Содержание
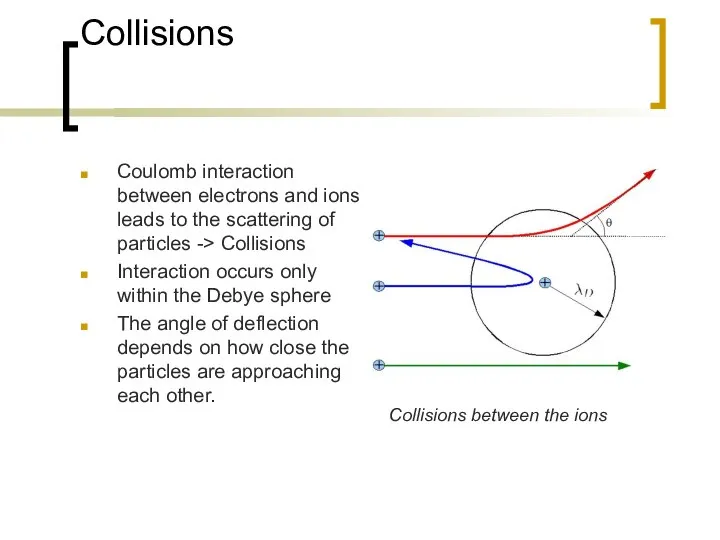
- 2. Collisions Coulomb interaction between electrons and ions leads to the scattering of particles -> Collisions Interaction
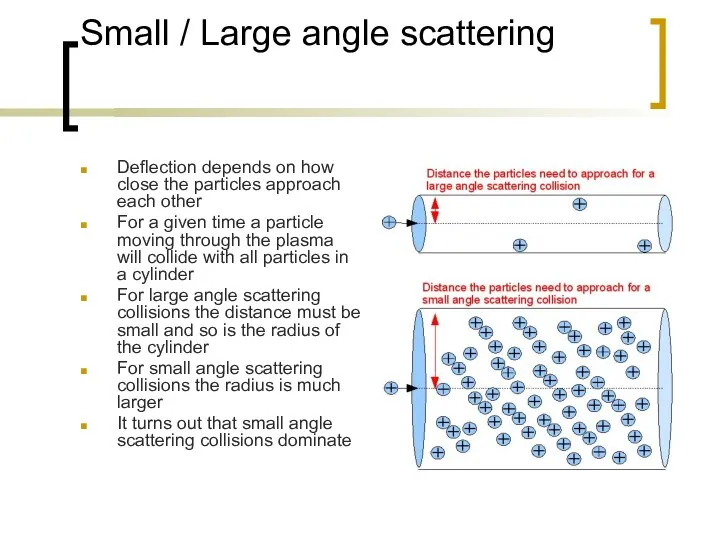
- 3. Small / Large angle scattering Deflection depends on how close the particles approach each other For
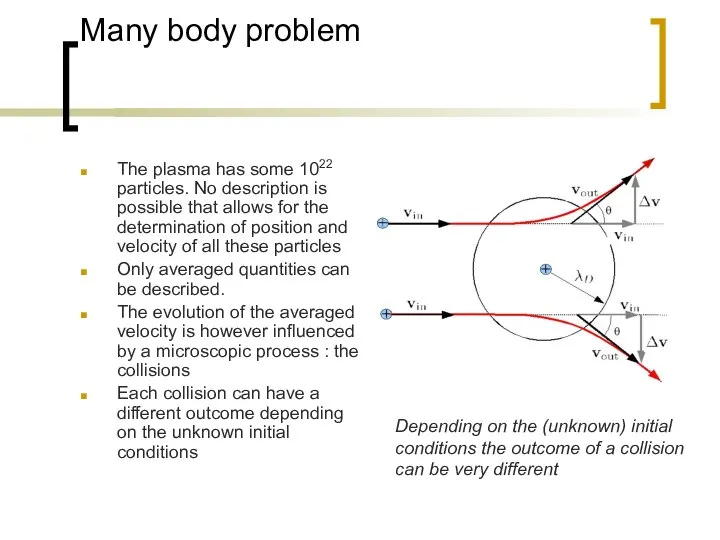
- 4. Many body problem The plasma has some 1022 particles. No description is possible that allows for
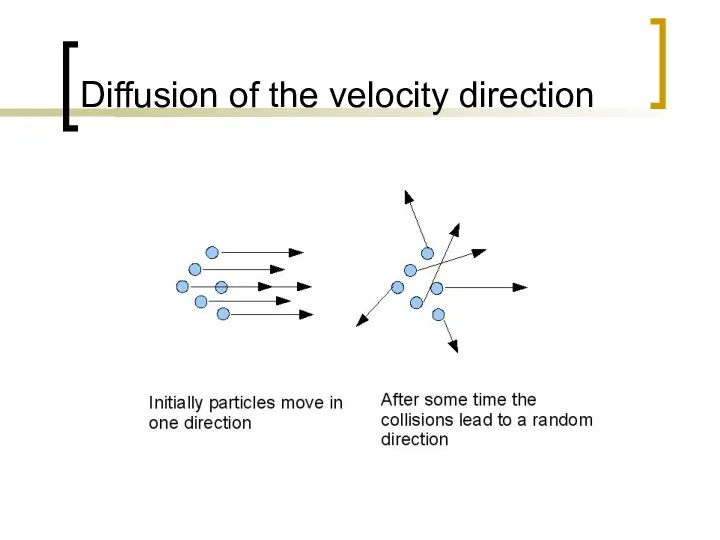
- 5. Diffusion of the velocity direction
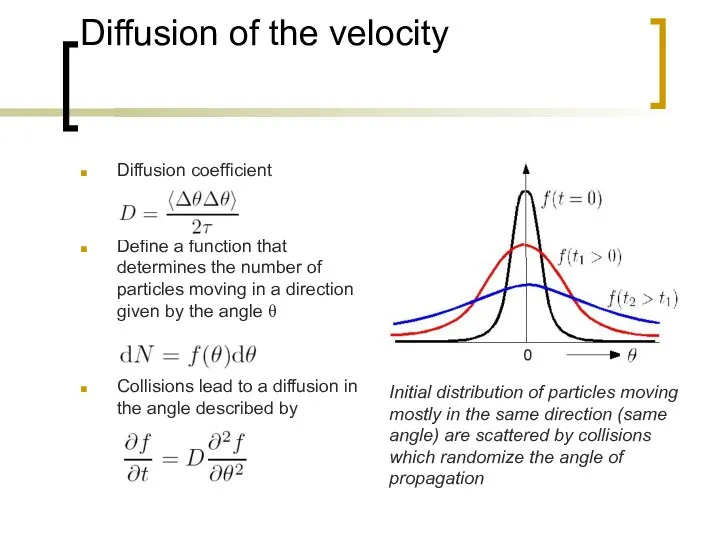
- 6. Diffusion of the velocity Diffusion coefficient Define a function that determines the number of particles moving
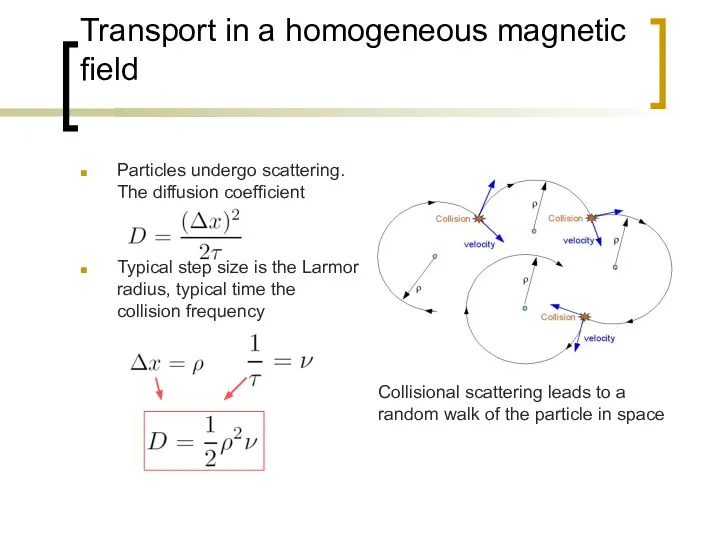
- 7. Transport in a homogeneous magnetic field Particles undergo scattering. The diffusion coefficient Typical step size is
- 9. Скачать презентацию
 Электрические цепи постоянного тока
Электрические цепи постоянного тока Исследование минералов под микроскопом
Исследование минералов под микроскопом Основы молекулярно-кинетической теории
