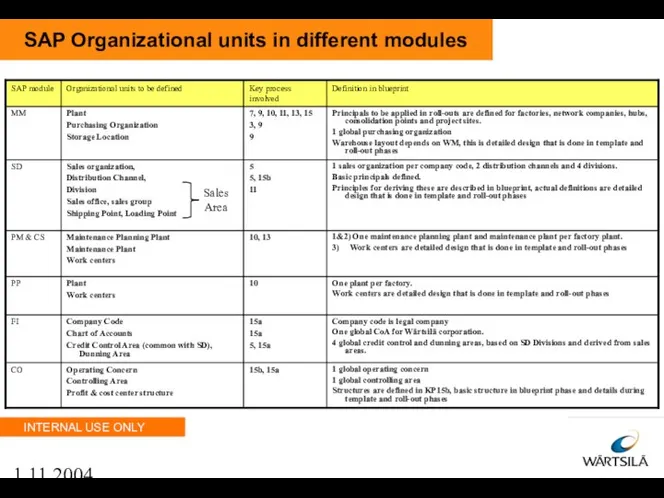
- 10. 1.11.2004 SAP Organizational units in different modules Sales Area
- 11. 1.11.2004 Integration of organisational structures
- 12. 1.11.2004 Operating Concern Operating concern is the highest reporting level in CO-PA and it defines the
- 13. 1.11.2004 Client Client is a commercially, organizationally, and technically self-contained unit within an SAP System. Clients
- 14. 1.11.2004 Master data in Financial accounting Important master data in Financial accounting Chart of accounts Company
- 15. 1.11.2004 Chart of Accounts The chart of accounts is a classification scheme consisting of a group
- 16. 1.11.2004 Chart of Accounts / Account groups
- 17. 1.11.2004 Chart of Accounts / Account groups
- 18. 1.11.2004 Company code The smallest organizational unit of Financial Accounting for which a complete self-contained set
- 19. 1.11.2004 Controlling structures Cost elements Cost centers Internal orders Activity types Business processes (ABC) Not in
- 20. 1.11.2004 Cost objects
- 21. 1.11.2004 Cost Element Accounting - (CO-OM-CEL) The part of accounting where you organise costs (and revenues)
- 22. 1.11.2004 Cost Center Accounting - (CO-OM-CCA) The part of accounting where you organise costs according to
- 23. 1.11.2004 Cost Center Accounting - (CO-OM-CCA) The numbering convention used in the productive system is based
- 24. 1.11.2004 Cost Allocation - (CO-OM-CCA) There are different cost allocation methods available in SAP but some
- 25. 1.11.2004 Cost Allocation - Assessment - (CO-OM-CCA) The cost allocation method called assessment has the following
- 26. 1.11.2004 Activity Types - (CO-OM-CCA) The activity type classifies the specific activities that are provided by
- 27. 1.11.2004 Example of Activity Type allocation - (CO-OM-CCA) Central & local control
- 28. 1.11.2004 Statistical key figures Statistical key figures are measurable quantities that can be assigned to cost
