Содержание
- 2. Module Aims The aim of the course is to introduce the basics of mobile Web service
- 3. Mobile technologies in health Source: The Economist
- 4. Wearable technologies Source: The Economist
- 5. Mobile technologies in Business
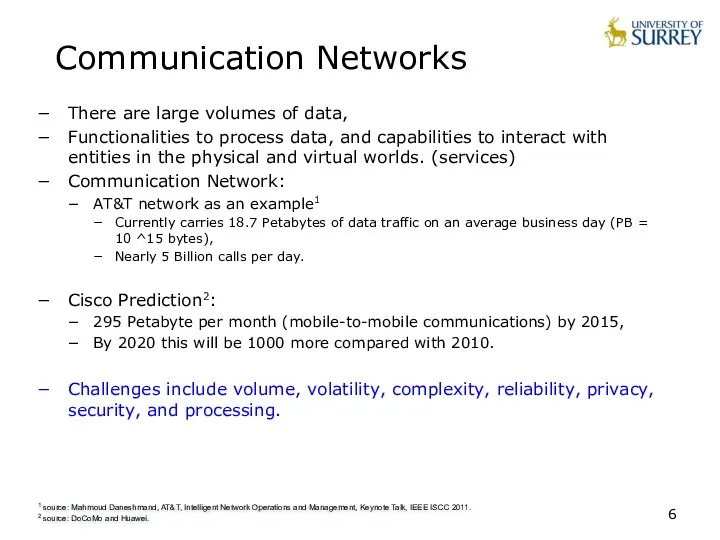
- 6. Communication Networks There are large volumes of data, Functionalities to process data, and capabilities to interact
- 7. Networks of the Future - Challenges Large-scale networks, huge volumes of data, dynamic and sometimes unreliable
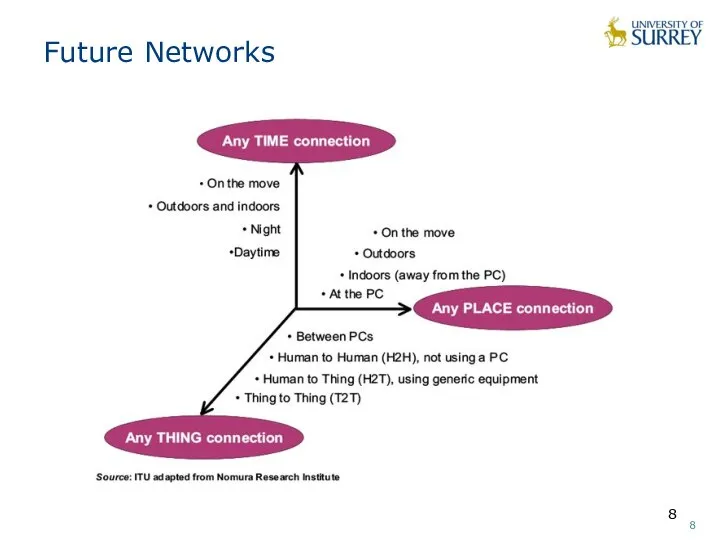
- 8. Future Networks
- 9. “Thing” connected to the internet Source: CISCO
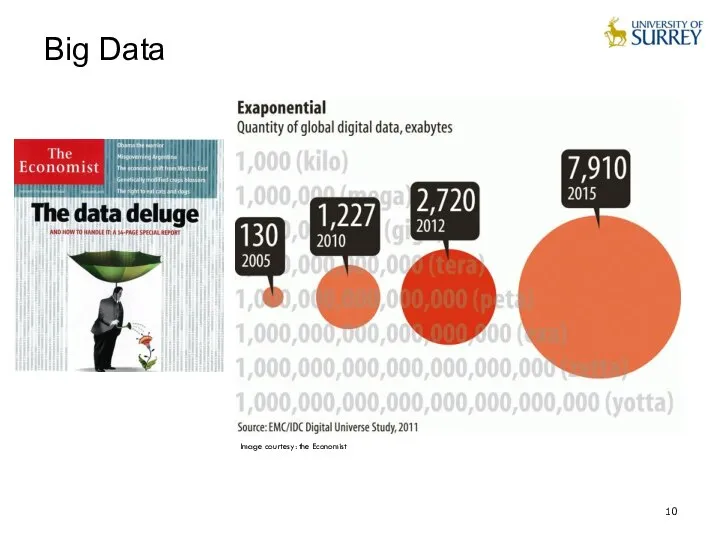
- 10. Image courtesy: the Economist Big Data
- 11. Large number of services Image courtesy: FTW Forschungszentrum Telekommunikation Wien
- 12. … but also Dynamicity and Quality: But it is not just about volume How can we
- 13. "intelligence is becoming ambient" Satya Nadella, Microsoft CEO
- 14. Services We need mobile and pervasive services that are: Flexible Interoperable Reliable Discoverable Support different QoS
- 15. Services on the Web Web Services provide data and services to other applications. Thee applications access
- 16. The role of metadata semantic tagging (machine-interpretable) data annotation and resource descriptions re-usable descriptions and vocabularies
- 17. Motivations- reusability and cost Source: Jerry King @ http://www.jerryking.com
- 18. Motivations- maintainability Source: gettyimages
- 19. Motivations- interoperability Image: courtesy: Economist
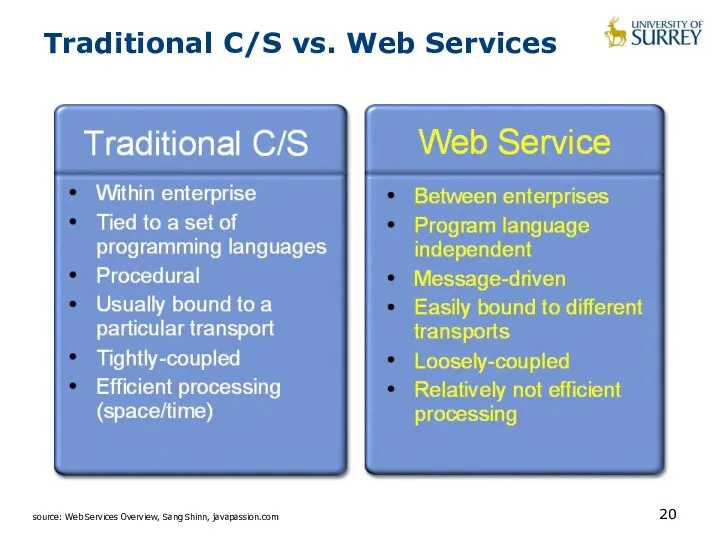
- 20. Traditional C/S vs. Web Services source: Web Services Overview, Sang Shinn, javapassion.com
- 21. Cloud-based services Image courtesy: Economist
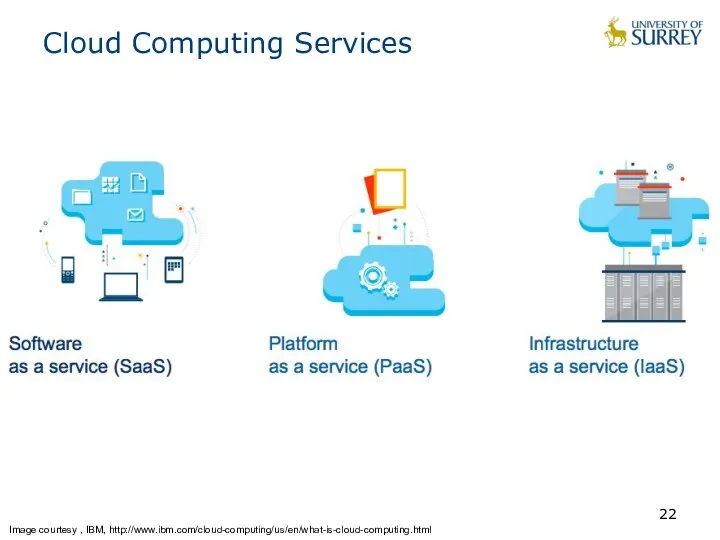
