Содержание
- 2. Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to: Describe the advantages of localizing an
- 3. Why Localize? The decision to create a version of an application for international use often happens
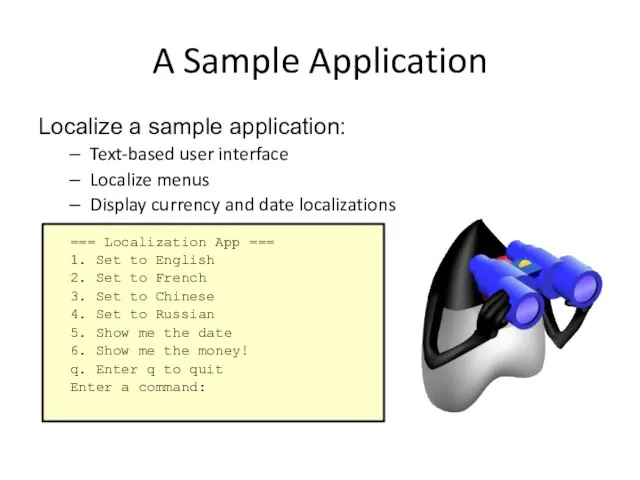
- 4. A Sample Application Localize a sample application: Text-based user interface Localize menus Display currency and date
- 5. Locale A Locale specifies a particular language and country: Language An alpha-2 or alpha-3 ISO 639
- 6. Resource Bundle The ResourceBundle class isolates locale-specific data: Returns key/value pairs stored separately Can be a
- 7. Resource Bundle File Properties file contains a set of key/value pairs. Each key identifies a specific
- 8. Sample Resource Bundle Files Samples for French and Chinese MessagesBundle_fr_FR.properties menu1 = Régler à l'anglais menu2
- 9. Quiz Which bundle file represents a language of Spanish and a country code of US? MessagesBundle_ES_US.properties
- 10. Initializing the Sample Application PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(System.out, true); // More init code here Locale
- 11. Sample Application: Main Loop public void run(){ String line = ""; while (!(line.equals("q"))){ this.printMenu(); try {
- 12. The printMenu Method Instead of text, resource bundle is used. messages is a resource bundle. A
- 13. Changing the Locale To change the Locale: Set currentLocale to the desired language. Reload the bundle
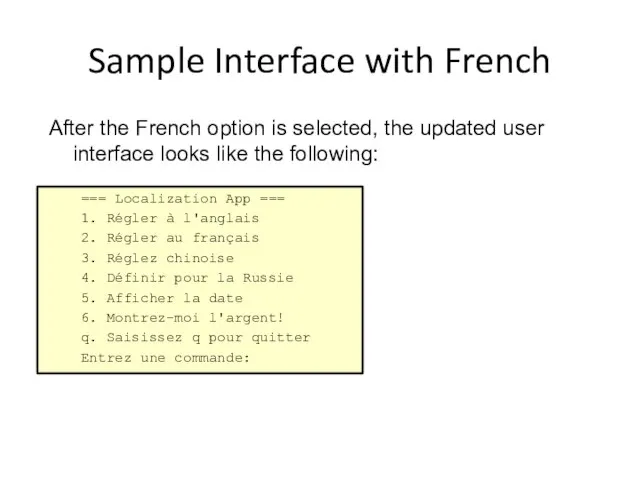
- 14. Sample Interface with French After the French option is selected, the updated user interface looks like
- 15. Format Date and Currency Numbers can be localized and displayed in their local format. Special format
- 16. Initialize Date and Currency The application can show a local formatted date and currency. The variables
- 17. Displaying a Date Format a date: Get a DateFormat object based on the Locale. Call the
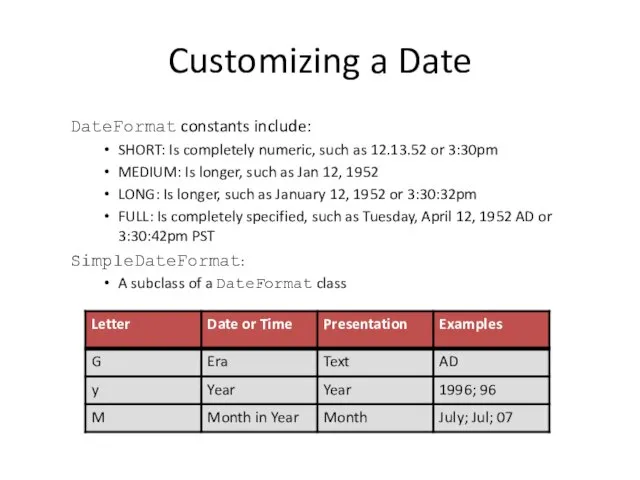
- 18. Customizing a Date DateFormat constants include: SHORT: Is completely numeric, such as 12.13.52 or 3:30pm MEDIUM:
- 19. Displaying Currency Format currency: Get a currency instance from NumberFormat. Pass the Double to the format
- 20. Quiz Which date format constant provides the most detailed information? LONG FULL MAX COMPLETE
- 22. Скачать презентацию















 Контроль и защита информации в автоматизированных системах
Контроль и защита информации в автоматизированных системах КОМПЬЮТЕРиЯ – КОМПЬЮТЕРиЯ – экономические модели решения социальных проблем г.Тверь Апрель 2006