- 29. 1.11.2004 Internal Orders - (CO-OM-OPA) Internal order is a tool in the controlling module that can
- 30. 1.11.2004 Examples on use of Internal Orders - (CO-OM-OPA) It has been planned to use Internal
- 31. 1.11.2004 Settlement of Real Internal Orders - (CO-OM-OPA) The real internal order can be settled to
- 32. 1.11.2004 Profit Center Accounting - (CO-PCA) The part of accounting where you analyse how profitable different
- 33. 1.11.2004 Profit Center Accounting - (CO-PCA) The numbering convention used in the productive system is based
- 34. 1.11.2004 Product Cost Controlling - (CO-PC) The part of accounting where you analyse what it costs
- 35. 1.11.2004 Master Data in Product Cost Controlling - (CO-PC) The following master data is used in
- 36. 1.11.2004 Profitability Analysis - (CO-PA) Profitability analysis is used to analyse the profitability of different market
- 37. 1.11.2004 Basic structure in CO-PA Central control To create the structure you need to define Characteristics
- 38. 1.11.2004 Cost and profit center structure Cost center Profit center Department Divisional business group Company Division
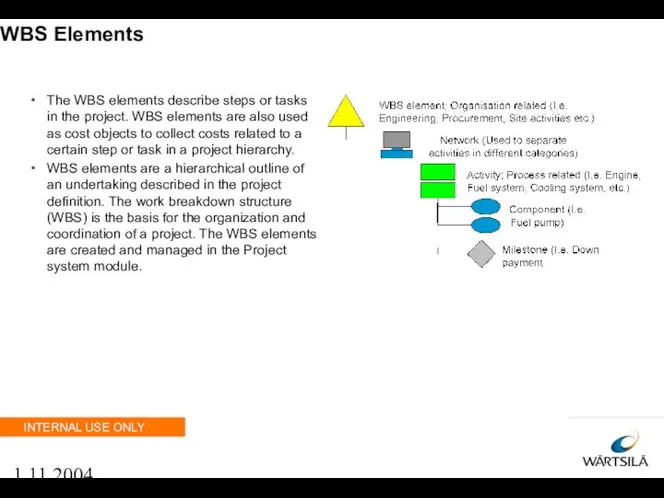
- 39. 1.11.2004 WBS Elements The WBS elements describe steps or tasks in the project. WBS elements are
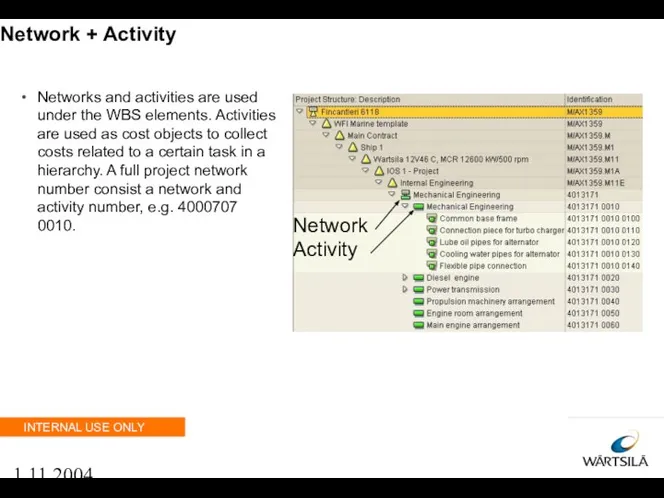
- 40. 1.11.2004 Network + Activity Networks and activities are used under the WBS elements. Activities are used
- 41. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 42. 1.11.2004 Integration When an FI document is created and posted to an expense account, an controlling
- 43. 1.11.2004 FI integration with MM Goods received (R) Invoice receipt(GR/IR) 2510 800 * Raw materials 1300
- 44. 1.11.2004 Purchase postings Check the FI-MM integration with transaction code ME23N. In this transaction you can
- 45. 1.11.2004 Account assignment for purchases and consumption We need to have costs for consumption (incl.goods issues)
