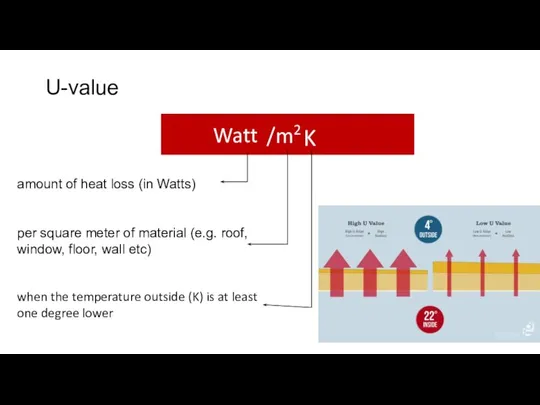
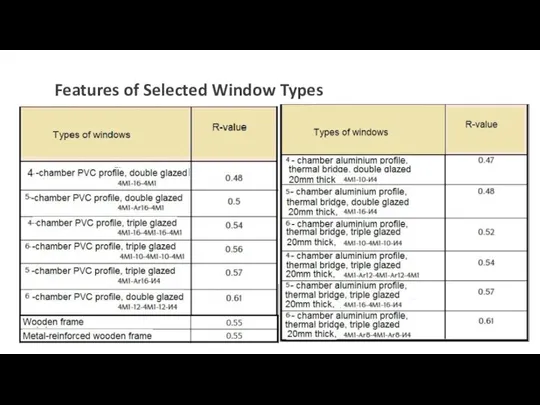
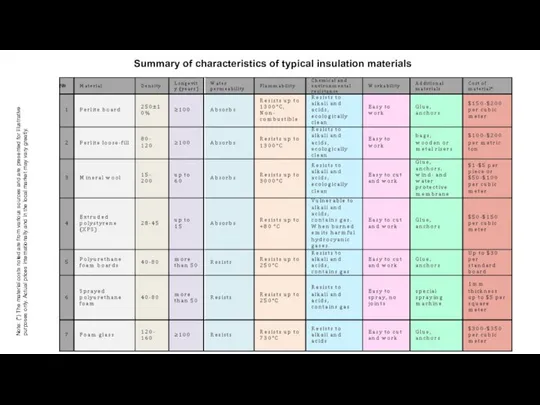
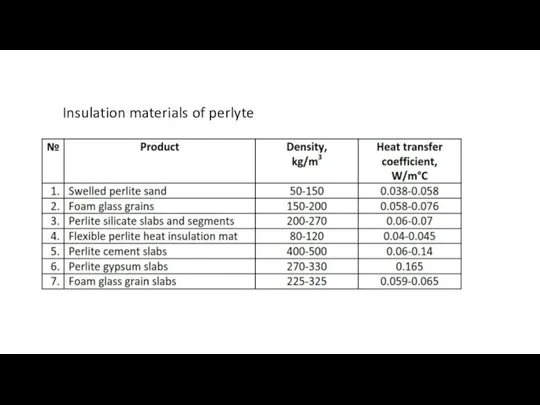
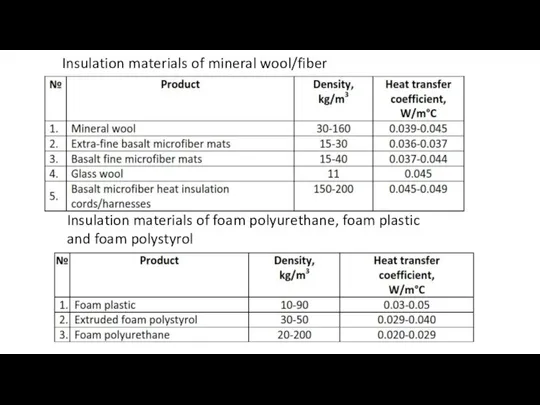
R-value. Thermal resistance
Lambda values (λ), combined with information on the thickness
of material, represent the thermal resistance of individual materials used in the building envelope, or their R-value.
Thickness measured in m2·°C/W
λ
The higher the R-value, the better it resists the heat transfer.
