Содержание
- 2. Objectives Evaluate a single condition using the IF function Evaluate multiple conditions using the AND function
- 3. Objectives Check for data entry errors using the IFERROR function Summarize data using the COUNTIF, SUMIF,
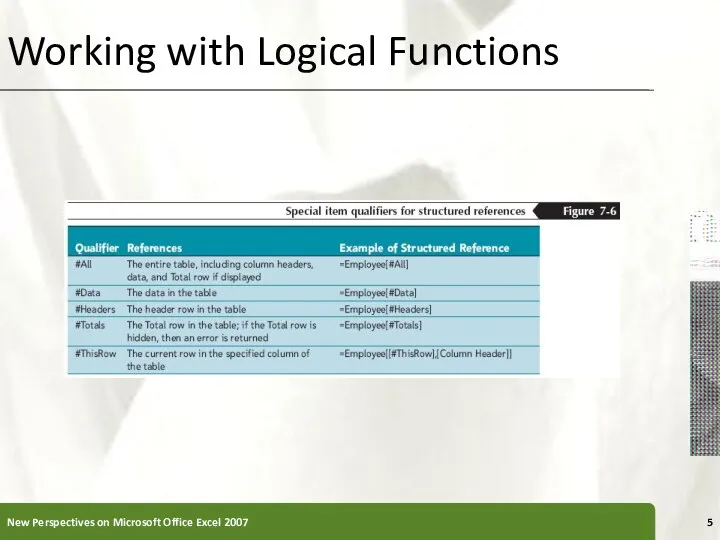
- 4. Working with Logical Functions IF Function IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false]) AND Function =IF(AND(G2="FT",M2>=1),K2*0.03,0) Structured References You can
- 5. Working with Logical Functions New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
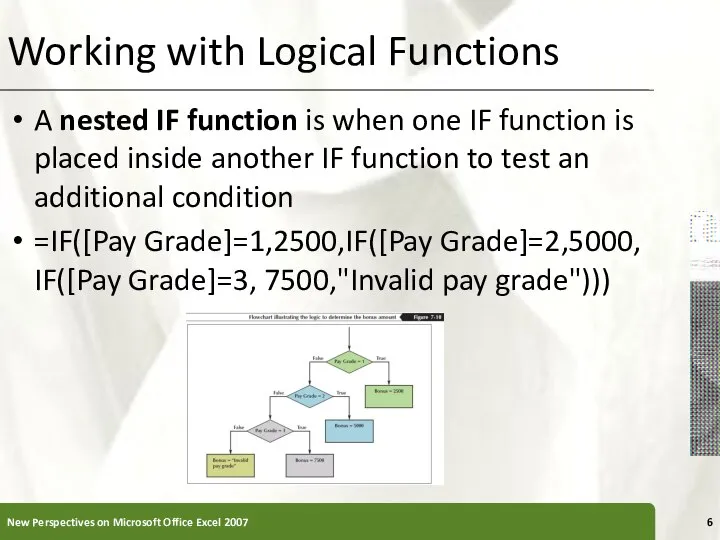
- 6. Working with Logical Functions A nested IF function is when one IF function is placed inside
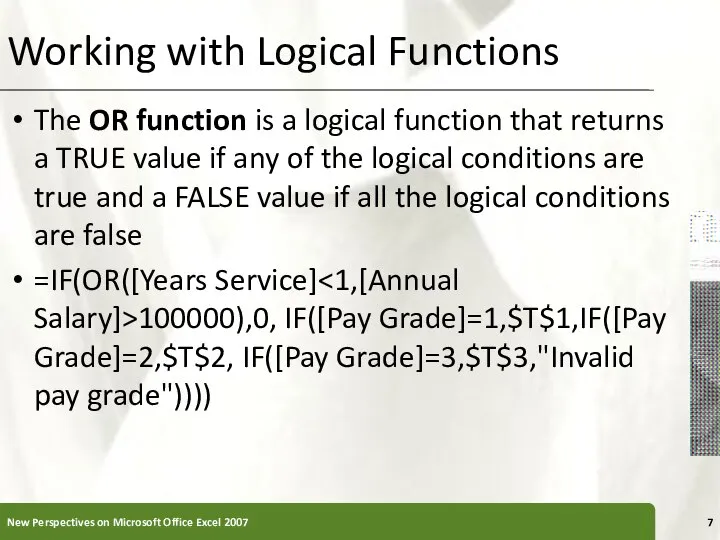
- 7. Working with Logical Functions The OR function is a logical function that returns a TRUE value
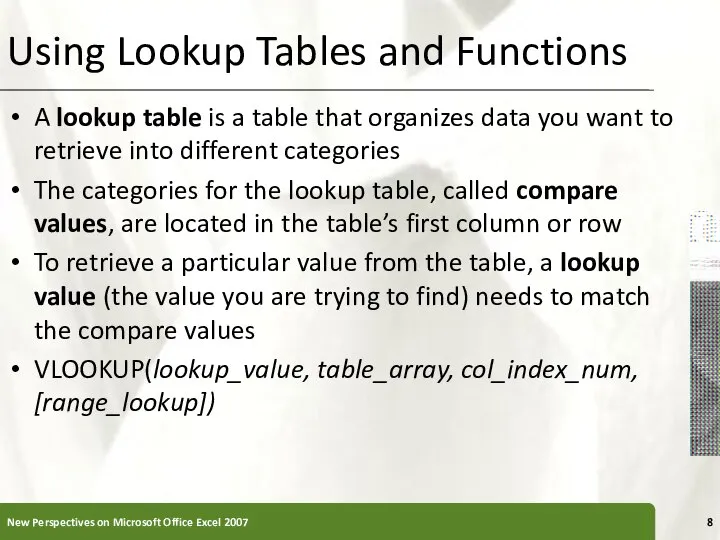
- 8. Using Lookup Tables and Functions A lookup table is a table that organizes data you want
