Содержание
- 2. Check your answers Atoms of elements are electrically neutral. True The mass of an electron is
- 3. Topic of the lesson The phenomenon of radioactivity. Radioisotopes. The nuclear reaction.
- 4. Learning objectives: - understand why isotopes occur and the nature of radioactivity - ability to write
- 5. Frontal questions: What is radiation? How can you prove that element is radioactive? How to determine
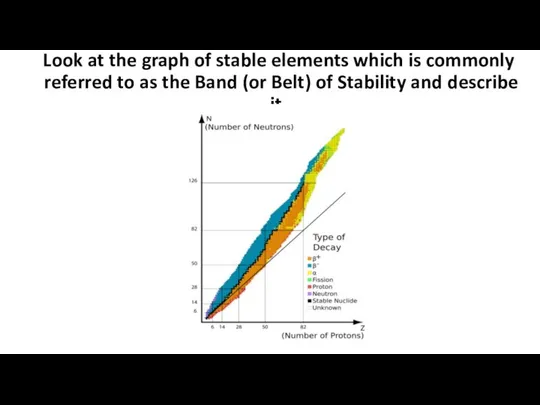
- 6. Look at the graph of stable elements which is commonly referred to as the Band (or
- 7. Q1. Identify the following as Alpha, beta, gamma or neutron:
- 8. Q2. Complete the following nuclear equations (the question marks)
- 9. Q3. Throium-232 undergoes radioactive decay until a stable isotope is reached. Write the nuclear reaction for
- 10. Summing up the lesson
- 12. Скачать презентацию








 Волокно капрон
Волокно капрон Полимеры, пластмассы и изделия из них
Полимеры, пластмассы и изделия из них Моделирование, как метод научного исследования. Ограниченный метод Хартри-Фока
Моделирование, как метод научного исследования. Ограниченный метод Хартри-Фока Электролиз: опыты к заданиям ЕГЭ
Электролиз: опыты к заданиям ЕГЭ Битумы и материалы на основе битумов
Битумы и материалы на основе битумов Камни мира. Минералы
Камни мира. Минералы Молярный объём газов
Молярный объём газов Катаболизм фенилаланина, тирозина
Катаболизм фенилаланина, тирозина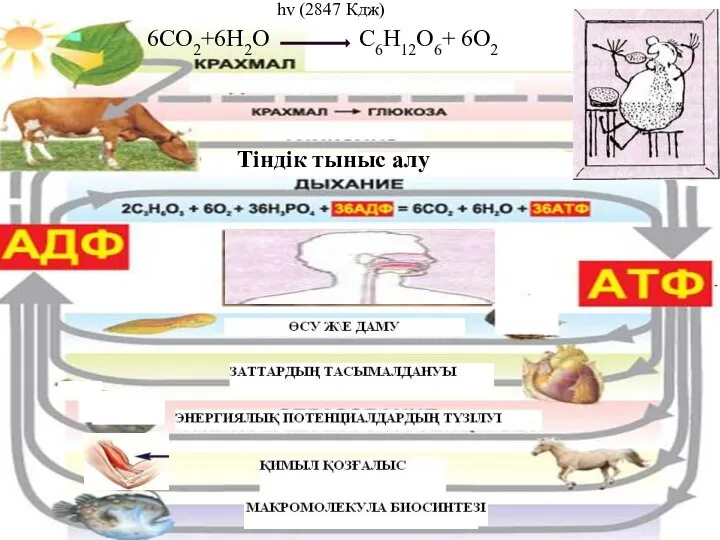 Биологиялық тотығу электрондардың тасымалдану тізбегі тотығудан фосфорлану
Биологиялық тотығу электрондардың тасымалдану тізбегі тотығудан фосфорлану Установка гидрокрекинга в составе завода глубокой переработки нефти ООО Кинеф
Установка гидрокрекинга в составе завода глубокой переработки нефти ООО Кинеф Зависимость свойств химических элементов от положения в ПСХЭ
Зависимость свойств химических элементов от положения в ПСХЭ Презентация по Химии "Химическая природа белка" - скачать смотреть
Презентация по Химии "Химическая природа белка" - скачать смотреть  АТФ (Аденозинтрифосфат)
АТФ (Аденозинтрифосфат) Азот. Физические и химические свойства азота
Азот. Физические и химические свойства азота Классификация и краткие характеристики основных групп токсикантов
Классификация и краткие характеристики основных групп токсикантов Хлороводород. Соляная кислота.
Хлороводород. Соляная кислота.  Уксусная кислота
Уксусная кислота Основания. Физические свойства оснований
Основания. Физические свойства оснований Плавиковая кислота или фтористоводородная кислота
Плавиковая кислота или фтористоводородная кислота Едкость Coca-Cola
Едкость Coca-Cola Химический элемент платина
Химический элемент платина Липидтер
Липидтер Подготовил учитель химии МОУ СОШ № 16 С. Александровского Александровского района Кононенко Светлана Юрьевна
Подготовил учитель химии МОУ СОШ № 16 С. Александровского Александровского района Кононенко Светлана Юрьевна Исследование содержания аскорбиновой кислоты в зимних сортах яблок, районированных в Петровском районе Ставропольского края
Исследование содержания аскорбиновой кислоты в зимних сортах яблок, районированных в Петровском районе Ставропольского края  Гравиметрические методы анализа
Гравиметрические методы анализа Дәрілік препараттардың синтезі мен олардың классификациясы
Дәрілік препараттардың синтезі мен олардың классификациясы Необратимый (совместный) гидролиз
Необратимый (совместный) гидролиз Хроматофокусирование: новые подходы в концентрировании и разделении
Хроматофокусирование: новые подходы в концентрировании и разделении