The cumulative thermal resistance of a mixed structure is comprised of individual R-values of the layers in the structure.
R=
R-Value (Thermal Resistance) --- Thermal resistance is the ability of a material to prevent the passage of heat. It’s the thickness of the material (in metres) divided by its conductivity. This is expressed as m2K/W.
If the material consists of several elements, the overall resistance is the total of the resistances of each element. The higher the R-value, the more efficient the insulation.
Example:
PIR Board: 0.022 W/mK and 100mm thick; R-value = 0.1 metres ÷ 0.022 = 4.54 m2K/W
Glass Fibre Roll: 0.044 W/mk and 100mm thick; R-value = 0.1 metres ÷ 0.044 = 2.27 m2K/W





 Пьезопреобразователи. Методы расчета. (Раздел 3)
Пьезопреобразователи. Методы расчета. (Раздел 3) Световое поле, обобщение и выводы
Световое поле, обобщение и выводы Манометры общепромышленного типа
Манометры общепромышленного типа Область стыка цилиндрической оболочки с днищем
Область стыка цилиндрической оболочки с днищем Устройство машинной иглы. Неполадки
Устройство машинной иглы. Неполадки Галилео Галилей Работа ученицы 7 класса «Б» Алексеевой Ольги
Галилео Галилей Работа ученицы 7 класса «Б» Алексеевой Ольги Механические и электромагнитные колебания и волны. (Раздел 07)
Механические и электромагнитные колебания и волны. (Раздел 07) Электромагнитные колебания 11 класс
Электромагнитные колебания 11 класс  Применение второго закона Ньютона в решении задач
Применение второго закона Ньютона в решении задач Высказывания о силе Знание – сила. Как в комаре сила. Сила силу ломит. Знает сила правду, да не любит сказывать. Сила ест
Высказывания о силе Знание – сила. Как в комаре сила. Сила силу ломит. Знает сила правду, да не любит сказывать. Сила ест Синхронизация хаотических автоколебаний. Часть 2
Синхронизация хаотических автоколебаний. Часть 2 Шекаралық қабат теңдеулерінің жуық шешімдері
Шекаралық қабат теңдеулерінің жуық шешімдері Выполнил: Ушанов Андрей
Выполнил: Ушанов Андрей Кислотные (свинцовые) аккумуляторные батареи
Кислотные (свинцовые) аккумуляторные батареи Ультразвук и инфразвук в природе
Ультразвук и инфразвук в природе Диод Шоттки
Диод Шоттки Законы последовательного соединения
Законы последовательного соединения Аттестационная работа. Методическая разработка по разделу физики сила трения в 9 классе
Аттестационная работа. Методическая разработка по разделу физики сила трения в 9 классе Исследование силы трения скольжения. Измерение коэффициента трения скольжения
Исследование силы трения скольжения. Измерение коэффициента трения скольжения Почему не тонут железные корабли?
Почему не тонут железные корабли? BCS Theory of Superconductivity
BCS Theory of Superconductivity Удельная теплота парообразования
Удельная теплота парообразования Сведения о технологии и условиях выполнения работ по техническому обслуживанию и ремонту
Сведения о технологии и условиях выполнения работ по техническому обслуживанию и ремонту Научные революции в естествознании и формирование научной картины мира
Научные революции в естествознании и формирование научной картины мира Физика наноструктур и элементы электроники
Физика наноструктур и элементы электроники Презентация по физике "Правила безопасного обращения с электричеством" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Правила безопасного обращения с электричеством" - скачать  Презентация по физике "Закон сохранения электрического заряда" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Закон сохранения электрического заряда" - скачать  ВНЕКЛАССНОЕ МЕРОПРИЯТИЕ Интеллектуальное казино Краснова Елена Ивановна учитель физики МОУ «Орнарская СОШ»
ВНЕКЛАССНОЕ МЕРОПРИЯТИЕ Интеллектуальное казино Краснова Елена Ивановна учитель физики МОУ «Орнарская СОШ»