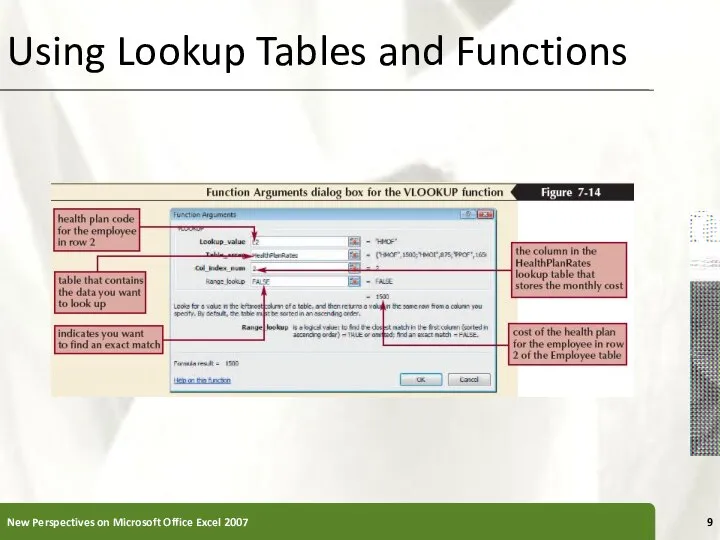
- 9. Using Lookup Tables and Functions New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
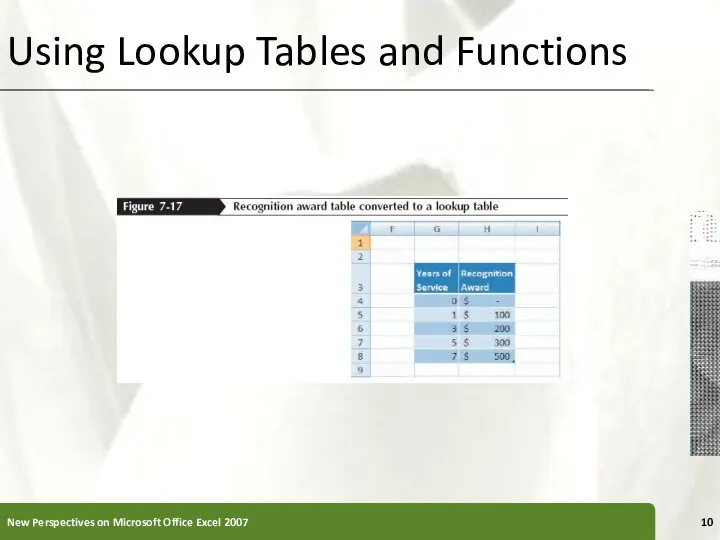
- 10. Using Lookup Tables and Functions New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
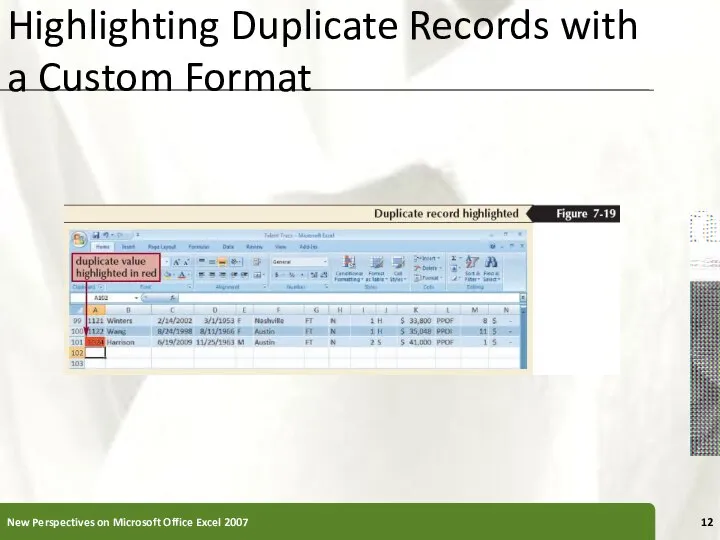
- 11. Highlighting Duplicate Records with a Custom Format Select the column you want to search for duplicates
- 12. Highlighting Duplicate Records with a Custom Format New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
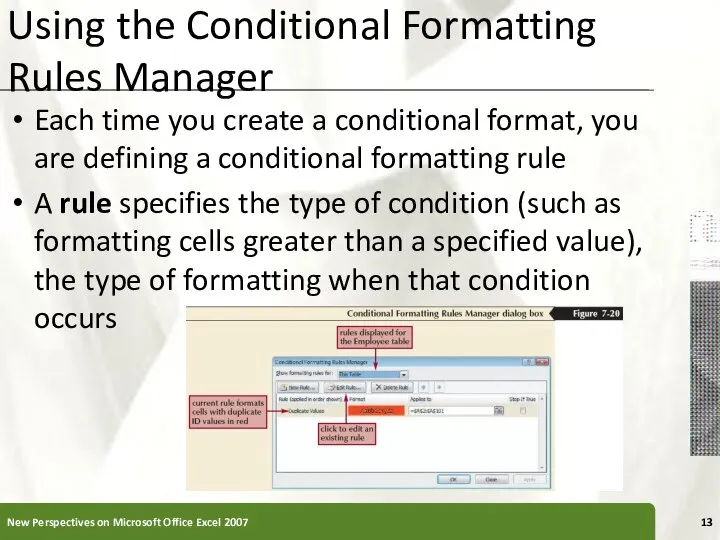
- 13. Using the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager Each time you create a conditional format, you are defining
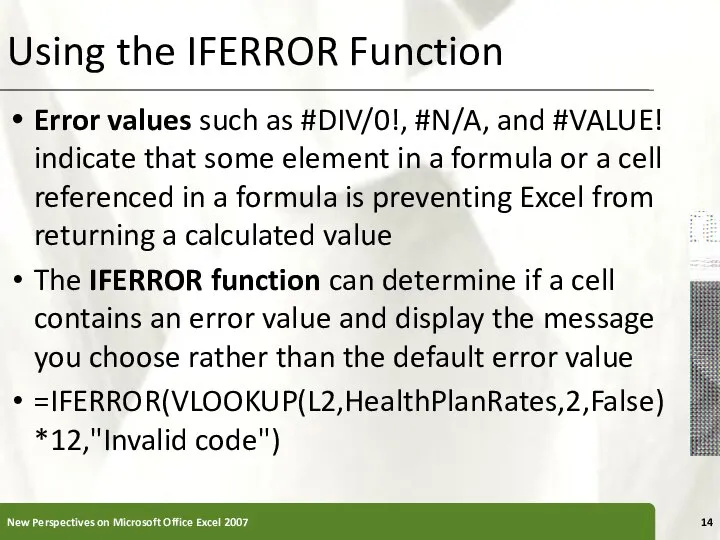
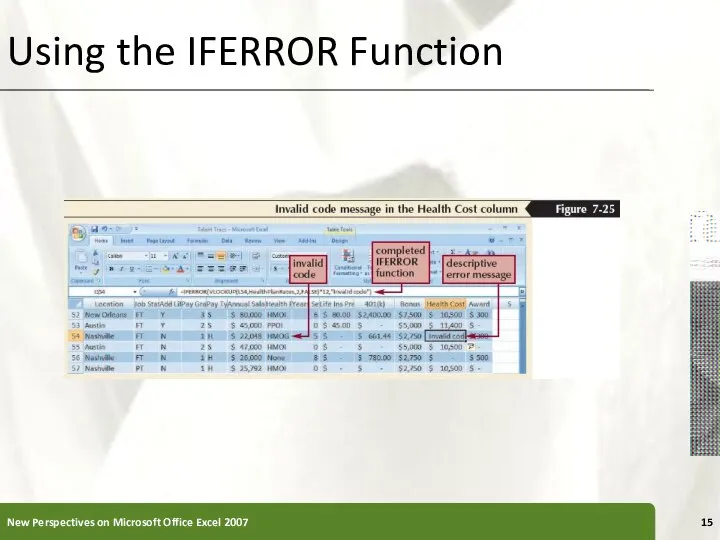
- 14. Using the IFERROR Function Error values such as #DIV/0!, #N/A, and #VALUE! indicate that some element
- 15. Using the IFERROR Function New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
