Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives 1 Why are information systems such an important aspect of everyday life? 2 How
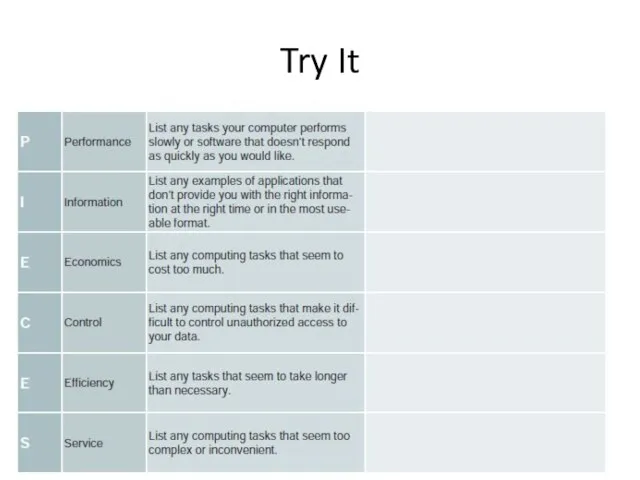
- 3. Try It
- 4. An information system collects, stores, and processes data to provide useful, accurate, and timely information, typically
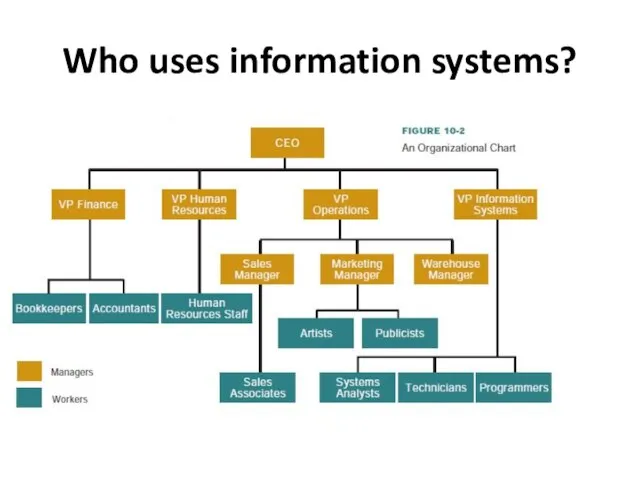
- 5. Who uses information systems?
- 6. How do information systems help the people in an organization?
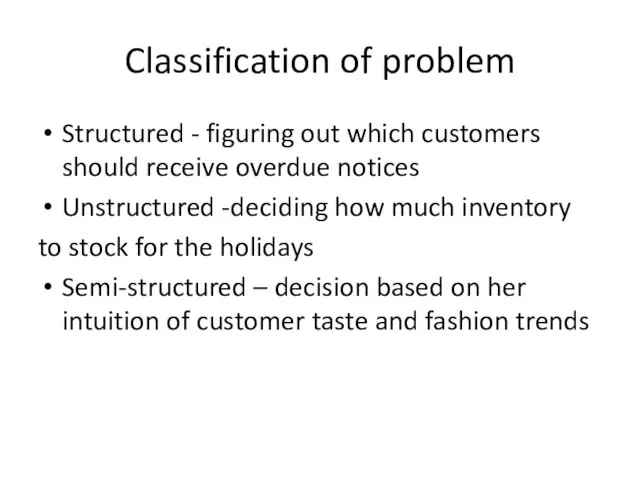