КОМПЬЮТЕРиЯ – КОМПЬЮТЕРиЯ – экономические модели решения социальных проблем г.Тверь Апрель 2006 Ассемблер
Ассемблер Разработка технической документации на построение локальной сети предприятия
Разработка технической документации на построение локальной сети предприятия Сервис Публичная кадастровая карта
Сервис Публичная кадастровая карта Диссернет (разоблачение плагиата в диссертациях) и медицина
Диссернет (разоблачение плагиата в диссертациях) и медицина Мир 3D принтеров
Мир 3D принтеров Как защитить свой компьютер
Как защитить свой компьютер Обновленные пакеты БИЗНЕС и ULTIMATE
Обновленные пакеты БИЗНЕС и ULTIMATE Автоматизация системы мотивации сотрудников
Автоматизация системы мотивации сотрудников Архитектура предприятия. Лекция №5
Архитектура предприятия. Лекция №5 Трассировка лучей в играх
Трассировка лучей в играх Web portal. Storyboard. Users
Web portal. Storyboard. Users Интернет
Интернет Создание мультимедийной презентации
Создание мультимедийной презентации Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Фотодело. Лучше один раз увидеть Чрезвычайные происшествия
Фотодело. Лучше один раз увидеть Чрезвычайные происшествия Быстрая сортировка (Quicksort). Повторяющиеся ключи. Применение сортировок
Быстрая сортировка (Quicksort). Повторяющиеся ключи. Применение сортировок SQL Язык структурированных запросов, применяемый для создания и управления данными в реляционных базах данных
SQL Язык структурированных запросов, применяемый для создания и управления данными в реляционных базах данных Приемы форматирования текстов. Списки.
Приемы форматирования текстов. Списки. Модуль 2 — Конфигурация OSPFv2 для одной области
Модуль 2 — Конфигурация OSPFv2 для одной области Презентация "Введение в мультимедийные базы данных 6" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Введение в мультимедийные базы данных 6" - скачать презентации по Информатике Информационные модели. Модель и моделирование
Информационные модели. Модель и моделирование Types of testing. Testing levels. Software Development Life Cycles modes
Types of testing. Testing levels. Software Development Life Cycles modes Устройства вывода информации (принтеры)
Устройства вывода информации (принтеры) Программный комплекс 1С:ХроноГраф Школа 3.0 ПРОФ
Программный комплекс 1С:ХроноГраф Школа 3.0 ПРОФ Конвейерный процессор. Лекция №11
Конвейерный процессор. Лекция №11 Строки. Массивы. Функции
Строки. Массивы. Функции