Содержание
- 2. What is a Project? High operating margins. Low to medium return on capital. Limited Life. Significant
- 3. What is a Project? (cont.) Projects have unique risks: Symmetric risks: Demand, price. Input/supply. Currency, interest
- 4. What Does a Project Need? Customized capital structure Asset specific governance systems to minimize cash flow
- 5. “Project finance” is not the same thing as “financing projects”.
- 6. What is Project Finance? Project Finance involves a corporate sponsor investing in and owning a single
- 7. Project Structure Structure highlights Disadvantages Motivations
- 8. Structure Highlights SPV - Independent, single purpose company formed to build and operate the project. Extensive
- 9. Structure Highlights (cont.) Highly concentrated equity and debt ownership One to three equity sponsors. Syndicate of
- 10. Disadvantages of Project Financing Often takes longer to structure than equivalent size corporate finance. Higher transaction
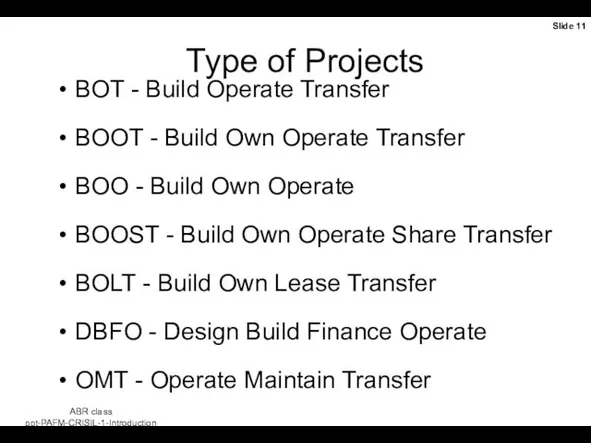
- 11. Type of Projects BOT - Build Operate Transfer BOOT - Build Own Operate Transfer BOO -
- 12. Means of Finance Equity Capital Mezzanine Finance Convertibles Preference Capital Sub-ordinated Debt Senior Debt Rupee Term
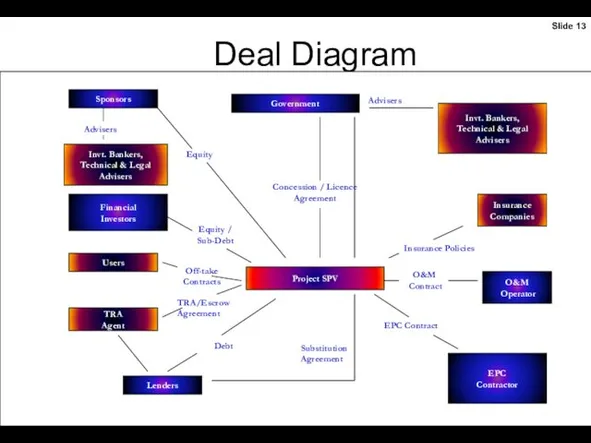
- 13. Financing Infrastructure Projects Deal Diagram Government Project SPV
- 14. Key Components Cash flow projections based on technical, market and financial analysis Risk allocation through project
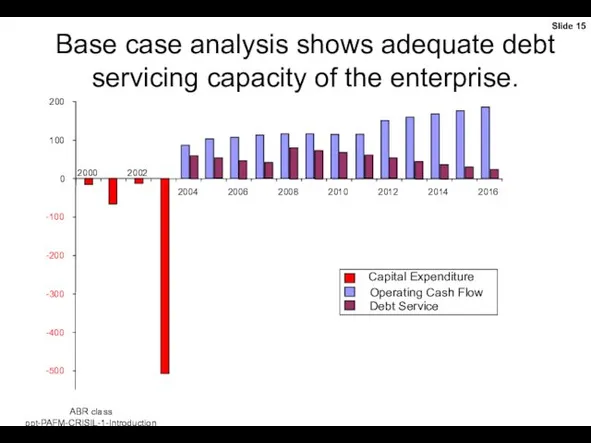
- 15. Base case analysis shows adequate debt servicing capacity of the enterprise. -500 -400 -300 -200 -100
- 16. Why Investors Use Project Finance High leverage Tax benefits Off-balance sheet financing Borrowing capacity Risk limitation
- 17. Benefits of Project Finance to Third Parties Lower product or service cost Additional investment in public
- 18. Case Study - 1 Project : 4-laning of 59 km on NH5 on annuity basis Concession
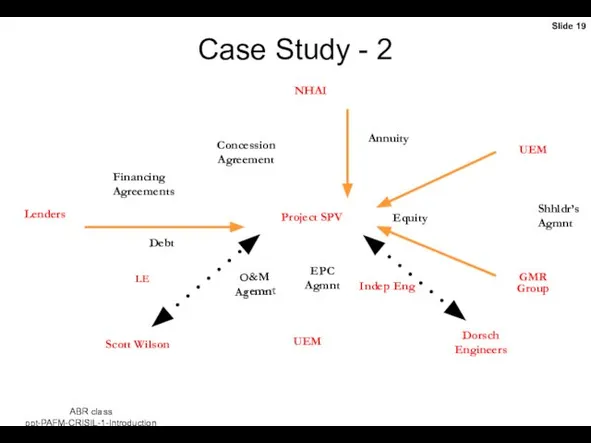
- 19. Case Study - 2 Project SPV NHAI Lenders UEM UEM GMR Group Dorsch Engineers Scott Wilson
- 20. INFRASTRUCTURE Transport – road including toll road, a bridge, rail system, a highway project, a port,
- 22. Скачать презентацию















 Интерактивная игра Финансовые ребусы
Интерактивная игра Финансовые ребусы Организация оплаты труда на предприятии
