Содержание
- 2. Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Explain the need
- 3. About PL/SQL PL/SQL: Stands for “Procedural Language extension to SQL” Is Oracle Corporation’s standard data access
- 4. About PL/SQL PL/SQL: Provides a block structure for executable units of code. Maintenance of code is
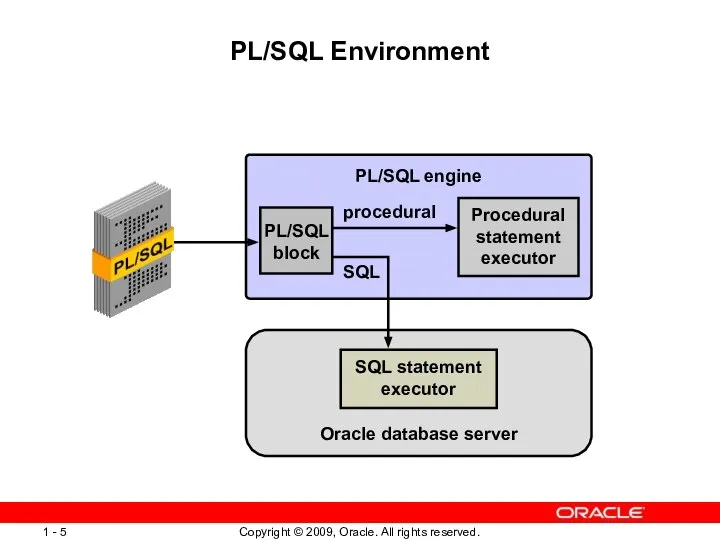
- 5. PL/SQL Environment PL/SQL engine Oracle database server SQL statement executor Procedural statement executor procedural SQL PL/SQL
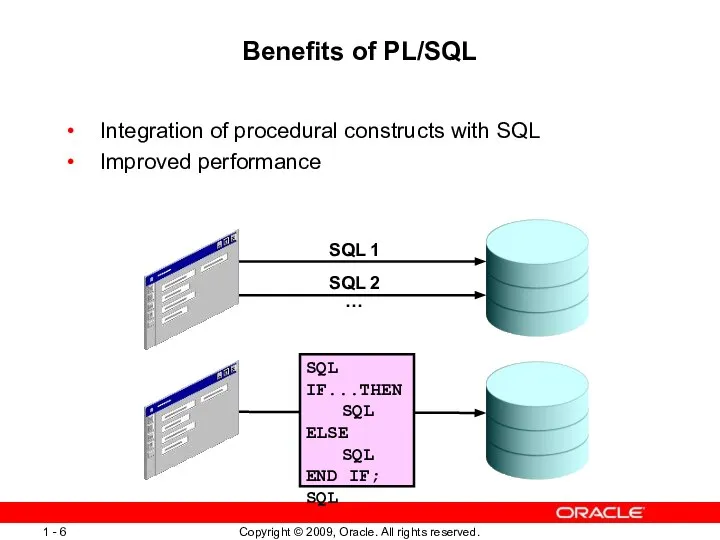
- 6. Benefits of PL/SQL Integration of procedural constructs with SQL Improved performance SQL IF...THEN SQL ELSE SQL
- 7. Benefits of PL/SQL Modularized program development Integration with Oracle tools Portability Exception handling
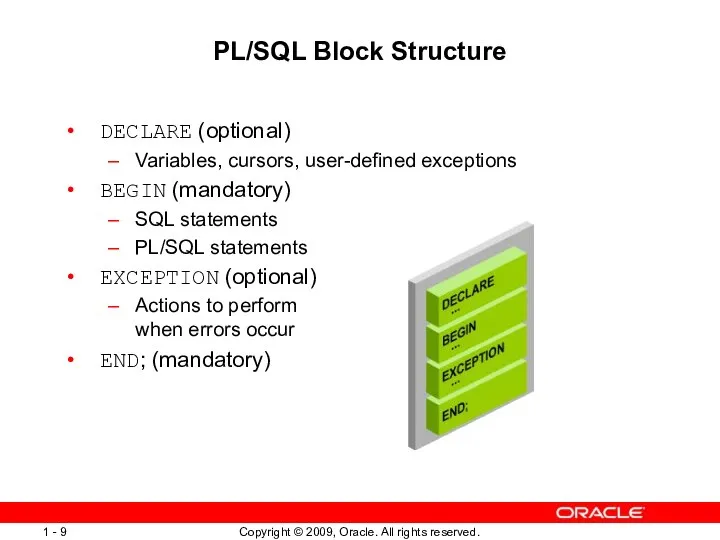
- 9. PL/SQL Block Structure DECLARE (optional) Variables, cursors, user-defined exceptions BEGIN (mandatory) SQL statements PL/SQL statements EXCEPTION
- 11. Block Types Anonymous Procedure Function [DECLARE] BEGIN --statements [EXCEPTION] END; PROCEDURE name IS BEGIN --statements [EXCEPTION]
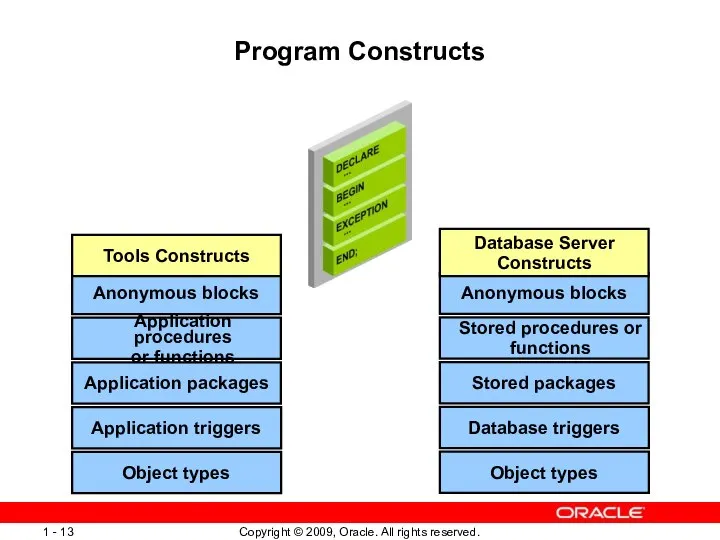
- 13. Program Constructs Application triggers Application packages Application procedures or functions Anonymous blocks Tools Constructs Object types
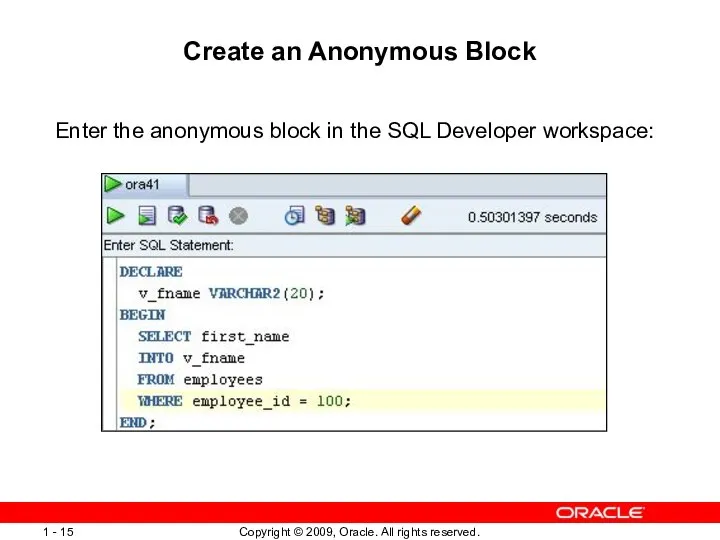
- 15. Create an Anonymous Block Enter the anonymous block in the SQL Developer workspace:
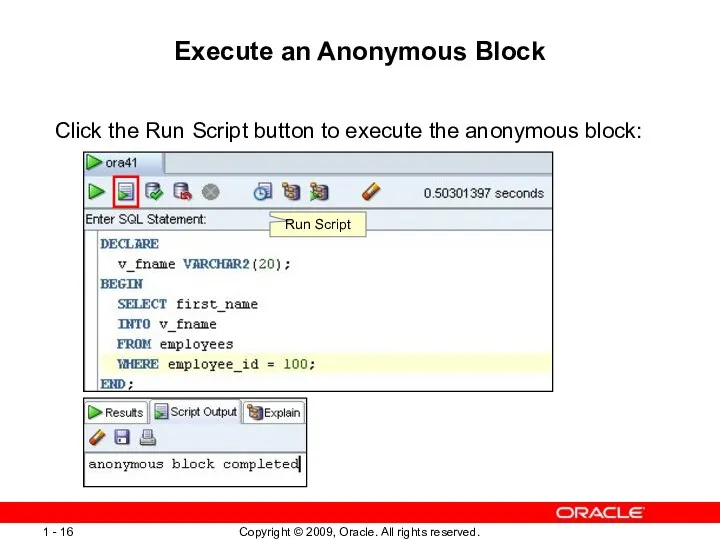
- 16. Execute an Anonymous Block Click the Run Script button to execute the anonymous block: Run Script
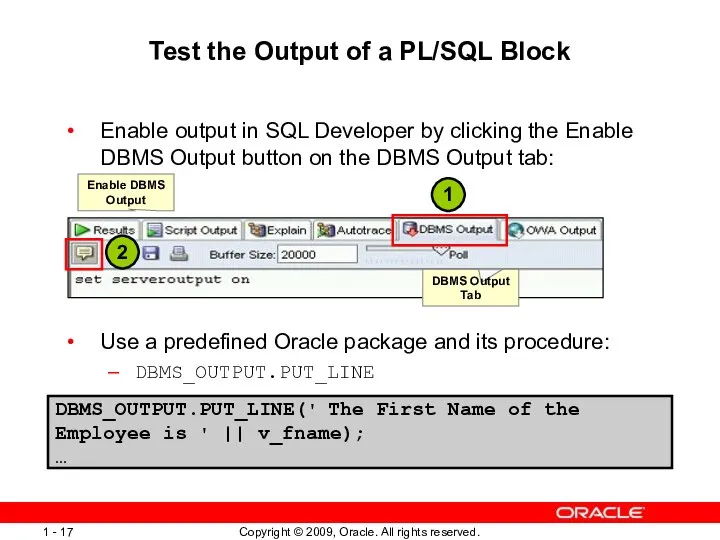
- 17. Test the Output of a PL/SQL Block Enable output in SQL Developer by clicking the Enable
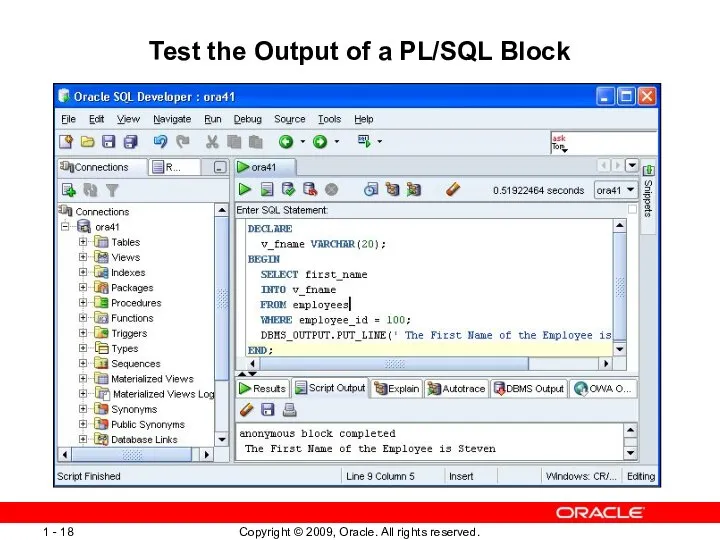
- 18. Test the Output of a PL/SQL Block