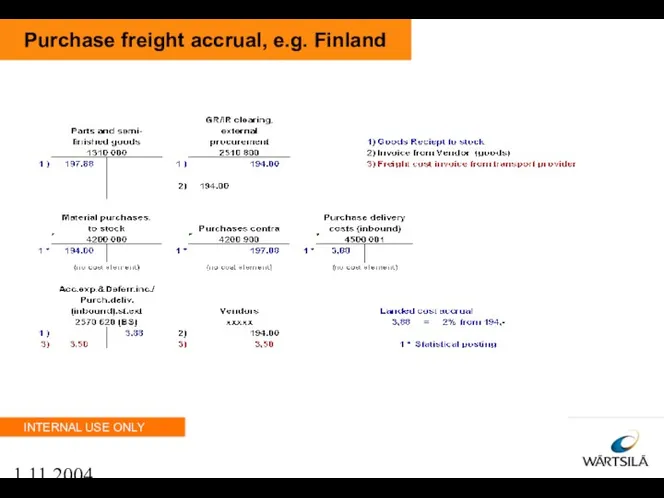
- 46. 1.11.2004 Purchase freight accrual, e.g. Finland
- 47. 1.11.2004 FI integration with SD SALES SHIPPING BILLING SD FI Sales order No document Outbound delivery
- 48. 1.11.2004 Sales and delivery postings You can check the integration from the order with the document
- 49. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 50. 1.11.2004 General ledger postings Enter G/L account postings G/L account master records Posting keys Manual postings
- 51. 1.11.2004 G/L account master records G/L account master records contain the data that is always needed
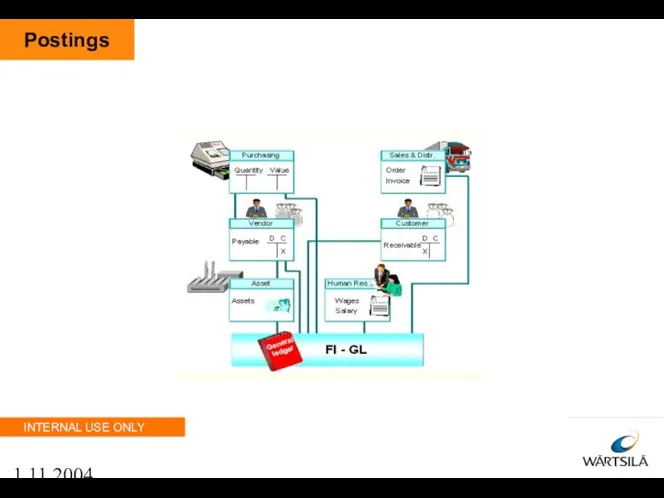
- 52. 1.11.2004 Postings
- 53. 1.11.2004 Posting keys You control processing of entered data with the posting key. Two-character numerical key
- 54. 1.11.2004 Document numbers Every document contains a document type in its header. The document type has
- 55. 1.11.2004 Manual postings You create G/L account document using a one-screen transaction. This is executed with
- 56. 1.11.2004 What Can You Do Before Posting a Document? After you have entered the document line
- 57. 1.11.2004 Change document With transaction FB02 you can change some fields in a document. You can
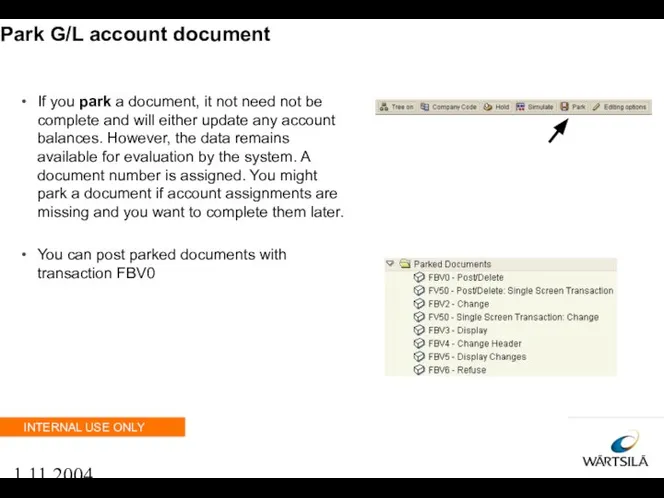
- 58. 1.11.2004 Park G/L account document If you park a document, it not need not be complete
- 59. 1.11.2004 Bank accounts E.g. Nordea EUR, IG Bank account 1970050 Incoming payments clearing account 1970055 Outgoing
- 60. 1.11.2004 Posting situations Projects Costs to parts sale Department costs Asset postings Warranty costs Rental incomes
- 61. 1.11.2004 Posting to assets If you need to post directly to a asset number, go to
- 62. 1.11.2004 Automatic postings With certain transactions, the system generates automatic postings. These are for example: Input
- 63. 1.11.2004 Reversal Corrections to the ledger Use transaction FB08 (Reverse document) to reverse an accounting document.