Организация оплаты труда на предприятии Теоретические основы кредитования
Теоретические основы кредитования Учет кассовых операций
Учет кассовых операций Ценные бумаги в финансовом менеджменте
Ценные бумаги в финансовом менеджменте Новации в отношениях субъектов розничных рынках электрической энергии
Новации в отношениях субъектов розничных рынках электрической энергии Тема 4.Расчетно-кассовые операции
Тема 4.Расчетно-кассовые операции Міжнародні фінанси
Міжнародні фінанси Податкова політика і податкова система держави
Податкова політика і податкова система держави Тақырып Корпорацияның айналымнан тыс активтерін басқару
Тақырып Корпорацияның айналымнан тыс активтерін басқару Необычные налоги Соединённых Штатов Америки
Необычные налоги Соединённых Штатов Америки Місце страхування в системі економічних категорій. Поняття страхування та його функції
Місце страхування в системі економічних категорій. Поняття страхування та його функції Анализ и внутренний аудит финансово-хозяйственной деятельности организации
Анализ и внутренний аудит финансово-хозяйственной деятельности организации Заем, кредит. Банковский вклад
Заем, кредит. Банковский вклад Финансовые инструменты: представление информации
Финансовые инструменты: представление информации Почему шаг RTS должен быть 5
Почему шаг RTS должен быть 5 Аудит процентов к уплате
Аудит процентов к уплате Об итогах работы УСЗН по исполнению переданных полномочий в 2021 году
Об итогах работы УСЗН по исполнению переданных полномочий в 2021 году Особенности и отличия немецкой и американской моделей бюджетного федерализма
Особенности и отличия немецкой и американской моделей бюджетного федерализма Вьетнамский донг
Вьетнамский донг Как начать собственное дело и зарегистрировать предприятие в Санкт-Петербурге
Как начать собственное дело и зарегистрировать предприятие в Санкт-Петербурге Улучшение финансового состояния ООО Онтарио
Улучшение финансового состояния ООО Онтарио Финансовая система. Налогово-бюджетная политика государства
Финансовая система. Налогово-бюджетная политика государства Пенсионный Фонд информирует
Пенсионный Фонд информирует Заемные обязательства
Заемные обязательства Способы погашения кредита
Способы погашения кредита Государственные и муниципальные финансовые ресурсы
Государственные и муниципальные финансовые ресурсы Technical support services for Riyad Bank
Technical support services for Riyad Bank