- 16. Summarizing Data Conditionally You can calculate the number of cells in a range that match criteria
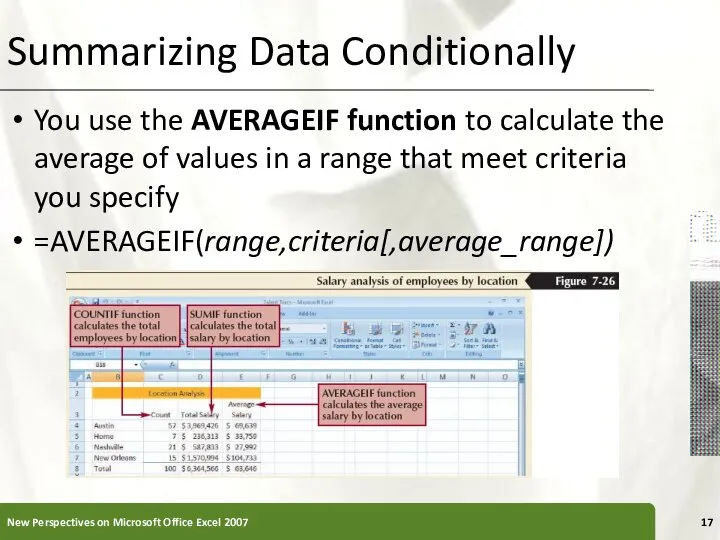
- 17. Summarizing Data Conditionally You use the AVERAGEIF function to calculate the average of values in a
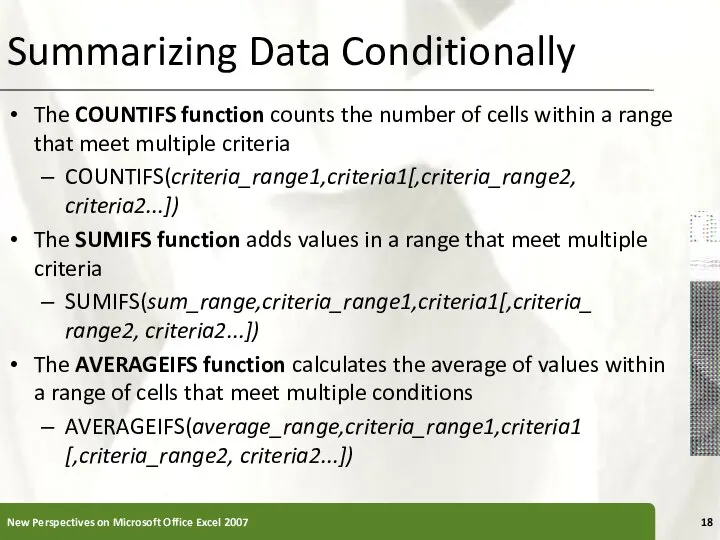
- 18. Summarizing Data Conditionally The COUNTIFS function counts the number of cells within a range that meet
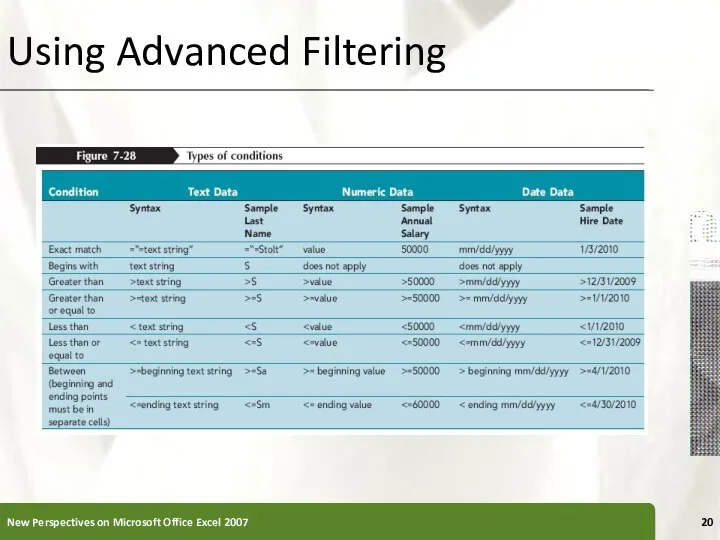
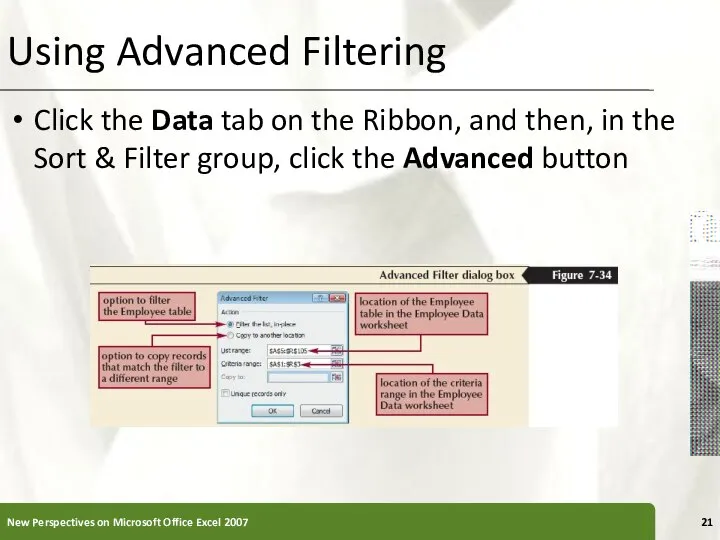
- 19. Using Advanced Filtering Advanced filtering, similar to filtering, displays a subset of the rows in a
- 20. Using Advanced Filtering New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
- 21. Using Advanced Filtering Click the Data tab on the Ribbon, and then, in the Sort &
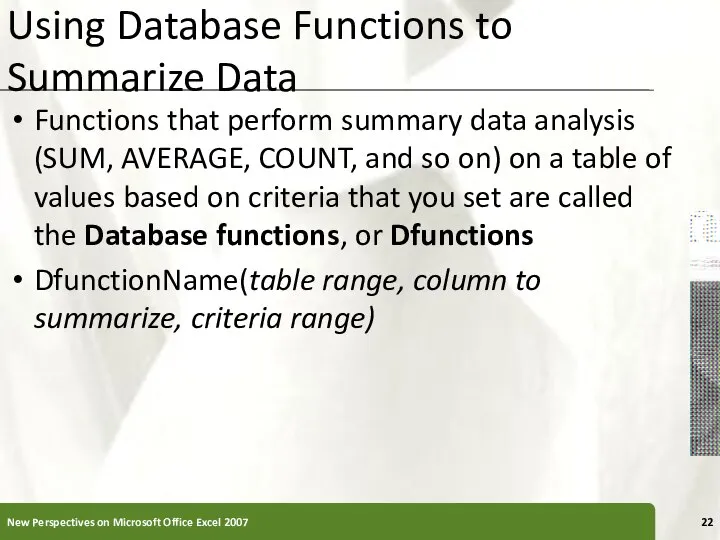
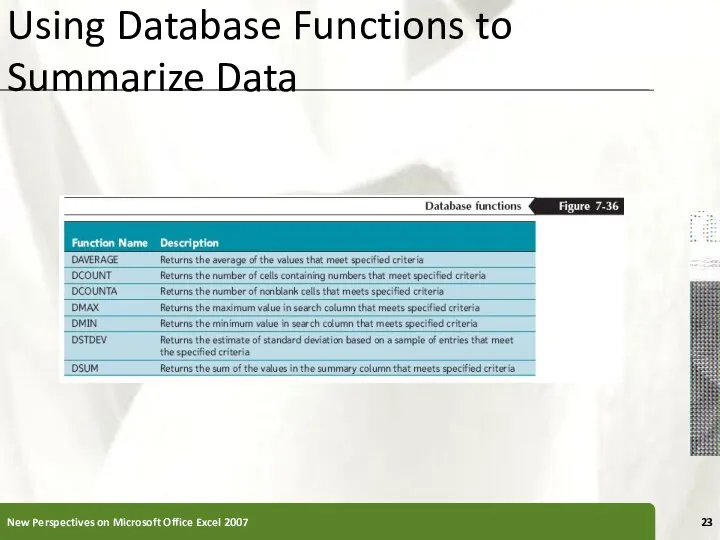
- 22. Using Database Functions to Summarize Data Functions that perform summary data analysis (SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, and