Основы молекулярно-кинетической теории Magnetic Resonance
Magnetic Resonance Auxiliary engines
Auxiliary engines Дисперсия света
Дисперсия света Тест по теме: Электромагнитное поле
Тест по теме: Электромагнитное поле Химическая кинетика
Химическая кинетика ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ПО ТЕМЕ:
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ПО ТЕМЕ:  Определение шума и вибрации
Определение шума и вибрации Рентгенівське випромінювання
Рентгенівське випромінювання  Презентация Прямолинейное равномерное движение
Презентация Прямолинейное равномерное движение  Олимпиадная физика
Олимпиадная физика Диагностирование двигателя по параметрам расхода топлива. Тема 12
Диагностирование двигателя по параметрам расхода топлива. Тема 12 Движение искусственных спутников
Движение искусственных спутников Уравнения теории упругости. Закон Гука для изотропного тела. Упругие постоянные. Объемная деформация. (Лекция 4)
Уравнения теории упругости. Закон Гука для изотропного тела. Упругие постоянные. Объемная деформация. (Лекция 4) Еда из микроволновки: польза или вред?
Еда из микроволновки: польза или вред? Проводники и электростатическое поле
Проводники и электростатическое поле Тепловозные дизели
Тепловозные дизели Проектная деятельность на уроках физики и во внеурочной деятельности
Проектная деятельность на уроках физики и во внеурочной деятельности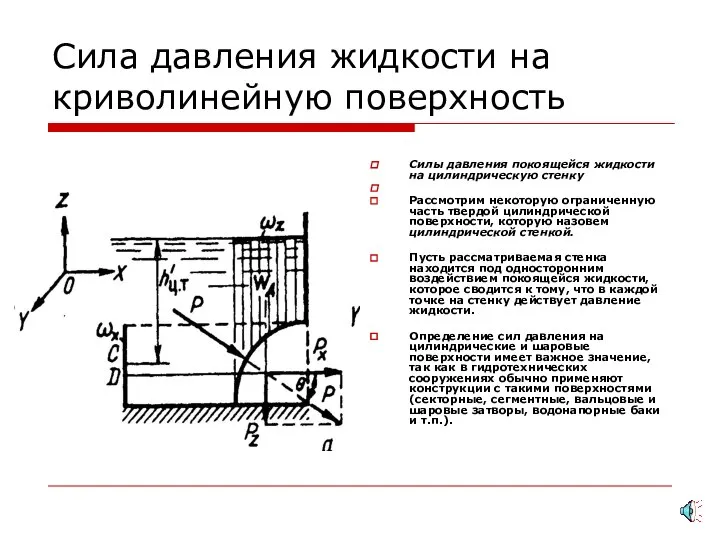 Сила давления жидкости на криволинейную поверхность
Сила давления жидкости на криволинейную поверхность Электр тізбектеріндегі өтпелі үрдістер
Электр тізбектеріндегі өтпелі үрдістер Химические реакторы
Химические реакторы Конкурс презентаций «Интерактивная мозаика» интерактивное пособие Беляева Надежда Владимировна МАОУ «СОШ №140» г. Перми учи
Конкурс презентаций «Интерактивная мозаика» интерактивное пособие Беляева Надежда Владимировна МАОУ «СОШ №140» г. Перми учи Кінематика абсолютно твердого тіла
Кінематика абсолютно твердого тіла Презентация по физике "Проводники и диэлектрики" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Проводники и диэлектрики" - скачать  Motions physics
Motions physics Презентация Сложение скоростей
Презентация Сложение скоростей