- 7. Classification of problem Structured - figuring out which customers should receive overdue notices Unstructured -deciding how
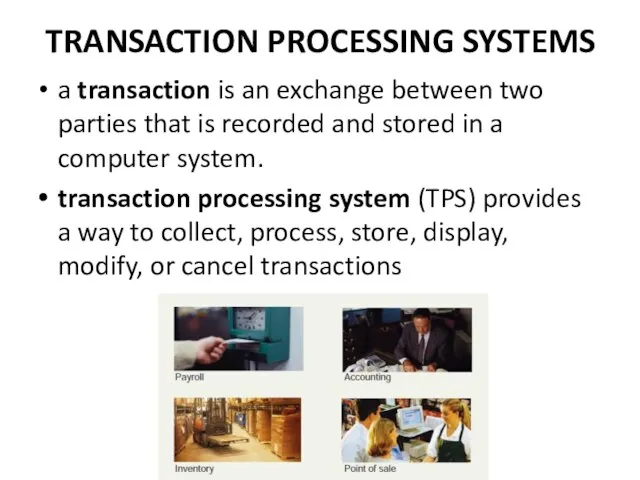
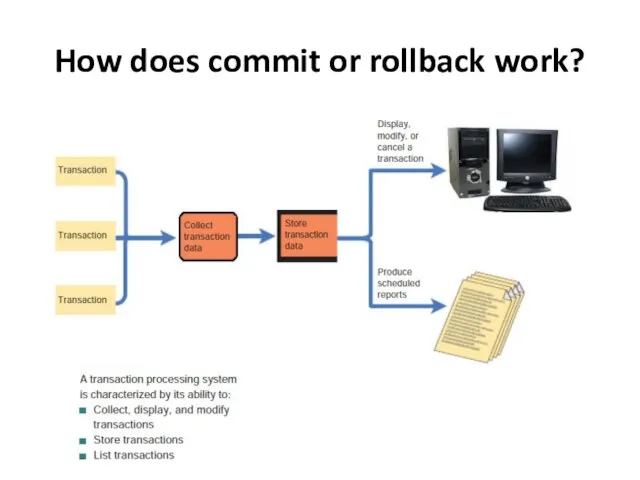
- 8. TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEMS a transaction is an exchange between two parties that is recorded and stored
- 9. transaction processing systems batch processing online processing referred to as an OLTP system (online transaction processing
- 10. How does commit or rollback work?