- 22. Cloud Computing Services Image courtesy , IBM, http://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/us/en/what-is-cloud-computing.html
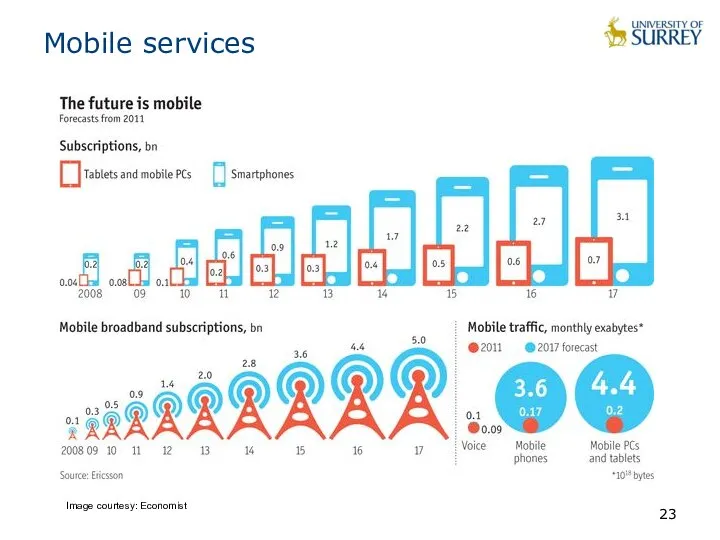
- 23. Mobile services Image courtesy: Economist
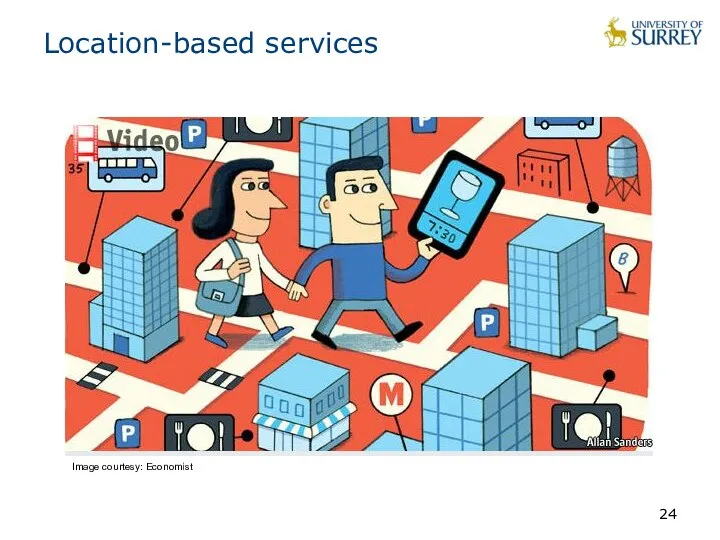
- 24. Location-based services Image courtesy: Economist
- 25. Topics Introduction to Semantic Web and metadata frameworks Semantic web Metadata Ontologies and common vocabularies RDF
- 26. Topics Ontology Querying SPARQL query language Semantic Web Services and Service Platforms Semantic Web services Service
- 27. Topics Mobile Web Services RESTful services Service evolution and delivery in mobile communication systems Wireless Application
- 29. Скачать презентацию















 Андроид нұсқалары
Андроид нұсқалары Презентация "Дискретные и непрерывные сигналы. Носители информации" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Дискретные и непрерывные сигналы. Носители информации" - скачать презентации по Информатике Презентация "Информатика. Компьютер в жизни общества" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Информатика. Компьютер в жизни общества" - скачать презентации по Информатике Публикация и продвижение Интернет-систем
Публикация и продвижение Интернет-систем Организация вычислений в электронных таблицах
Организация вычислений в электронных таблицах Разработка автоматизированной информационной системы - введения документооборота на предприятии Fresh
Разработка автоматизированной информационной системы - введения документооборота на предприятии Fresh Операционная система Windows
Операционная система Windows История развития компьютерной техники
История развития компьютерной техники История компании “Apple Computer”
История компании “Apple Computer” Risk-based testing
