Содержание
- 2. Course Overview The course provides an overview of the major conceptual paradigms of Information and Communication
- 3. Lecture 1 Overview of Today’s Lecture Definition of ICT. The subject of ICT and its objectives
- 4. What technologies? What do you understand by Information and Communication Technologies?
- 5. Defining ICTs Standard definitions: ICT (information and communications technology - or technologies) is an umbrella term
- 6. The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society Telecommunications ICT in Education
- 7. The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society Telecommunications Telecommunication is the
- 8. The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society ICT in Education ICT
- 9. The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society ICT in Public Sector
- 10. The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society ICT in Health ICT
- 11. The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society ICT in Agriculture and
- 12. Standards in the ICT field Application and administration Scoping requirements Functional Performance Criteria Hardware Platforms and
- 13. A new generation of components and systems ICT1 – 2016: Smart Cyber-Physical Systems ICT2 – 2016:
- 14. Smart Cyber-Physical Systems The challenge is to design, programme and implement highly distributed and connected digital
- 15. CPS: Computing Perspective Two types of computing systems Desktops, servers, PCs, and notebooks Embedded The next
- 16. CPS: Systems Perspective Cyber-Physical Systems
- 17. CPS Definition A CPS is a system in which: information processing and physical processes are so
- 18. National Health Information Network, Electronic Patient Record initiative Medical records at any point of service Hospital,
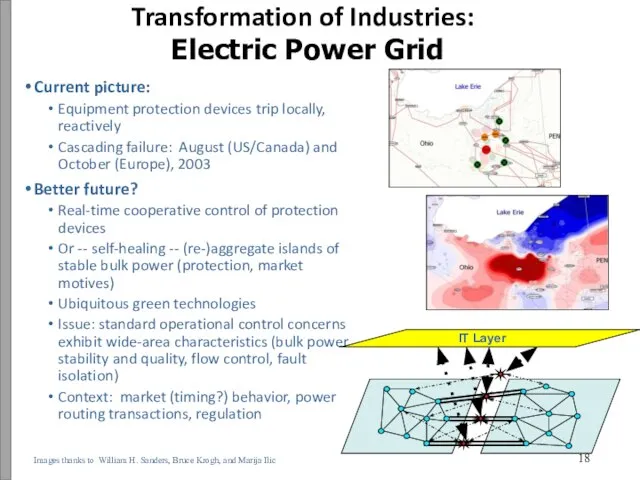
- 19. Current picture: Equipment protection devices trip locally, reactively Cascading failure: August (US/Canada) and October (Europe), 2003
- 20. SSI – Smart System Integration The challenge is to be able to develop and manufacture smart
- 21. Customized and low energy computing Information and Communication Technologies are becoming a core component of products
- 22. What is Cloud Computing? Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class
- 23. What is Cloud Computing? In addition, the platform provides on demand services, that are always on,
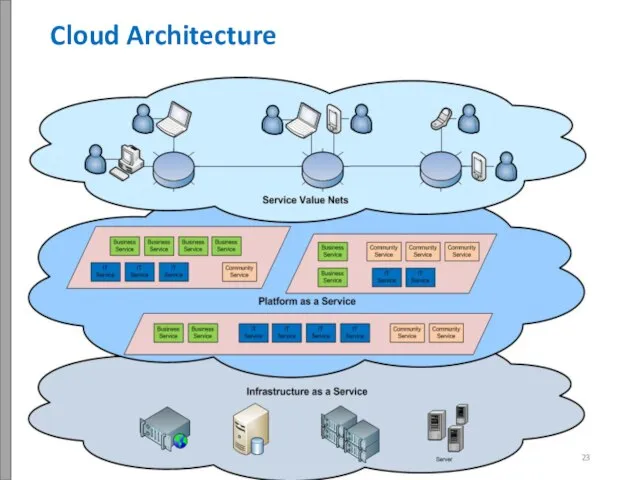
- 24. Cloud Architecture
- 25. Do you Use the Cloud?