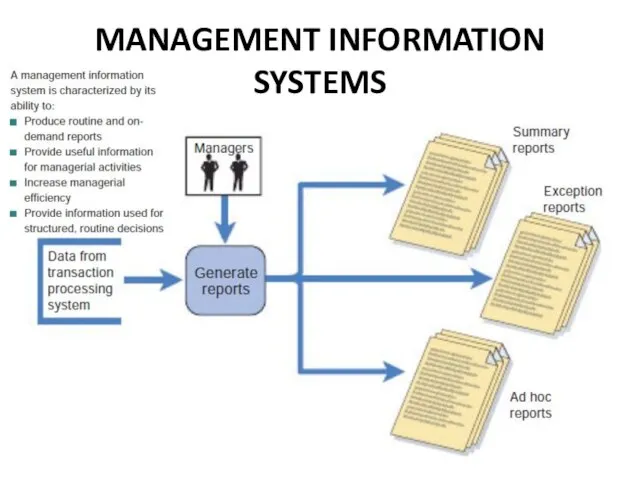
- 11. MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS
- 12. How does an MIS differ from a TPS?
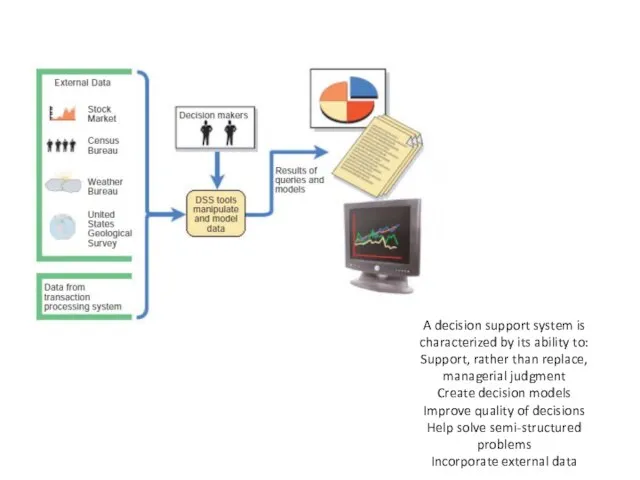
- 13. DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS A decision support system (DSS) helps people make decisions by directly manipulating data,
- 14. A decision support system is characterized by its ability to: Support, rather than replace, managerial judgment
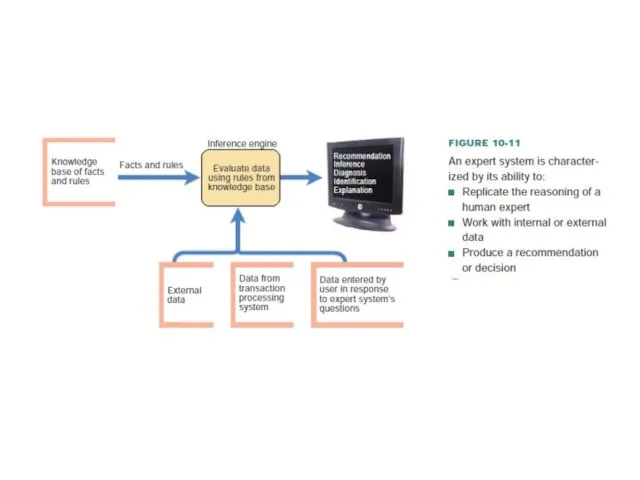