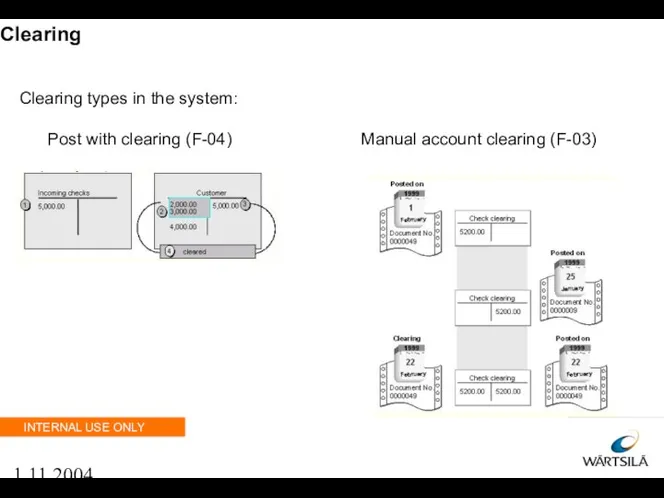
- 64. 1.11.2004 Clearing Clearing types in the system: Post with clearing (F-04) Manual account clearing (F-03)
- 65. 1.11.2004 Post with clearing When posting with clearing the following Steps need to be executed: Insert
- 66. 1.11.2004 Account clearing With transaction F-03 you can clear a G/L account. The steps are to:
- 67. 1.11.2004 Automatic clearing With transaction F.13 you can process the account clearing automatically. This transaction is
- 68. 1.11.2004 VAT TAX The VAT processing is made with country specific tax procedures in SAP system.
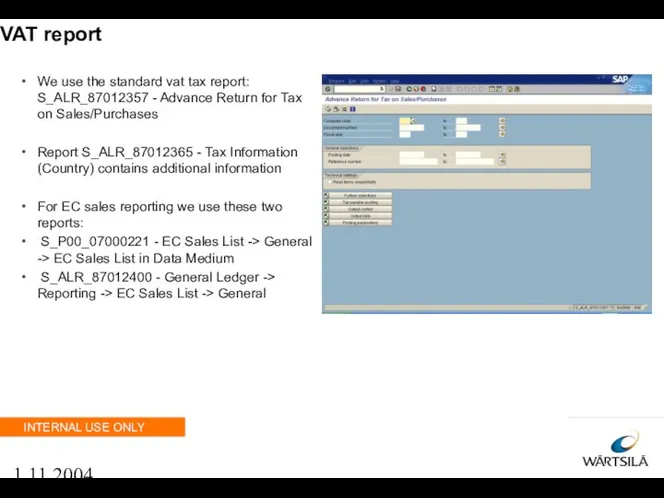
- 69. 1.11.2004 VAT report We use the standard vat tax report: S_ALR_87012357 - Advance Return for Tax
- 70. 1.11.2004 Withholding tax When a customer that is authorized to deduct withholding tax pays invoices from
- 71. 1.11.2004 Print forms With transaction FB12 you generate an request for Account statement or Open item
- 72. 1.11.2004 Reports When you post documents to an account, the system automatically updates the account balance.
- 73. 1.11.2004 Reports From the General ledger information system you can run several reports. E.g.: S_ALR_87012277 -
- 74. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 75. 1.11.2004 Overview The Accounts Payable application component records and manages accounting data for all vendors. It
- 76. 1.11.2004 Master data The vendor master data include the following data: General vendor data (include such
- 77. 1.11.2004 Postings If purchase invoice handling system is not in use for your company, you insert
- 78. 1.11.2004 Postings If your company use Basware purchase invoice processing system (IP). Invoices are scanned and
- 79. 1.11.2004 Reports Line items for vendor invoices can be checked with transaction: FBL1N – Vendor line
- 80. 1.11.2004 Reports From the Accounts payable – Information system you can run reports for: Vendor balances
- 81. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 82. 1.11.2004 Overview Purpose: To keep track of customers and the transactions involved in them. Its job
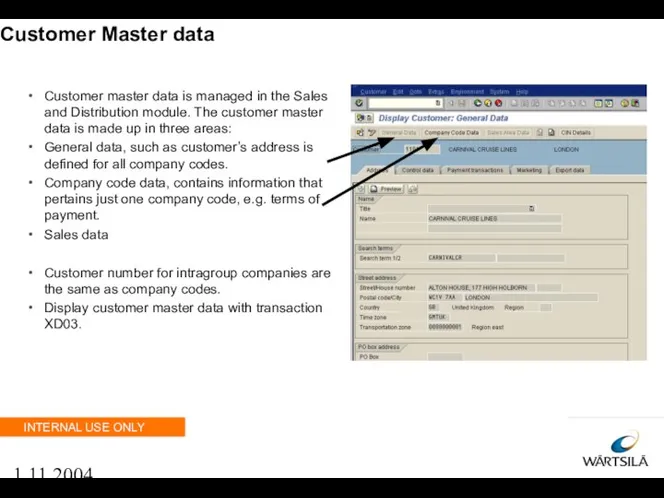
- 83. 1.11.2004 Customer Master data Customer master data is managed in the Sales and Distribution module. The
- 84. 1.11.2004 Postings Customer invoices are created in the SD module. Create sales order with transaction VA01
- 85. 1.11.2004 Weekly procedures to ensure the validity Blocked Billing Documents in SD The menu path to
- 86. 1.11.2004 Dunning With dunning you can: Select open items that are overdue Dunn customer by sending
- 87. 1.11.2004 Reports for Accounts receivable These standard reports are available in Accounts receivable.