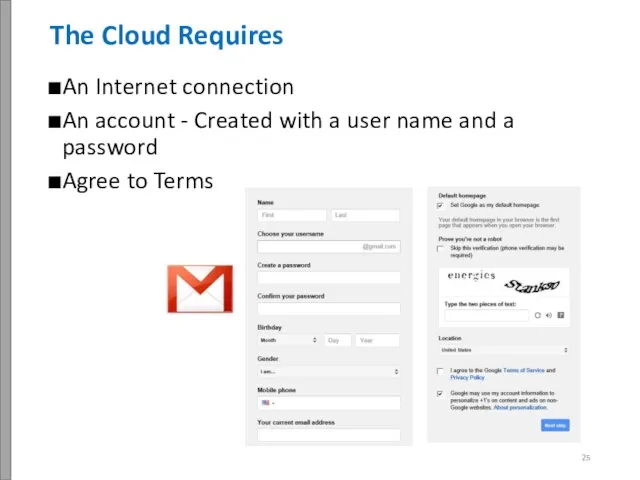
- 26. An Internet connection An account - Created with a user name and a password Agree to
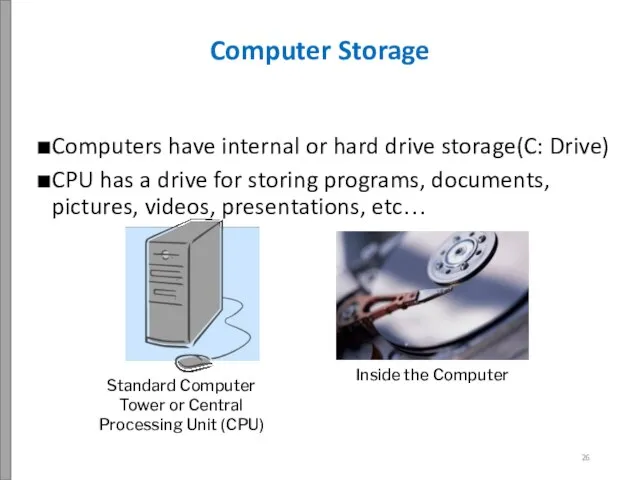
- 27. Computers have internal or hard drive storage(C: Drive) CPU has a drive for storing programs, documents,
- 28. Content is stored on THAT computer To use content must return to THAT computer Cannot access
- 29. Purchase programs Load to the computer Each computer would need the program loaded and stored on
- 30. External Storage External Hard Drive CD/DVD Thumb Drive SD Card Micro SD Card Allows your content
- 31. Multiple work stations talk to one unit that stores information and data. Data is not saved
- 32. When you do a “save as” on your computer, you choose where to save the material.
- 33. Create an Account – User name and password Content lives with the account in the cloud
- 34. Download a cloud based app to a computer you own The app lives on your Computer
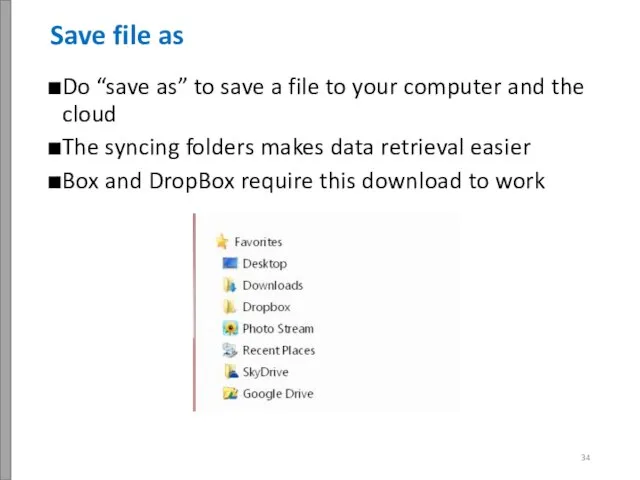
- 35. Do “save as” to save a file to your computer and the cloud The syncing folders
- 36. Log-in to the online storage account Click upload a file Find the file on hard drive,
- 37. Google Docs SkyDrive Box Document Creation
- 38. Creation is happening in the cloud Saving is going to the cloud To retrieve files, must
- 39. Photo editing software Online banking apps Social media apps Communication Other Software services
- 40. Group of instructions that directs a computer is called an program No computer can do anything
- 41. Programs designed to perform specific tasks is called known as Application software Multiprogramming system execute more
- 42. The process of writing computer instructions in a programming language is known as Coding A computer
- 43. Personnel who design, program, operate and maintain computer equipment refers to Peopleware A step-by-step procedure used
- 44. ICT in Industrial Leadership Components and systems Smart embedded components and systems, micro-nano-bio systems, organic electronics,
- 45. ICT in Leadership Content technologies and information management Technologies for language, learning, interaction, digital preservation, content
- 46. Cybersecurity Computer security, also known as cybersecurity or IT security, is the protection of computer systems
- 47. List of required textbooks and additional resources Required Textbook: Brown G., Sargent B., and Watson D.