- 15. EXPERT SYSTEMS AND NEURAL NETWORKS An expert system, sometimes referred to as a knowledge-based system, is
- 17. A neural network uses computer circuitry to simulate the way a brain might process information, learn,
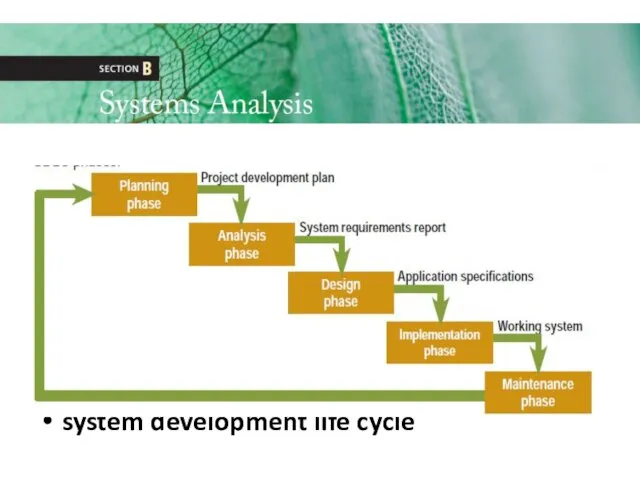
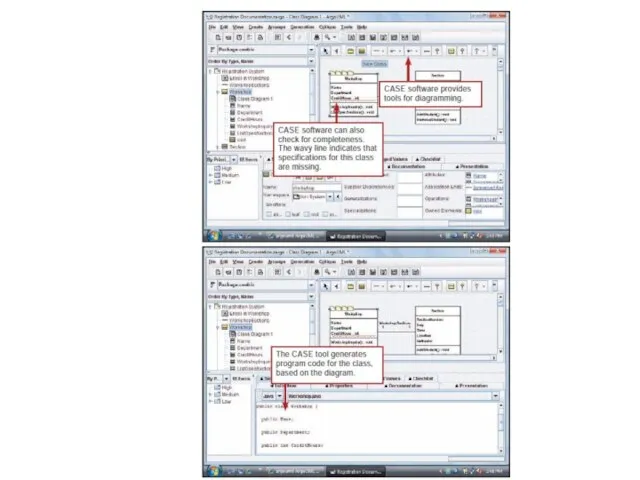
- 18. system development life cycle
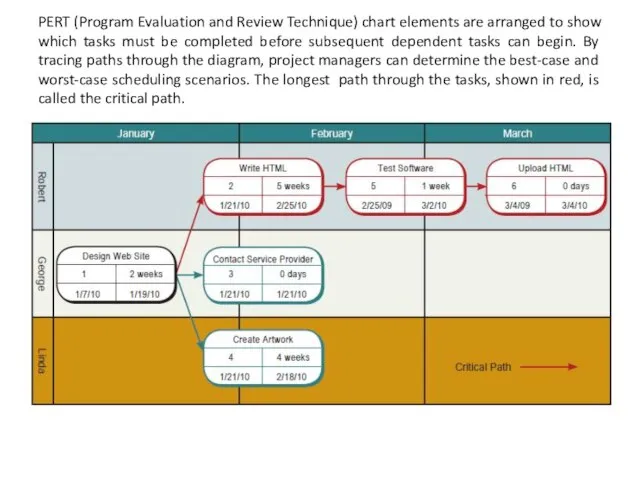
- 20. PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) chart elements are arranged to show which tasks must be
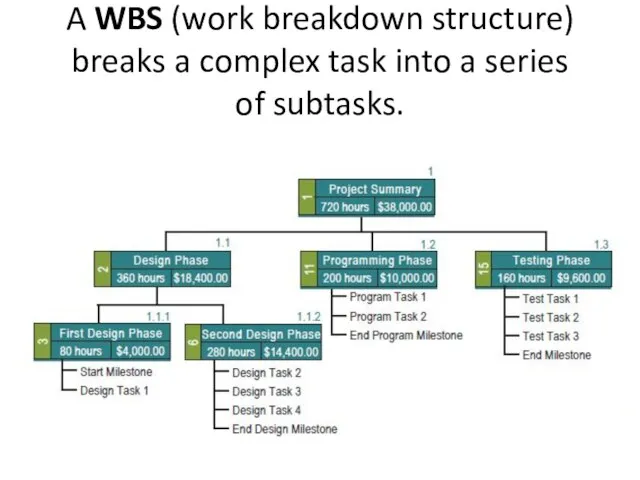