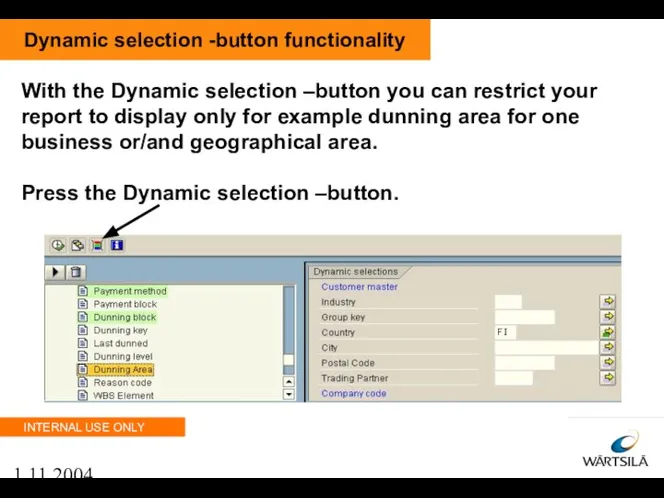
- 88. 1.11.2004 Dynamic selection -button functionality With the Dynamic selection –button you can restrict your report to
- 89. 1.11.2004 FBL5N With this transaction you can display open and cleared customer items. You also have
- 90. 1.11.2004 S_ALR_87012172 With this report you can display customer balances sorted by G/L account and customer
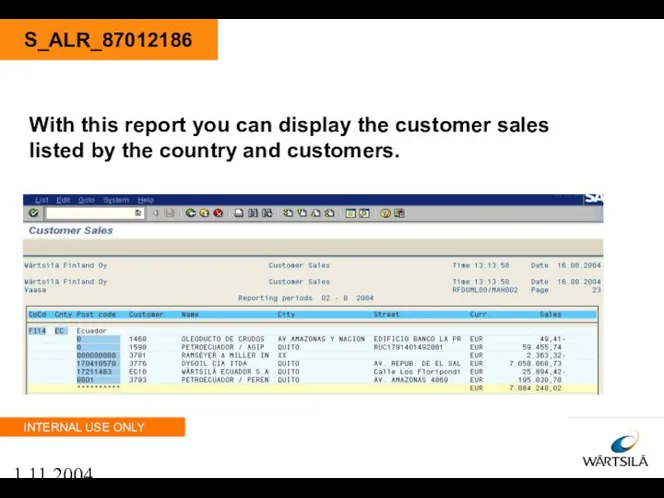
- 91. 1.11.2004 S_ALR_87012186 With this report you can display the customer sales listed by the country and
- 92. 1.11.2004 S_ALR_87012168 With this transaction you can run a due date analyze of customer: Total of
- 93. 1.11.2004 S_ALR_87012197 With this transaction you can list all customer line items. This report lists open
- 94. 1.11.2004 S_ALR_87012174 With this report you a list of open items for a customer.