Risk-based testing Внедрение SQL-кода
Внедрение SQL-кода Инструкция оператора SD. Этап обработки запроса
Инструкция оператора SD. Этап обработки запроса Правила лицензирования ОС при использовании решений NComputing
Правила лицензирования ОС при использовании решений NComputing Принципи організації розподілених інформаційних систем на основі баз даних та експертних систем в освіті
Принципи організації розподілених інформаційних систем на основі баз даних та експертних систем в освіті Сводные таблицы
Сводные таблицы Комунікація як інструмент підвищення привабливості громади
Комунікація як інструмент підвищення привабливості громади Размещение данных в таблицах в документах HTML5
Размещение данных в таблицах в документах HTML5 Виртуальные машины
Виртуальные машины Файлы. Определение понятий
Файлы. Определение понятий Передача и хранение информации
Передача и хранение информации Спецификация требований к ПО. (Лекция 5)
Спецификация требований к ПО. (Лекция 5) Состояние и перспективы информатизации в Республике Беларусь
Состояние и перспективы информатизации в Республике Беларусь Компьютерный сервис. Комплексные пакеты настроек смартфонов и планшетов
Компьютерный сервис. Комплексные пакеты настроек смартфонов и планшетов B3: Анализ программы Что нужно знать: основные конструкции языка программирования: объявление переменных оператор присваивания
B3: Анализ программы Что нужно знать: основные конструкции языка программирования: объявление переменных оператор присваивания Web-технологии в управлении техническими системами
Web-технологии в управлении техническими системами C# Start урок 2
C# Start урок 2 Электронная почта
Электронная почта Свойства логических операций. Логические элементы
Свойства логических операций. Логические элементы