- 21. A WBS (work breakdown structure) breaks a complex task into a series of subtasks.
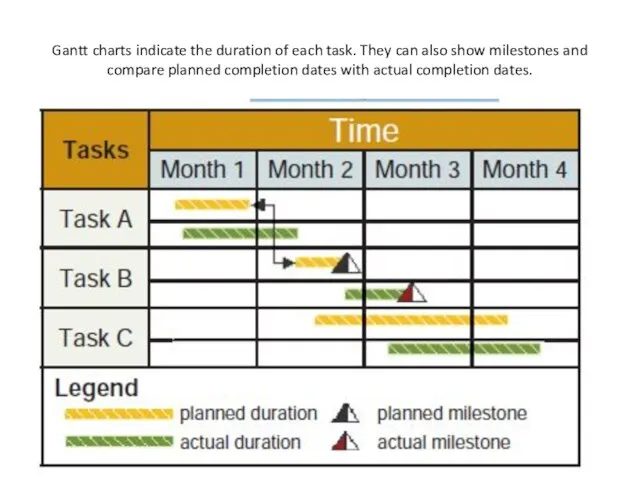
- 22. Gantt charts indicate the duration of each task. They can also show milestones and compare planned
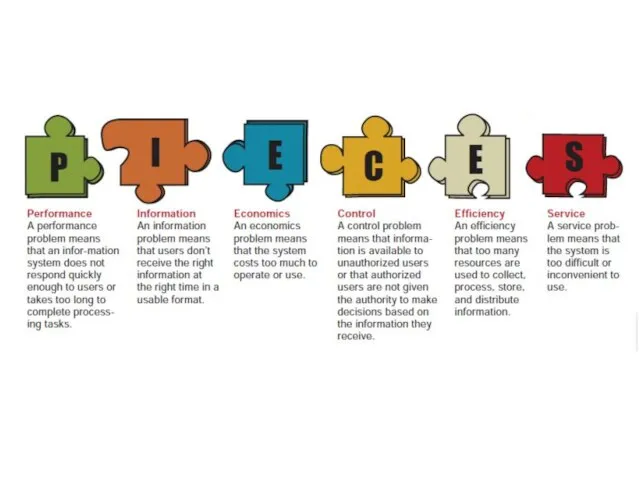
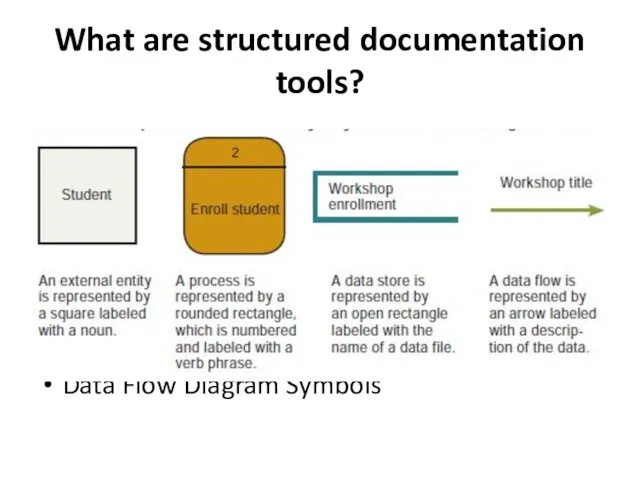
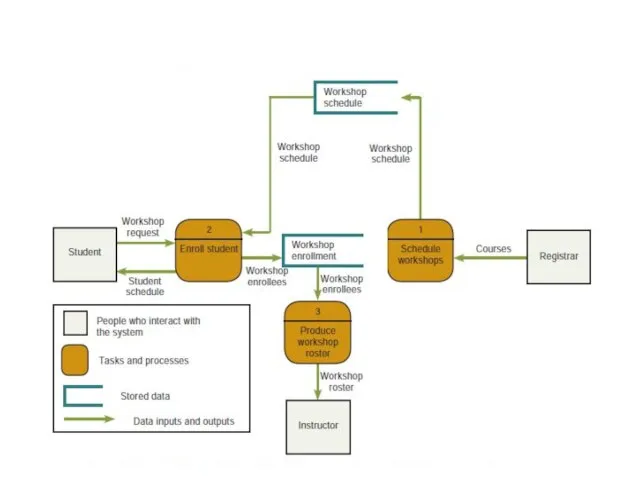
- 23. What are structured documentation tools? Data Flow Diagram Symbols
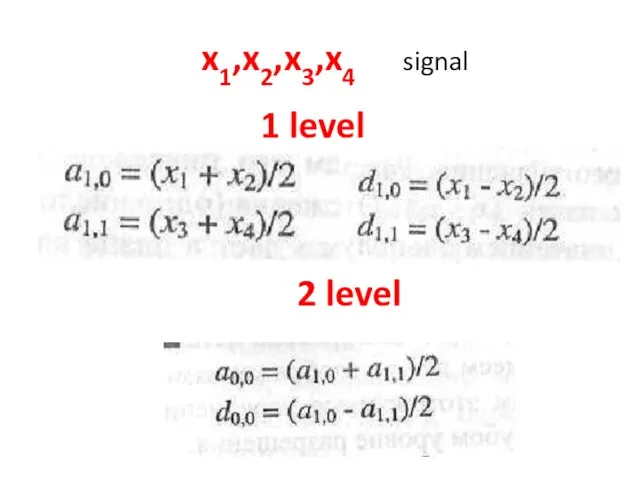
- 27. x1,x2,x3,x4 signal 1 level 2 level
