Содержание
- 4. In the end, market research is about improving the marketing efforts of business organisations Research Purposes
- 5. Classifying Customers A target market consists of a whole group of potential customers, drawn from the
- 6. Types of specialization 1) concentration of efforts on the same segment 2) selection specialization 3) product
- 7. Why Use Different Methods? Each different method has its advantages and disadvantages Each may only be
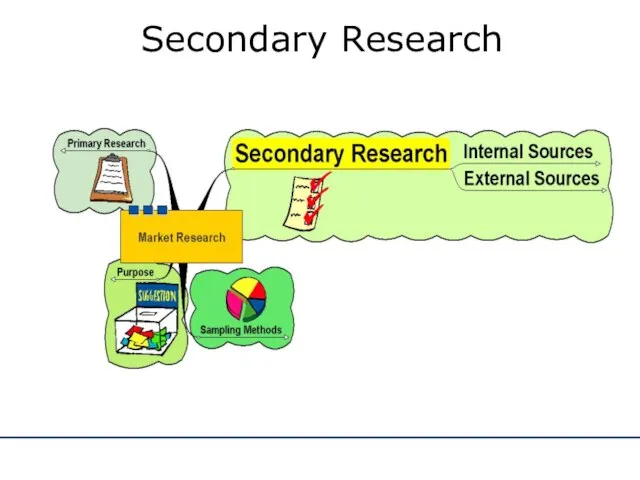
- 8. Secondary Research
- 9. Internal Sources Company Accounts Internal Reports and Analysis Stock Analysis Retail data - loyalty cards, till
- 10. Information sources 1. Literature search Getting hold of all available material on a particular theme. Material
- 12. Primary Research Characteristics - First hand information - Expensive to collect, analyse and evaluate - Can
- 13. Quantitative and Qualitative Information: Quantitative – based on numbers – 56% of 18 year olds drink
- 14. Information sources 2. Talking to people Useful in the early stages Includes meetings with customers and
- 15. Information sources 3. Focus groups These are used to: Explore ideas and attitudes Test new approaches
- 16. Information sources 4. Personal interviews Produce in depth information Are carried out face-to-face Can be very
- 17. Information sources 5. Telephone surveys The fastest way of gathering information, especially from large sample sizes
- 18. Information sources 6. Postal surveys Ideal for large sample sizes If sample covers wide area Generally
- 20. Random (случайная выборка) Samples – equal chance of anyone being picked May select those not in
- 21. Quota Sampling Again – by segment Not randomly selected Specific number on each segment are interviewed,
- 22. Advantages of Market Research Helps focus attention on objectives Aids(помогает) forecasting, planning and strategic development May
- 23. Disadvantages of Market Research Information only as good as the methodology used Can be inaccurate or
- 25. Mix-methodologies - mixed methods research, rather successfully combining the advantages of qualitative and quantitative methods. The
- 27. Скачать презентацию























 Дополнительная гарантия Сервис ДНС
Дополнительная гарантия Сервис ДНС Способы естественного улучшения ПФ
Способы естественного улучшения ПФ Критерии идеи
Критерии идеи Чехлы на iPhone 4/4S
Чехлы на iPhone 4/4S Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqQua
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqQua Морской круиз по Скандинавии из Санкт-Петербурга
Морской круиз по Скандинавии из Санкт-Петербурга Оценка эффективности рекламной деятельности на телевидении
Оценка эффективности рекламной деятельности на телевидении Унікальні умови надання техніки при найбільшій швидкості видачі
Унікальні умови надання техніки при найбільшій швидкості видачі Новогодняя детская программа
Новогодняя детская программа M.A.G. деревянные галстук-бабочки
M.A.G. деревянные галстук-бабочки Шаги к первоклассному сервису
Шаги к первоклассному сервису Каталог-презентация кухонных плит LOFRATELLI-2018
Каталог-презентация кухонных плит LOFRATELLI-2018 Робота з медіа
Робота з медіа Посредники
Посредники Программы развития бизнеса корпорации Сибирское здоровье
Программы развития бизнеса корпорации Сибирское здоровье Sistema di motivazione
Sistema di motivazione Детальніше про новинки К 04/2015
Детальніше про новинки К 04/2015 Товары по уходу за стомой
Товары по уходу за стомой WiMAX. Бизнес модель
WiMAX. Бизнес модель Avon Клуб Премиум
Avon Клуб Премиум Обзор работы системы
Обзор работы системы Kaka delivery service
Kaka delivery service Розробка рекламної поліграфічної продукції для студентського міні-кафе
Розробка рекламної поліграфічної продукції для студентського міні-кафе Дослідження ринку. Маркетинг
Дослідження ринку. Маркетинг Ко-маркетинг
Ко-маркетинг Апарт-отели мира. Туристический ваучер
Апарт-отели мира. Туристический ваучер Интернет-портал Ижсвадьба. Продажа сайта
Интернет-портал Ижсвадьба. Продажа сайта Руководство по работе с сайтом Taobao
Руководство по работе с сайтом Taobao