- 19. Quiz A PL/SQL block must consist of the following three sections: A Declarative section which begins
- 20. Summary In this lesson, you should have learned how to: Integrate SQL statements with PL/SQL program
- 21. Practice 1: Overview This practice covers the following topics: Identifying the PL/SQL blocks that execute successfully
- 23. Скачать презентацию




![Block Types Anonymous Procedure Function [DECLARE] BEGIN --statements [EXCEPTION] END; PROCEDURE](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1327486/slide-10.jpg)




 Основні категорії теорії баз даних і типи зв’язків між ними
Основні категорії теорії баз даних і типи зв’язків між ними Управление компьютером с помощью меню
Управление компьютером с помощью меню Техническое задание. Система голосования v3. Регистрация. Страница регистрации на сайте
Техническое задание. Система голосования v3. Регистрация. Страница регистрации на сайте Решение логических задач с помощью нескольких таблиц
Решение логических задач с помощью нескольких таблиц Домеханические и механические счетные машины
Домеханические и механические счетные машины Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office Презентация "Апробация электронных учебников в общеобразовательных учреждениях" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Апробация электронных учебников в общеобразовательных учреждениях" - скачать презентации по Информатике Схемотехника комбинационных узлов
Схемотехника комбинационных узлов Работа на клавиатуре. Назначение клавиш
Работа на клавиатуре. Назначение клавиш Информационные технологии
Информационные технологии Набор Lego Mindstorms EV3 Education
Набор Lego Mindstorms EV3 Education САОД (stl)
САОД (stl) Методолия моделирования социально-экономических процессов