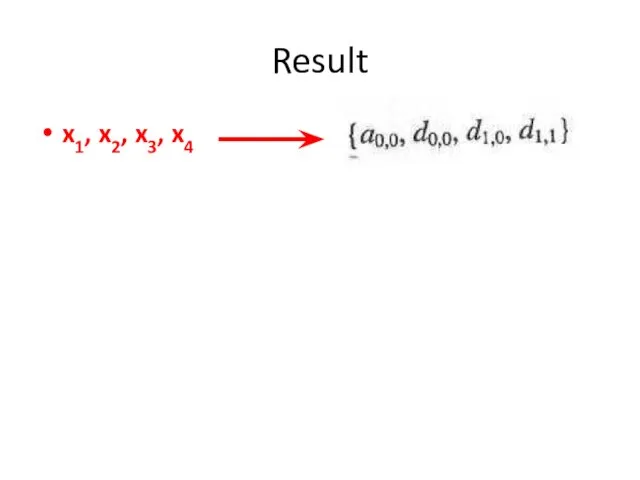
- 28. Result x1, x2, x3, x4
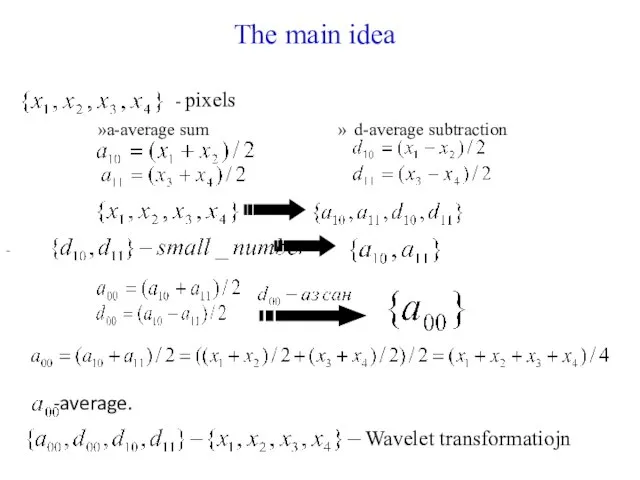
- 34. - pixels - The main idea
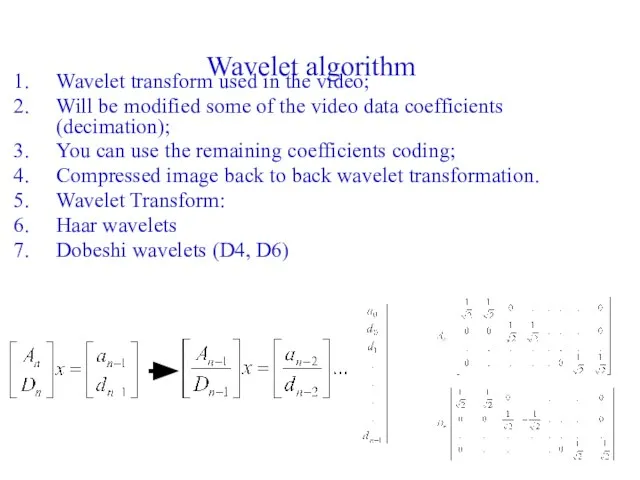
- 35. Wavelet algorithm Wavelet transform used in the video; Will be modified some of the video data
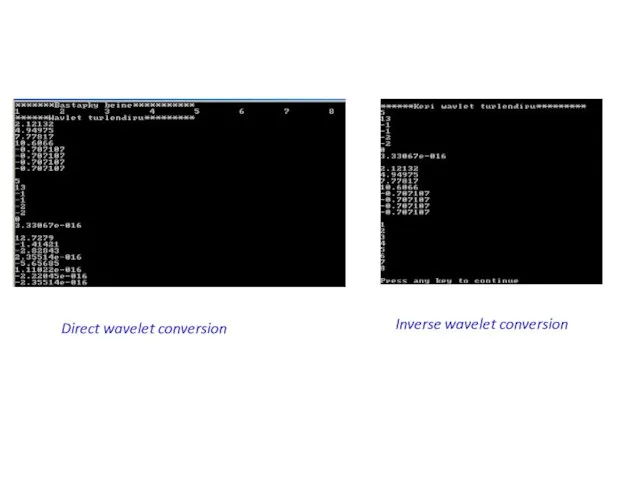
- 36. Direct wavelet conversion Inverse wavelet conversion
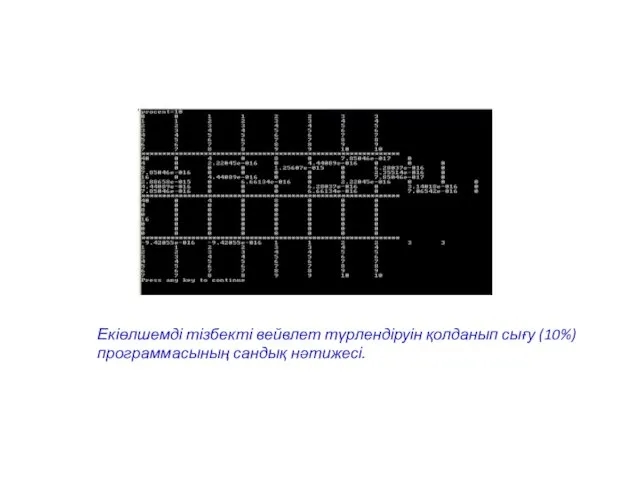
- 37. Екіөлшемді тізбекті вейвлет түрлендіруін қолданып сығу (10%) программасының сандық нәтижесі.
