Содержание
- 2. Multiplication Rule The Multiplication Rule can be used to find the probability of two or more
- 3. Multiplication Rule Tip Find the probability the first event occurs. Find the probability the second event
- 4. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability A coin is tossed and a die is rolled.
- 5. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability A card is drawn from a deck and replaced;
- 6. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability The probability that a salmon swims successfully through a
- 7. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability Two cards are selected from a standard deck without
- 8. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability A Harris poll found the 46% of Americans say
- 9. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability The probability that a salmon swims successfully through a
- 10. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability Find the probability that none of the three salmon
- 11. Using the Multiplication Rule to find Probability Find the probability that at least one of the
- 12. Dependent Events When the outcome or occurrence of the first event affects the outcome or occurrence
- 13. Conditional Probability To find probabilities when events are dependent, use the multiplication rule with a modification
- 14. Finding Conditional Probability Two cards are selected in sequence from a standard deck. Find the probability
- 15. Finding Conditional Probability Three cards are drawn from an ordinary deck and not replaced. Find the
- 16. Finding Conditional Probability The table at the left shows the results of a study in which
- 18. Скачать презентацию















 Презентация по математике "Интегралы в решении практических задач и профильной направленности" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "Интегралы в решении практических задач и профильной направленности" - скачать бесплатно Сложение отрицательных чисел. Кроссворд
Сложение отрицательных чисел. Кроссворд Factorising Quadratics
Factorising Quadratics Сумма и произведение вероятностей
Сумма и произведение вероятностей Урок математики 3 класс УМК «Перспективная начальная школа»
