Содержание
- 2. Part 1 What Are Web Services? Services are everywhere. Why? Web-services and SOA History of Web-services
- 3. What Are Web Services? “Web service is a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction
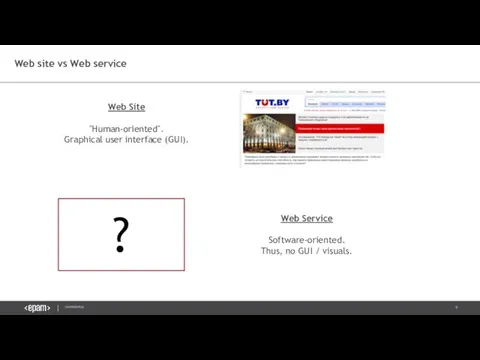
- 4. Web Site "Human-oriented". Graphical user interface (GUI). Web Service Software-oriented. Thus, no GUI / visuals. ?
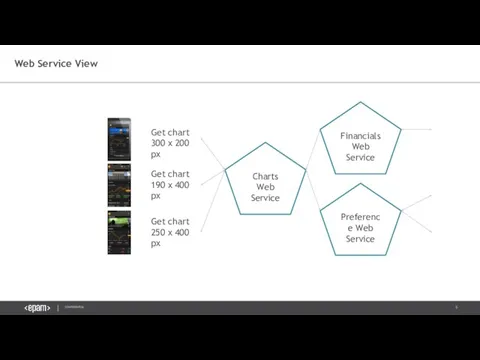
- 5. Web Service View Get chart 190 x 400 px Get chart 300 x 200 px Get
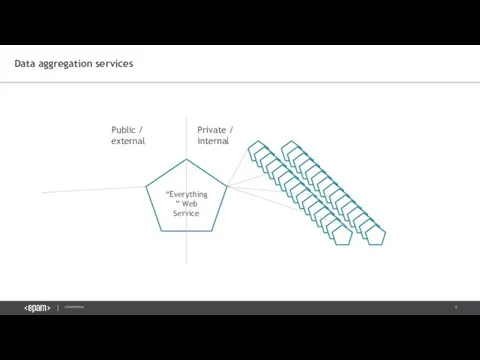
- 6. Data aggregation services “Everything” Web Service Public / external Private / internal
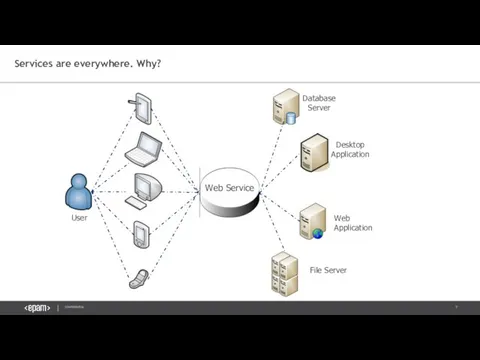
- 7. Services are everywhere. Why? Database Server Desktop Application Web Application User File Server Web Service
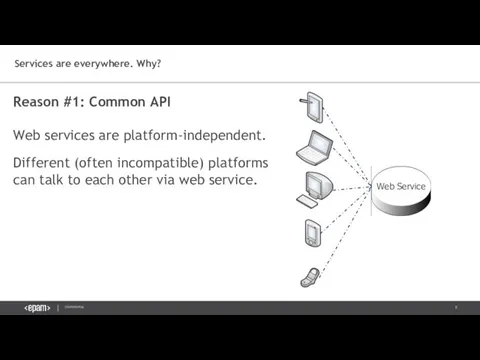
- 8. Reason #1: Common API Web services are platform-independent. Different (often incompatible) platforms can talk to each
- 9. Reason #2: High compatibility Web services often use simple trusted technologies – XML and HTTP. HTTP
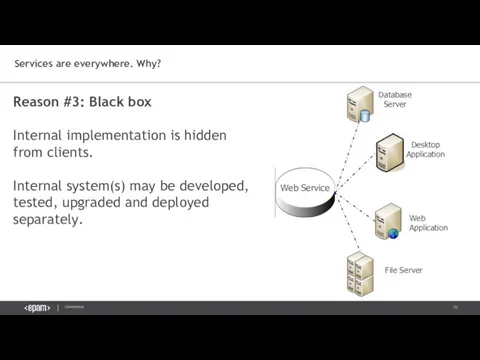
- 10. Reason #3: Black box Internal implementation is hidden from clients. Internal system(s) may be developed, tested,
- 11. Reason #4: Security Web service API defines allowed manipulations. This provides limited access to internal systems.