- 38. 1. List ten information systems that you’ve used. 2. Describe how information systems help organizations fulfill
- 51. Скачать презентацию








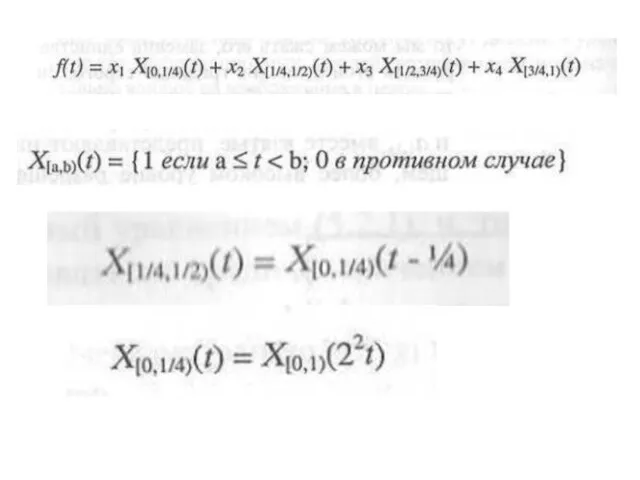
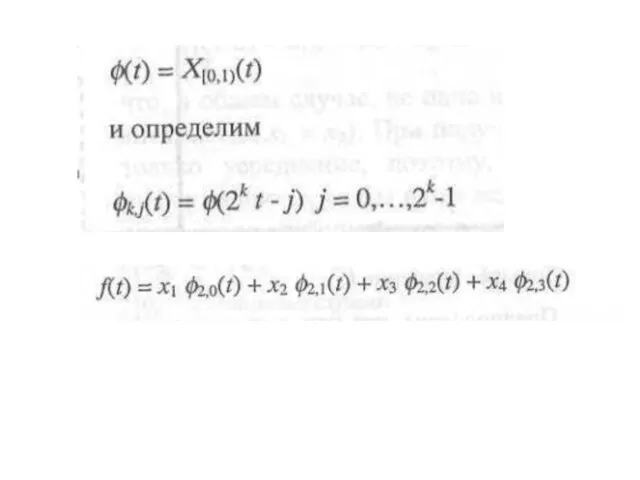
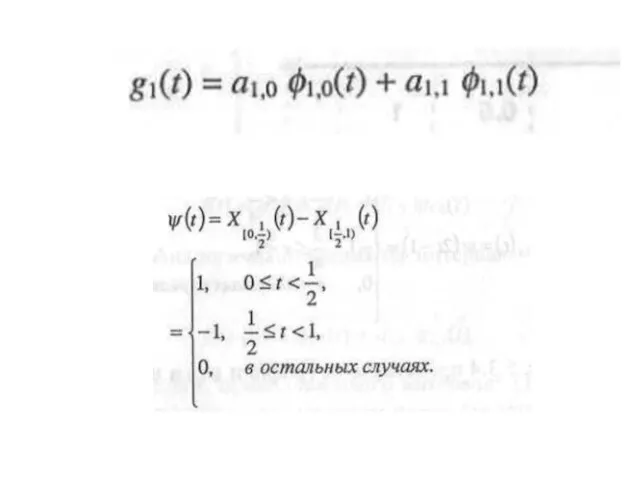
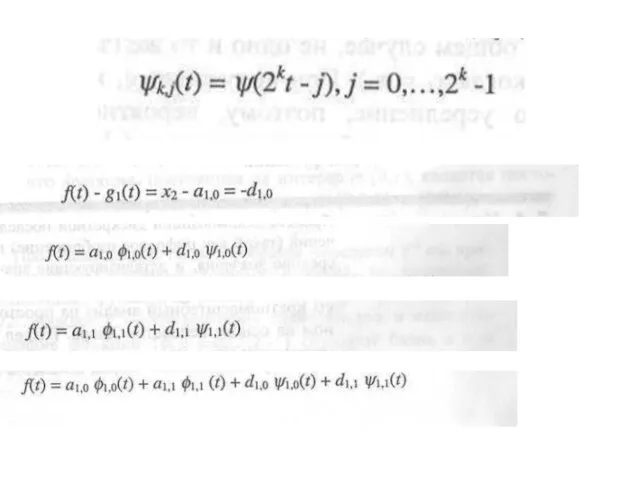
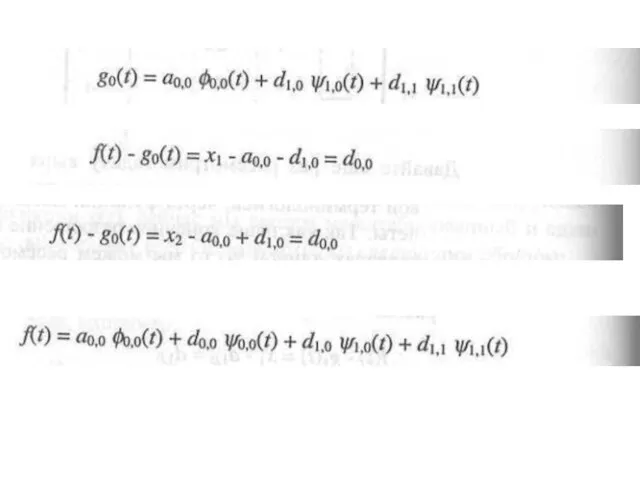












 Культурология видеогигр
Культурология видеогигр Алгоритм Из опыта работы Ермаковой В. В., учителя информатики МБОУ СОШ № 19 города Белово
Алгоритм Из опыта работы Ермаковой В. В., учителя информатики МБОУ СОШ № 19 города Белово Формирование информации. Свойства информации
Формирование информации. Свойства информации Язык SQL. Сложноподчиненные запросы
Язык SQL. Сложноподчиненные запросы Виды телефонных аппаратов: от Белла до IP- телефонов
Виды телефонных аппаратов: от Белла до IP- телефонов Система Logo Writer
Система Logo Writer Электронная библиотека национальной библиотеки Республики Саха (Якутия)
Электронная библиотека национальной библиотеки Республики Саха (Якутия) Назначение базы данных
Назначение базы данных Проблема отношений к сайтам знакомств
Проблема отношений к сайтам знакомств Презентация Операторы цикла
Презентация Операторы цикла Обработка числовой информации в электронных таблицах
Обработка числовой информации в электронных таблицах Операционная система MS DOS