- 95. 1.11.2004 S_ALR_87012176 With this report you can analyze your customer open items. This report displays also
- 96. 1.11.2004 Reports for Credit management These standard reports are available in the area of credit management
- 97. 1.11.2004 FCV3 – Early warning list You use the early warning list to display and print
- 98. 1.11.2004 Commissions Go to transaction FBL3N Select G/L accounts: 7540000 Sales comm., parts ext. 7540100 Sales
- 99. 1.11.2004 Commissions Go to transaction FBL5N Select from the Dynamic selection –button the dunning area. You
- 100. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 101. 1.11.2004 Payment program You run the payment proposial and execute the payment file to be sent
- 102. 1.11.2004 Import electronic bank statement The first step is to import the electronic bank statement from
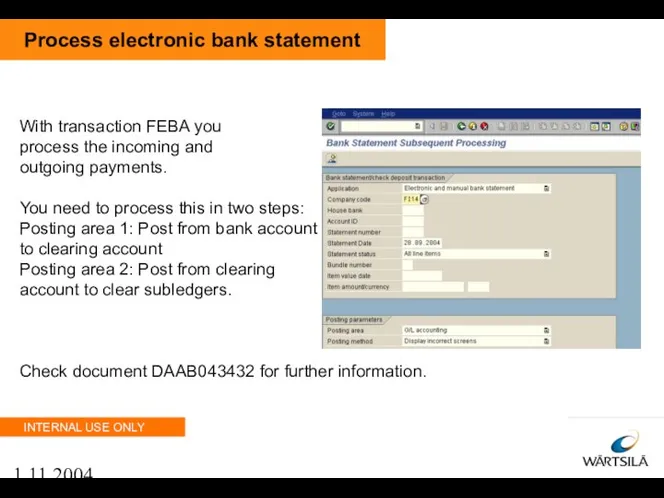
- 103. 1.11.2004 Process electronic bank statement With transaction FEBA you process the incoming and outgoing payments. You
- 104. 1.11.2004 Processing incoming payments Processing an incoming payment includes two processes: Posting the payment to the
- 105. 1.11.2004 Clearing of customer invoices Clearing of customer invoices, payments and credit notes. Transaction F-32 is
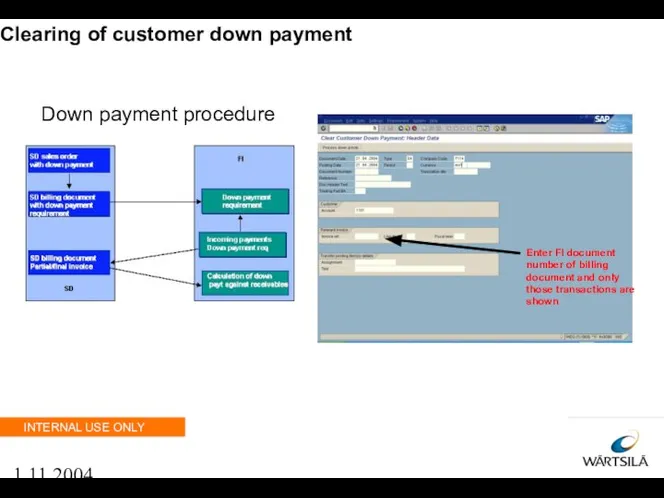
- 106. 1.11.2004 Clearing of customer down payment Down payment procedure Enter FI document number of billing document
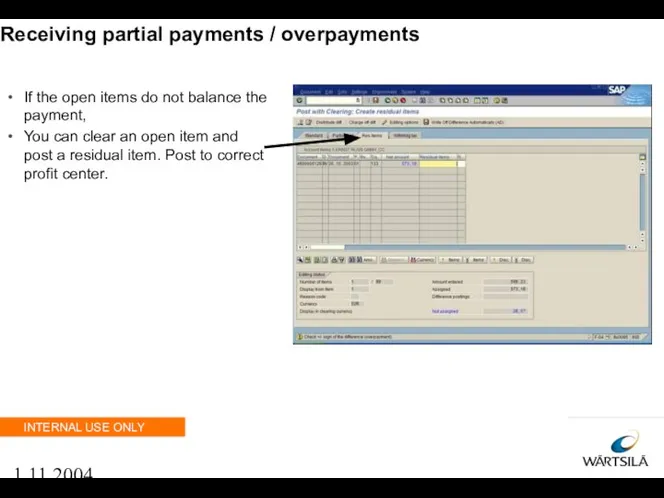
- 107. 1.11.2004 Receiving partial payments / overpayments If the open items do not balance the payment, You
- 108. 1.11.2004 Introduction 1. General introduction 2. Process recap 3. SAP main structures 4. Integration 5. General
- 109. 1.11.2004 Check list before start to do Period end postings Check: No entries on dummy profit
- 110. 1.11.2004 Process for unrealized and realized exchange rate
- 111. 1.11.2004 Foreign currency valuation Customer invoice Valuation 03.2004 Valuation 04.2004 Payment received 05.2004 A/R revaluat,. ext.
