Содержание
- 2. Lists An ordered group of items Does not need to be the same type Could put
- 3. Methods of Lists List.append(x) adds an item to the end of the list List.extend(L) Extend the
- 4. Examples of other methods a = [66.25, 333, 333, 1, 1234.5] //Defines List print a.count(333), a.count(66.25),
- 5. Using Lists as Stacks The last element added is the first element retrieved To add an
- 6. Using Lists as Queues First element added is the first element retrieved To do this collections.deque
- 7. List Programming Tools Filter(function, sequence) Returns a sequence consisting of the items from the sequence for
- 8. Map Function Map(function, sequence) Calls function(item) for each of the sequence’s items Computes the cube for
- 9. Reduce Function Reduce(function, sequence) Returns a single value constructed by calling the binary function (function) Computes
- 10. The del statement A specific index or range can be deleted
- 11. Tuples Tuple A number of values separated by commas Immutable Cannot assign values to individual items
- 12. Sets An unordered collection with no duplicate elements Basket = [‘apple’, ‘orange’, ‘apple’, ‘pear’] Fruit =
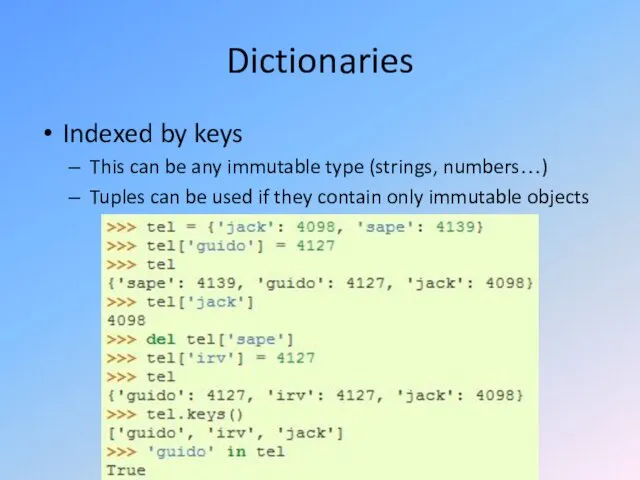
- 13. Dictionaries Indexed by keys This can be any immutable type (strings, numbers…) Tuples can be used
- 14. Looping Techniques Iteritems(): for retrieving key and values through a dictionary
- 15. Looping Techniques Enumerate(): for the position index and values in a sequence
- 16. Zip(): for looping over two or more sequences
- 18. Скачать презентацию


![Examples of other methods a = [66.25, 333, 333, 1, 1234.5]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/478654/slide-3.jpg)











 Всероссийская акция «Час кода»
Всероссийская акция «Час кода» с помощью электронных таблиц OpenOffice.org Calc.
с помощью электронных таблиц OpenOffice.org Calc.  Программные средства информационных технологий управления предприятием
Программные средства информационных технологий управления предприятием Видеокарты Выполнил: Шавензов Денис 2007 год ГОУ ЦО №1861 «Загорье»
Видеокарты Выполнил: Шавензов Денис 2007 год ГОУ ЦО №1861 «Загорье» Презентация Использование современных информационных технологий в сфере профессиональной деятельности
Презентация Использование современных информационных технологий в сфере профессиональной деятельности  Создание и редактирование графических объектов с помощью программ для обработки векторной графики
Создание и редактирование графических объектов с помощью программ для обработки векторной графики Ассемблер
Ассемблер Презентация "Водяные системы охлаждения" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Водяные системы охлаждения" - скачать презентации по Информатике Локальные сети
Локальные сети Развитие вычислительной техники
Развитие вычислительной техники Биты и байты
Биты и байты Управление и манипулирование объектами
Управление и манипулирование объектами НАГЛЯДНЫЕ ФОРМЫ ПРЕДСТАВЛЕНИЯ ИНФОРМАЦИИ
НАГЛЯДНЫЕ ФОРМЫ ПРЕДСТАВЛЕНИЯ ИНФОРМАЦИИ Циклы. Оператор повторения (9 класс)
Циклы. Оператор повторения (9 класс) БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ В СЕТИ ИНТЕРНЕТ
БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ В СЕТИ ИНТЕРНЕТ  Профессиональные сети. Переводческие сайты и форумы
Профессиональные сети. Переводческие сайты и форумы Блок-схема сайта
Блок-схема сайта Безопасность операционных систем (Практическая работа №3)
Безопасность операционных систем (Практическая работа №3) Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления
Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления Новые сервисы 1С ИТС!
Новые сервисы 1С ИТС! Создание ИИС на основе встраиваемых и модульных устройств
Создание ИИС на основе встраиваемых и модульных устройств ЭЛЕКТРОННЫЕ ТАБЛИЦЫ: Общие сведения
ЭЛЕКТРОННЫЕ ТАБЛИЦЫ: Общие сведения Безопасность детей в сети Интернет
Безопасность детей в сети Интернет Recall the concept
Recall the concept лабораторная работа 8(Косач АИ 213)
лабораторная работа 8(Косач АИ 213) Информационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности
Информационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности Разработки Google
Разработки Google Кванториум Scratch. Программирование
Кванториум Scratch. Программирование