Операционная система MS DOS Как устроен компьютер
Как устроен компьютер Программное обеспечение для создания и редактирования мультимедийных презентаций (OpenOffice.org Impress)
Программное обеспечение для создания и редактирования мультимедийных презентаций (OpenOffice.org Impress) Что умеет компьютер?
Что умеет компьютер? Эксплуатация информационных систем
Эксплуатация информационных систем Структура простой программы на C++
Структура простой программы на C++ Paint
Paint Кодирование информации в компьютере
Кодирование информации в компьютере Кодирование звуковой информации
Кодирование звуковой информации Разработка образовательного продукта ГИС АПК Брянской области
Разработка образовательного продукта ГИС АПК Брянской области Презентация на тему Электронный документ и файл
Презентация на тему Электронный документ и файл Программное обеспечение ГИС. Виды программного обеспечения.
Программное обеспечение ГИС. Виды программного обеспечения. Открытый урок
Открытый урок Лекция 5. Файлы в Си
Лекция 5. Файлы в Си Мои таланты. Мое хобб - киберспорт
Мои таланты. Мое хобб - киберспорт Основні тренди у веб-дизайні. Сторітеллінг
Основні тренди у веб-дизайні. Сторітеллінг Двоичное кодирование звуковой информации 10 класс гимназия 22 город Майкоп
Двоичное кодирование звуковой информации 10 класс гимназия 22 город Майкоп