Методолия моделирования социально-экономических процессов Патерни проектування
Патерни проектування Continuous integration
Continuous integration Сказка о том, откуда возникла наука Информатика
Сказка о том, откуда возникла наука Информатика Презентация "Путешествие на остров Информация" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Путешествие на остров Информация" - скачать презентации по Информатике Web - каталоги. Принципы организации и применения поисковых машин. Стратегии поиска информации
Web - каталоги. Принципы организации и применения поисковых машин. Стратегии поиска информации Середовище описання і виконання алгоритмів
Середовище описання і виконання алгоритмів HTML. Язык описания Web-страниц
HTML. Язык описания Web-страниц Двоичная система счисления
Двоичная система счисления Технологии разработки ПО. Основные понятия и определения
Технологии разработки ПО. Основные понятия и определения Операционная система(ОС)
Операционная система(ОС) Решение расчётной задачи в среде электронной таблицы EXCEL
Решение расчётной задачи в среде электронной таблицы EXCEL Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа дополнительного образования Мир программирования Scratch
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа дополнительного образования Мир программирования Scratch Презентация "Накопители на гибких магнитных дисках (НГМД)" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Накопители на гибких магнитных дисках (НГМД)" - скачать презентации по Информатике Мой любимый Интернет. Библиотечный урок по информационной культуре для среднего школьного возраста
Мой любимый Интернет. Библиотечный урок по информационной культуре для среднего школьного возраста Отчет о практической работе
Отчет о практической работе