Содержание
- 2. Linear Equation is the equation in which Variables are multiplied by constants and summed No variables
- 3. Linear equation in two variables x and y describes the straight line on the xy-plane
- 4. Parallel and perpendicular Two straight lines with slopes m1 and m2 are parallel if m1=m2. Two
- 5. Applications to business and economics
- 6. Linear Cost Model Linear Cost Model Total Costs = Variable Costs + Fixed Costs depend on
- 7. Break-even Analysis If TC > TR a loss If TC If TC = TR no loss
- 8. Supply and Demand Law of Supply - a relation specifying the amount of any commodity that
- 10. Скачать презентацию







 В царстве смекалки
В царстве смекалки Правильные и неправильные дроби
Правильные и неправильные дроби Трапеция. Свойства трапеции. Геометрия, 7 класс
Трапеция. Свойства трапеции. Геометрия, 7 класс Взаимное пересечение поверхностей
Взаимное пересечение поверхностей Четные и нечетные числа
Четные и нечетные числа Равные множества. (1 класс)
Равные множества. (1 класс) Сделай изучение обыкновенных дробей увлекательным делом.
Сделай изучение обыкновенных дробей увлекательным делом. Площади многоугольников
Площади многоугольников Параллельность прямых
Параллельность прямых Объём усечённого конуса
Объём усечённого конуса Потенциальная яма в импульсном представлении
Потенциальная яма в импульсном представлении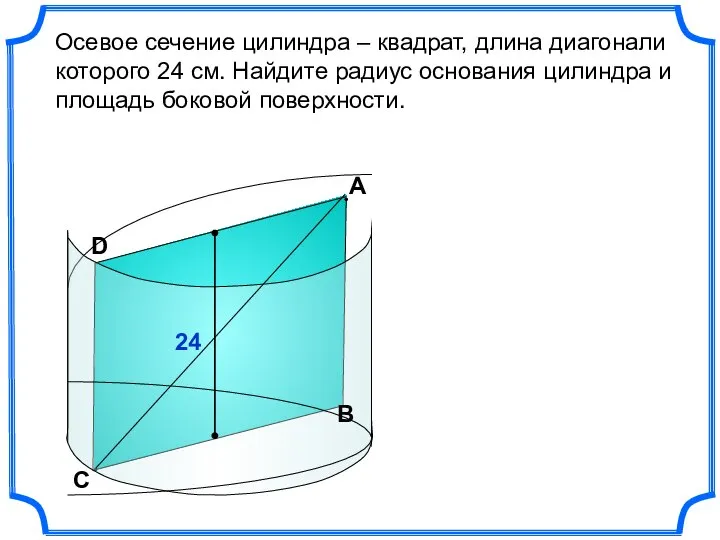 Осевое сечение цилиндра
Осевое сечение цилиндра Удобно для ЕГЭ, ГИА
Удобно для ЕГЭ, ГИА  Преобразование временных рядов в последовательности гистограмм как метод получения космофизической информации
Преобразование временных рядов в последовательности гистограмм как метод получения космофизической информации Математическая индукция
Математическая индукция Задачи на построение сечений
Задачи на построение сечений Решение задач на составление уравнений
Решение задач на составление уравнений Вводные задачи 1)Разность двух целых чисел умножили на их произведение могло ли получится число 4263267871? Ответ: нет 1.(ч-ч)чч=ч; 2
Вводные задачи 1)Разность двух целых чисел умножили на их произведение могло ли получится число 4263267871? Ответ: нет 1.(ч-ч)чч=ч; 2 Способы сложения
Способы сложения Деление обыкновенных дробей
Деление обыкновенных дробей Решение прикладных стереометрия задач. Урок №2. 10 класс
Решение прикладных стереометрия задач. Урок №2. 10 класс Решение систем уравнений
Решение систем уравнений Окружность и круг
Окружность и круг Виды треугольников и применение их в жизни
Виды треугольников и применение их в жизни Готовимся к контрольной работе Учитель МОУ лицей №1: Бугаёва Н.И. г. Цимлянск, Ростовская область
Готовимся к контрольной работе Учитель МОУ лицей №1: Бугаёва Н.И. г. Цимлянск, Ростовская область Предел функции. Вычисление пределов рациональных и дробно-рациональных функций
Предел функции. Вычисление пределов рациональных и дробно-рациональных функций Свойства степени с натуральным показателем. Основание степени, показатель степени , степень
Свойства степени с натуральным показателем. Основание степени, показатель степени , степень Треугольники. Пространственные фигуры, состоящие из треугольников
Треугольники. Пространственные фигуры, состоящие из треугольников