- 112. 1.11.2004 Foreign currency valuation (unrealized) Bank accounts Vendor / Customer / Bank accounts with open items
- 113. 1.11.2004 Re-posting of unrealized exchange rate Re-posting of exchange rate is done with transaction F-05 From
- 114. 1.11.2004 Valuation of Bank accounts Valuation 31.3 Reversal 1.4 Balance 31.3 USD, IG bank acc. 1970230
- 115. 1.11.2004 Exchange rate difference (realized) and Cash discounts With transaction F.50 you re-allocate realized exchange rate
- 116. 1.11.2004 Goods received / Invoice received (GR/IR) Clearing To GR/IR clearing account is posted goods received
- 117. 1.11.2004 Recurring entry Recurring entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly. Recurring entries can be
- 119. Скачать презентацию




































































































 Бухгалтерский учет и анализ производственных результатов
Бухгалтерский учет и анализ производственных результатов Накопительная пенсия
Накопительная пенсия Мукомольное производство ООО Царская-Услада. Проект для инвестирования
Мукомольное производство ООО Царская-Услада. Проект для инвестирования Елдер арасындағы валюталық, қаржылық және несиелік қатынастар
Елдер арасындағы валюталық, қаржылық және несиелік қатынастар Налогообложение в сфере недвижимости
Налогообложение в сфере недвижимости Краудфандинг
Краудфандинг Виды инвестирования
Виды инвестирования Производственные ресурсы: оборотный капитал
Производственные ресурсы: оборотный капитал Пособие по безработице
Пособие по безработице Риск и доходность финансовых активов
Риск и доходность финансовых активов Принципи організації бухгалтерського обліку на підприємстві
Принципи організації бухгалтерського обліку на підприємстві Фондовый рынок
Фондовый рынок Признаки платежеспособности Банкнот Банка России
Признаки платежеспособности Банкнот Банка России Управление движением денежных потоков на предприятии ПАО Ростелеком. Конференция
Управление движением денежных потоков на предприятии ПАО Ростелеком. Конференция Основы финансового менеджмента MBA
Основы финансового менеджмента MBA Финансы в экономике
Финансы в экономике Основы международных валютнокредитных и финансовых отношений
Основы международных валютнокредитных и финансовых отношений Налоговые проверки
Налоговые проверки Бюджет для граждан, разработанный на основе решения о бюджете муниципального района
Бюджет для граждан, разработанный на основе решения о бюджете муниципального района Становление и развитие кредитной системы Российской Федерации
Становление и развитие кредитной системы Российской Федерации Налог на добавленную стоимость
Налог на добавленную стоимость Учет и анализ в коммерческих банках
Учет и анализ в коммерческих банках Налогоплательщики и плательщики сборов. Тема 10
Налогоплательщики и плательщики сборов. Тема 10 Қазақстан Республикасының инвестициялық саясаты
Қазақстан Республикасының инвестициялық саясаты Классификация налогов
Классификация налогов Rede X Ваш Новый Ритм Жизни
Rede X Ваш Новый Ритм Жизни Понятие финансов и финансовой системы
Понятие финансов и финансовой системы Statement of Financial Position. Lecture 7
Statement of Financial Position. Lecture 7