- 23. Using Database Functions to Summarize Data New Perspectives on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
- 25. Скачать презентацию
![Working with Logical Functions IF Function IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false]) AND Function](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1149495/slide-3.jpg)


 Графическая информация
Графическая информация Презентация "Введение в мультимедийные базы данных 6" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Введение в мультимедийные базы данных 6" - скачать презентации по Информатике Системы счисления. Блиц-опрос
Системы счисления. Блиц-опрос Ввод и редактирование алгоритмов в среде конструктора алгоритмом
Ввод и редактирование алгоритмов в среде конструктора алгоритмом Уроки Usability из мультфильма Дом
Уроки Usability из мультфильма Дом Руководство по PGP для Windows
Руководство по PGP для Windows Интернет как способ межкультурной коммуникации
Интернет как способ межкультурной коммуникации Система управления базами данных MS Аccess
Система управления базами данных MS Аccess Рекомендации по созданию и оценке педагогической эффективности учебнообразовательных презентаций Microsoft Powerpoint
Рекомендации по созданию и оценке педагогической эффективности учебнообразовательных презентаций Microsoft Powerpoint Реляционная алгебра
Реляционная алгебра Ассиметричное шифрование
Ассиметричное шифрование Гиперссылки
Гиперссылки Чат бот
Чат бот Основные теги HTML
Основные теги HTML  Întroducere în teoria reţelelor de calculatoare. Noţiuni de bază
Întroducere în teoria reţelelor de calculatoare. Noţiuni de bază Системы счисления
Системы счисления Работа с таблицами в Microsoft Office Word 2007
Работа с таблицами в Microsoft Office Word 2007 Разработка АИС для учета передвижения продукции
Разработка АИС для учета передвижения продукции Поколение ЭВМ История возникновения электронно-вычислительных машин
Поколение ЭВМ История возникновения электронно-вычислительных машин  Computer software
Computer software Базовый курс пользователя ПК
Базовый курс пользователя ПК Анимация. Цвети-семицветик
Анимация. Цвети-семицветик Программирование на языке высокого уровня. Битовые операции
Программирование на языке высокого уровня. Битовые операции Основы языка гипертекстовой разметки документов
Основы языка гипертекстовой разметки документов Телекоммуникационные решения на базе технологии МсWill (NG - 1)
Телекоммуникационные решения на базе технологии МсWill (NG - 1) Циклы в python
Циклы в python Проектирование информационных систем. Лекция 2. Аспекты разработки ИС: стандарты моделирования IDEF, стандарты планирования MRP
Проектирование информационных систем. Лекция 2. Аспекты разработки ИС: стандарты моделирования IDEF, стандарты планирования MRP Создание базы данных «Приемная комиссия»
Создание базы данных «Приемная комиссия»