- 12. Open infrastructure Platform and language transparency Modular design Benefits
- 13. Integrating network-accessible services, which are interoperable because each has an interface that clearly defines the operations
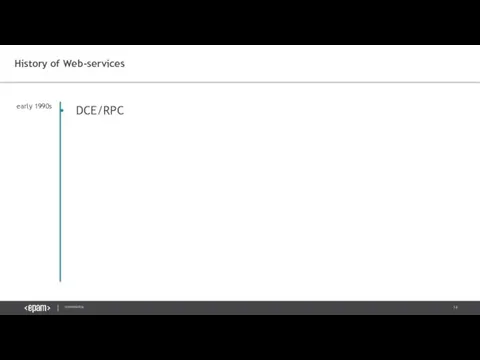
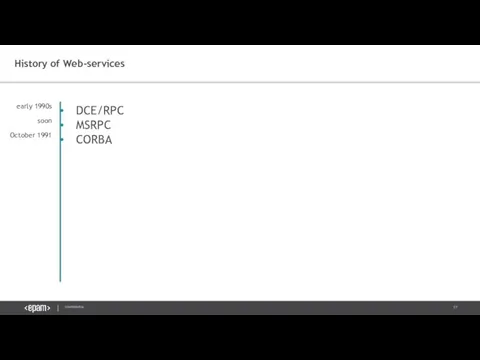
- 14. DCE/RPC History of Web-services early 1990s
- 15. History of Web-services > DCE/RPC > IDL /* echo.idl */ [uuid(2d6ead46-05e3-11ca-7dd1-426909beabcd), version(1.0)] interface echo { const
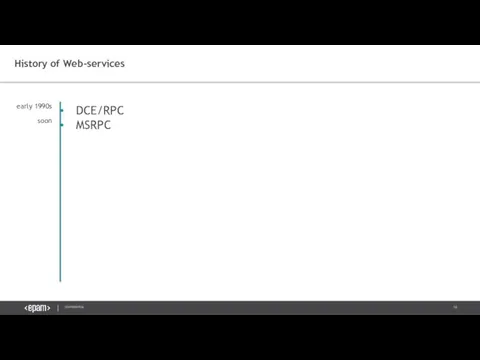
- 16. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC early 1990s soon
- 17. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA early 1990s soon October 1991
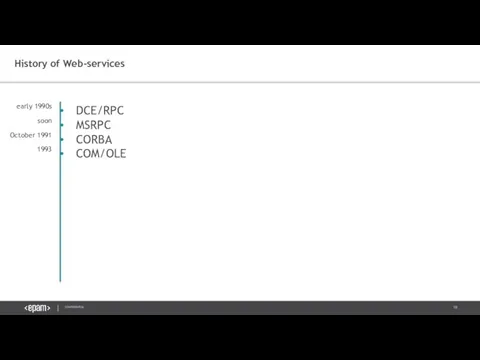
- 18. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE early 1990s soon October 1991 1993
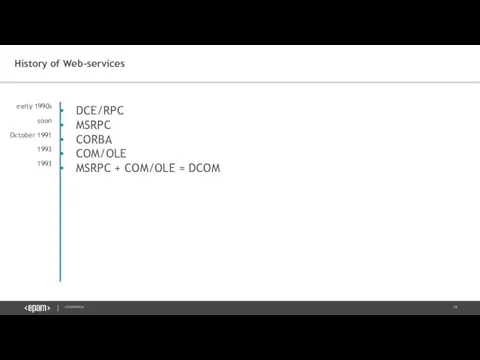
- 19. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE MSRPC + COM/OLE = DCOM early 1990s soon October
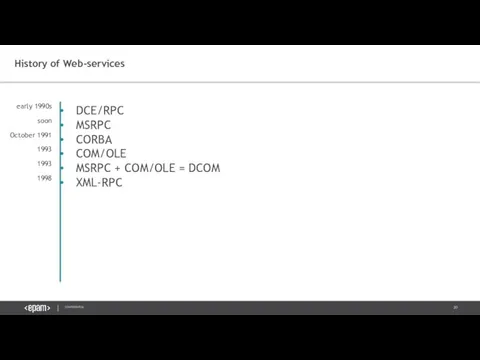
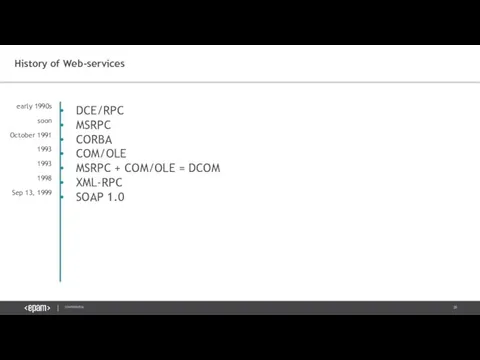
- 20. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE MSRPC + COM/OLE = DCOM XML-RPC early 1990s soon
- 21. History of Web-services > XML-RPC Request stock.getPrice IBM Response 34.5
- 22. History of Web-services > XML-RPC > Datatypes Integer: or Boolean: with value of 0/1 or true/false
- 23. History of Web-services > XML-RPC vs DCE/RPC XML-RPC Text HTTP (later SMTP) DCE/RPC Binary Any other
- 24. Benefits and drawbacks Benefits Robust standard with long history and solid support from nearly all programming
- 25. XML-RPC Demo
- 26. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE MSRPC + COM/OLE = DCOM XML-RPC SOAP 1.0 early
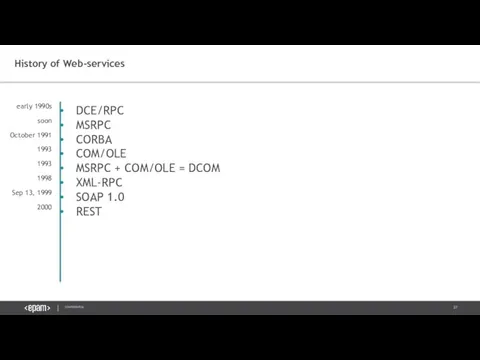
- 27. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE MSRPC + COM/OLE = DCOM XML-RPC SOAP 1.0 REST
- 28. REST Request/Response Example Request POST /stock Host: www.stocks.com Authorization: Basic xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Accept: application/json Content-Length: nnn Content-Type:
- 29. Benefits Can use any encoding (XML, JSON, etc.) Easy and relatively fast implementation Doesn’t require contract
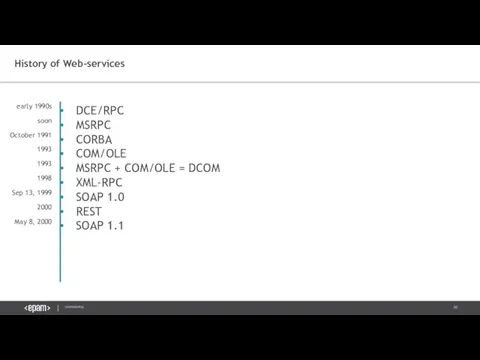
- 30. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE MSRPC + COM/OLE = DCOM XML-RPC SOAP 1.0 REST
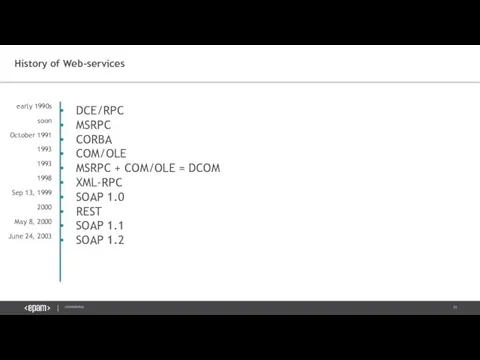
- 31. History of Web-services DCE/RPC MSRPC CORBA COM/OLE MSRPC + COM/OLE = DCOM XML-RPC SOAP 1.0 REST
- 32. SOAP Request/Response Example Request POST /stock HTTP/1.1 Host: www.stocks.org Content-Type: application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8 Content-Length: nnn xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope" soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