Урок математики 3 класс УМК «Перспективная начальная школа» Экономико-математическое моделирование
Экономико-математическое моделирование Конкурс Знатоков квадратичной функции
Конкурс Знатоков квадратичной функции Способы быстрого счета
Способы быстрого счета Сабақтың тақырыбы: Дискреттік математика негіздері. Лекция 2
Сабақтың тақырыбы: Дискреттік математика негіздері. Лекция 2 Основные теоремы теории вероятностей
Основные теоремы теории вероятностей Алгебра прогрессии
Алгебра прогрессии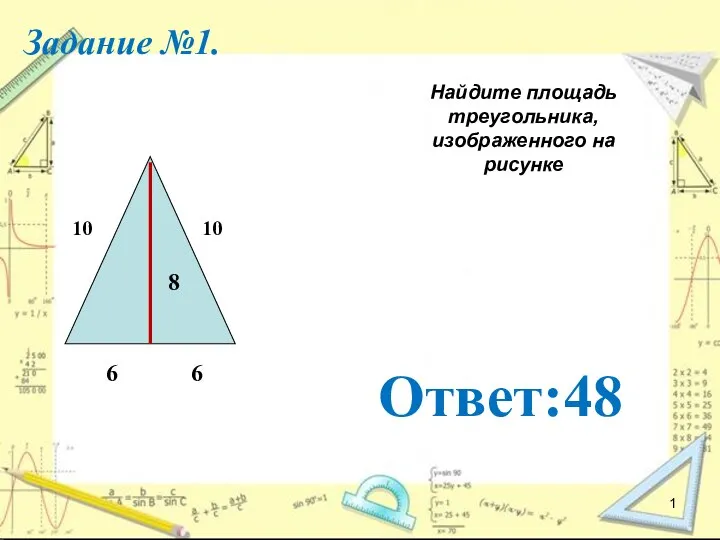 Площадь прямоугольника. Решение задач
Площадь прямоугольника. Решение задач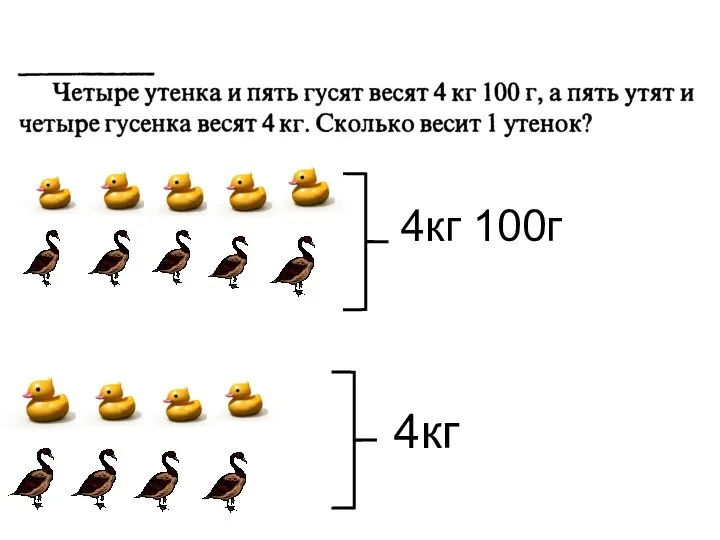 Уравнение. Задача на определение веса
Уравнение. Задача на определение веса Тест. Задания В10, ЕГЭ по математике
Тест. Задания В10, ЕГЭ по математике Теория кривых. Репер Френе
Теория кривых. Репер Френе Повторение. 10 класс. Геометрия
Повторение. 10 класс. Геометрия Учитель математики МОУ «СОШ №4» города Новочебоксарска Чувашской Республики Шарова Валентина Степановна
Учитель математики МОУ «СОШ №4» города Новочебоксарска Чувашской Республики Шарова Валентина Степановна Занимательные задачи по математике Выполнили: Баринова Катя Крылова Света Галкина Лера 7А класс
Занимательные задачи по математике Выполнили: Баринова Катя Крылова Света Галкина Лера 7А класс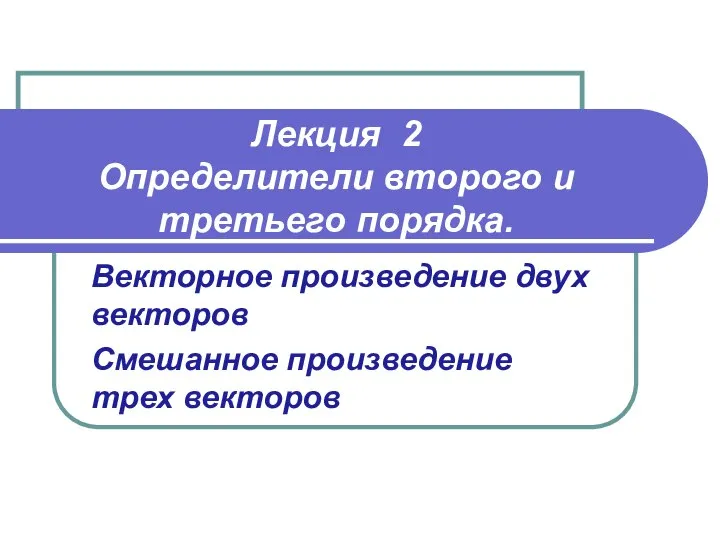 Определители второго и третьего порядка. (Лекция 2)
Определители второго и третьего порядка. (Лекция 2) Примеры расчета матриц
Примеры расчета матриц Длина окружности и площадь круга
Длина окружности и площадь круга Действие деления
Действие деления Движение в пространстве. Виды движения. Симметрия
Движение в пространстве. Виды движения. Симметрия Второй признак равенства треугольников
Второй признак равенства треугольников Функции у = sin x и y = cos x и их свойства и графики
Функции у = sin x и y = cos x и их свойства и графики Повторение. Алгебра 9 класс (урок 1)
Повторение. Алгебра 9 класс (урок 1) Корреляция. Причинность. Детерминизм
Корреляция. Причинность. Детерминизм Способы решений уравнений и неравенств с параметром
Способы решений уравнений и неравенств с параметром