When you use unclear and non-descript names for variables, classes, and
functions, you’re essentially obfuscating the application logic from any programmer who reads the code, including yourself.
3. Use Descriptive Names
What does a variable named dxy actually mean? Who knows. You’d probably have to read the entire chunk of code to reverse engineer its meaning. On the other hand, the meaning of a variable like distanceBetweenXY is instantly recognizable.
But, this doesn't necessarily apply to temporary variables. They can be as short as a single character.
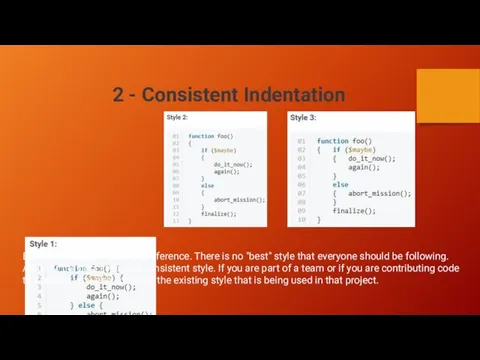
Consistent Naming Scheme
mysql_real_escape_string()
MysqlRealEscapeString()






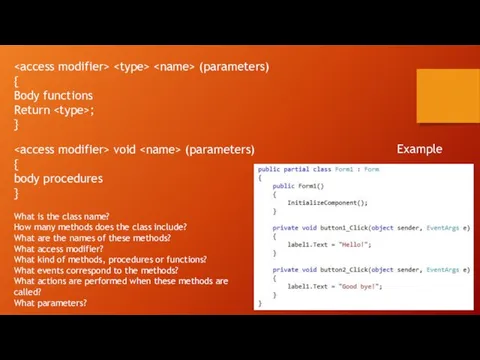



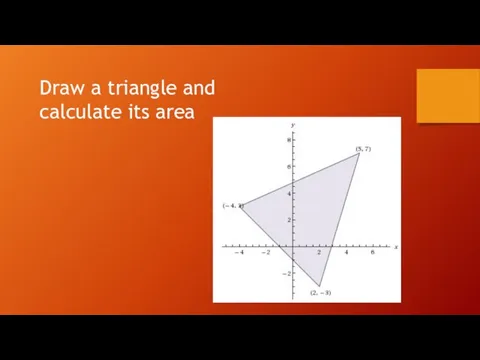





 Тест по теме : «АЛГОРИТМ?» Готовы начать тестирование ?
Тест по теме : «АЛГОРИТМ?» Готовы начать тестирование ? Сканер (англ. scanner) — устройство, которое анализируя какой-либо объект (обычно изображение, текст), создаёт цифровую копию изображе
Сканер (англ. scanner) — устройство, которое анализируя какой-либо объект (обычно изображение, текст), создаёт цифровую копию изображе Электронная таблица Excel 2003
Электронная таблица Excel 2003 Текстовый процессор Microsoft Word
Текстовый процессор Microsoft Word Network camera. Latest firmware feature
Network camera. Latest firmware feature CASE-средство IBM Rational Rose 2003
CASE-средство IBM Rational Rose 2003 Лекция №4 Информационные процессы и информационные системы как предмет изучения правовой информатики. Информатизация правот
Лекция №4 Информационные процессы и информационные системы как предмет изучения правовой информатики. Информатизация правот Основы логики
Основы логики Файловые системы
Файловые системы Сетевое моделирование
Сетевое моделирование Фреймворк Laravel
Фреймворк Laravel Настрою интернет-рекламу
Настрою интернет-рекламу Создание запросов в СУБД Access
Создание запросов в СУБД Access Презентация "Двоичный код" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Двоичный код" - скачать презентации по Информатике Тема: Создание Web- страниц.
Тема: Создание Web- страниц.  Внутренние устройства ПК
Внутренние устройства ПК Полиномиальные хэш-функции
Полиномиальные хэш-функции Виртуальная память
Виртуальная память История языков программирования
История языков программирования РЕН ТВ — российский федеральный телеканал
РЕН ТВ — российский федеральный телеканал Полезные ссылки
Полезные ссылки Введение в специальность. Введение в технологии параллельного программирования
Введение в специальность. Введение в технологии параллельного программирования Обработка информации. Информатика, 5 класс
Обработка информации. Информатика, 5 класс Линейные программы
Линейные программы Ошибки при выборе шаблонов титульных листов, оформлении и Антиплагиат
Ошибки при выборе шаблонов титульных листов, оформлении и Антиплагиат Чарльз Бэббидж (Charles Babbage)
Чарльз Бэббидж (Charles Babbage) Безопасность систем баз данных. Управление доступом в СУБД
Безопасность систем баз данных. Управление доступом в СУБД Программное обеспечение компьютера. (7 класс)
Программное обеспечение компьютера. (7 класс)