- 33. Benefits Robust standard with long history and solid support from nearly all programming languages WSDL allows
- 35. Скачать презентацию
















 Бесконтактные платежи
Бесконтактные платежи Графовые модели программы. Алгоритм оптимизации информационного графа по ширине пи высоте. Лекция 4
Графовые модели программы. Алгоритм оптимизации информационного графа по ширине пи высоте. Лекция 4 Администрирование в OC Astra Linux
Администрирование в OC Astra Linux Файлы и файловая система
Файлы и файловая система Подготовка к итоговой контрольной. (6 класс)
Подготовка к итоговой контрольной. (6 класс) Классификация ПО по способу использования
Классификация ПО по способу использования Проектировка и разработка игры в жанре RPG
Проектировка и разработка игры в жанре RPG Создание Web-страниц на языке HTML
Создание Web-страниц на языке HTML Программирование с использованием строковых переменных
Программирование с использованием строковых переменных Информация и информационные процессы. 11 класс
Информация и информационные процессы. 11 класс Файлдық жүйелер мен ДҚБЖ арасындағы негізгі айырмашылық
Файлдық жүйелер мен ДҚБЖ арасындағы негізгі айырмашылық Роль информации в жизни общества
Роль информации в жизни общества Защита информации в телекоммуникационных системах
Защита информации в телекоммуникационных системах Безопасный интернет. Игра для 7 - 9-х классов
Безопасный интернет. Игра для 7 - 9-х классов Схема компьютера. Взаимодействие устройств компьютера
Схема компьютера. Взаимодействие устройств компьютера Программирование на языках высокого уровня
Программирование на языках высокого уровня Перевод чисел из одной позиционной системы в другую
Перевод чисел из одной позиционной системы в другую Разработка web-сайта для ООО Авангард
Разработка web-сайта для ООО Авангард Система условных знаков для представления информации
Система условных знаков для представления информации Главные правила классической типографики
Главные правила классической типографики Изображения в памяти компьютера
Изображения в памяти компьютера Коаксиальный кабель
Коаксиальный кабель Pascal ABC Модуль GraphABC
Pascal ABC Модуль GraphABC Презентация по информатике Информация и её свойства
Презентация по информатике Информация и её свойства  Измерение информации
Измерение информации Программа Figma
Программа Figma Презентация "Передача информации презентация 5 класс." - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Передача информации презентация 5 класс." - скачать презентации по Информатике Презентация "RHINO 5200" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "RHINO 5200" - скачать презентации по Информатике