- 49. Скачать презентацию







































 Компьютерная графика. Графический редактор
Компьютерная графика. Графический редактор Android Basic Training MU
Android Basic Training MU Трассировка лучей в играх
Трассировка лучей в играх Системное и прикладное программное обеспечение
Системное и прикладное программное обеспечение A2. Автоматизация процесса управления проектами B2S/B2G/B2O М
A2. Автоматизация процесса управления проектами B2S/B2G/B2O М Тема: Информационное моделирование 8 класс
Тема: Информационное моделирование 8 класс Базы и банки данных. История развития ВТ и СУБД
Базы и банки данных. История развития ВТ и СУБД HTML Учебник для «чайничков»
HTML Учебник для «чайничков»  Локальные компьютерные сети
Локальные компьютерные сети Корпоративная память
Корпоративная память Интернет-зависимость у подростков
Интернет-зависимость у подростков Кодирование звуковой информации. 9 класс
Кодирование звуковой информации. 9 класс Основы программирования
Основы программирования Виды компьютерной графики. 8 класс
Виды компьютерной графики. 8 класс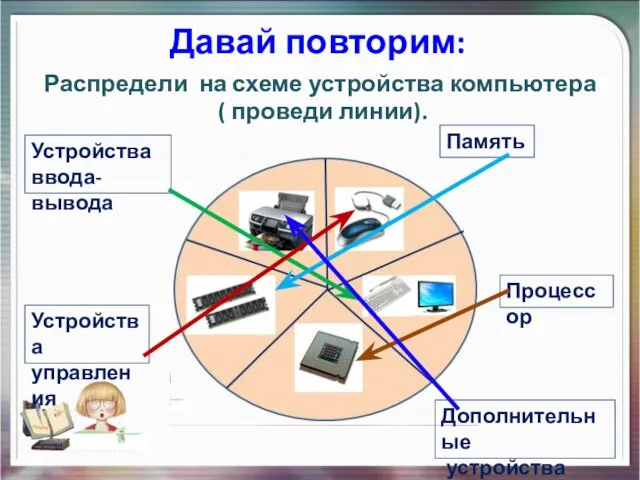 Системные программы и операционная система
Системные программы и операционная система Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word Системы счисления
Системы счисления Базы данных
Базы данных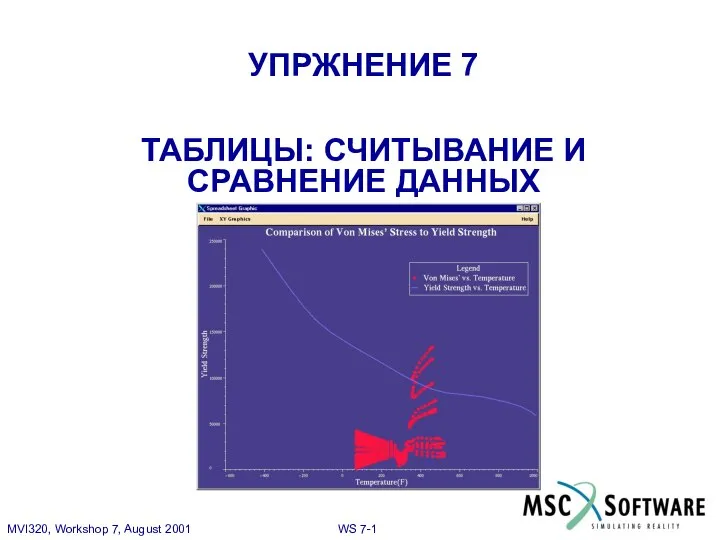 Презентация "MSC.Mvision Workshop 7" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "MSC.Mvision Workshop 7" - скачать презентации по Информатике Определение РМД
Определение РМД Муниципальная статистика и местная информационная база
Муниципальная статистика и местная информационная база Школьники и Интернет. Новые информационные возможности и новые угрозы
Школьники и Интернет. Новые информационные возможности и новые угрозы Логические основы компьютера Элементарные логические схемы. Наглядное пособие. Автор: Сергеев Е.В. учитель информатики М
Логические основы компьютера Элементарные логические схемы. Наглядное пособие. Автор: Сергеев Е.В. учитель информатики М Скорость передачи информации
Скорость передачи информации Работаем художниками-иллюстраторами
Работаем художниками-иллюстраторами Алгоритмы, свойства, виды
Алгоритмы, свойства, виды Режимы и способы обработки данных
Режимы и способы обработки данных Обобщающий урок по теме: «ИНФОРМАЦИЯ » Цель урока: ОБОБЩИТЬ И СИСТЕМАТИЗИРОВАТЬ ЗНАНИЯ И УМЕНИЯ ПО ТЕМЕ «ИНФОРМАЦИЯ»
Обобщающий урок по теме: «ИНФОРМАЦИЯ » Цель урока: ОБОБЩИТЬ И СИСТЕМАТИЗИРОВАТЬ ЗНАНИЯ И УМЕНИЯ ПО ТЕМЕ «ИНФОРМАЦИЯ»