Содержание
- 2. Plan: Epistaxis Classification Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical manefestations Diagnosis Differential diagnosis Emergency care Conclusion Bibliography
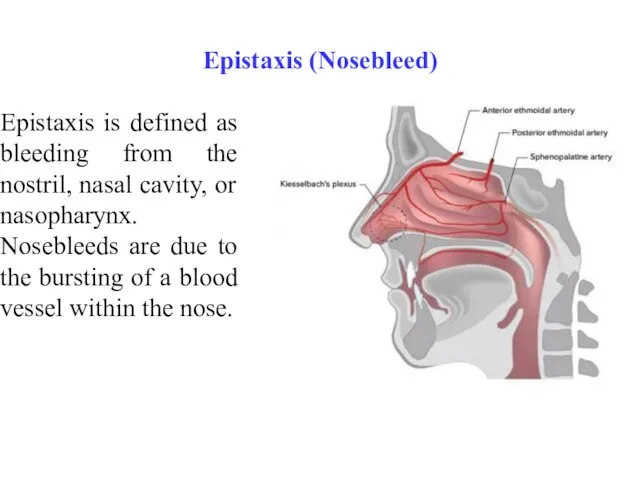
- 3. Epistaxis (Nosebleed) Epistaxis is defined as bleeding from the nostril, nasal cavity, or nasopharynx. Nosebleeds are
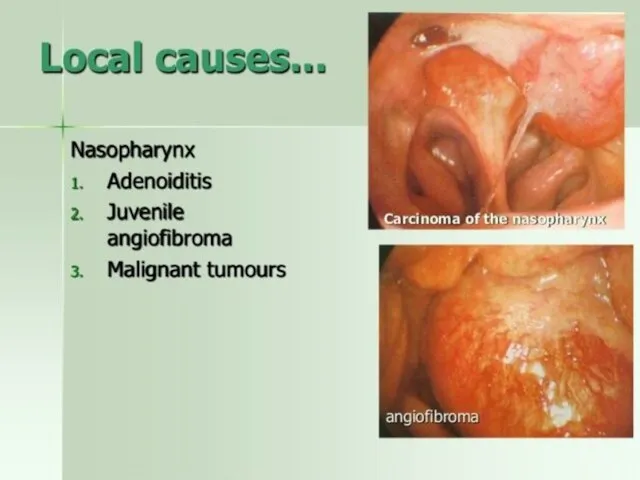
- 6. Classification of epistaxis by location; by frequency of occurrence (recurrent, which is repeated intermittently; sporadic, rarely
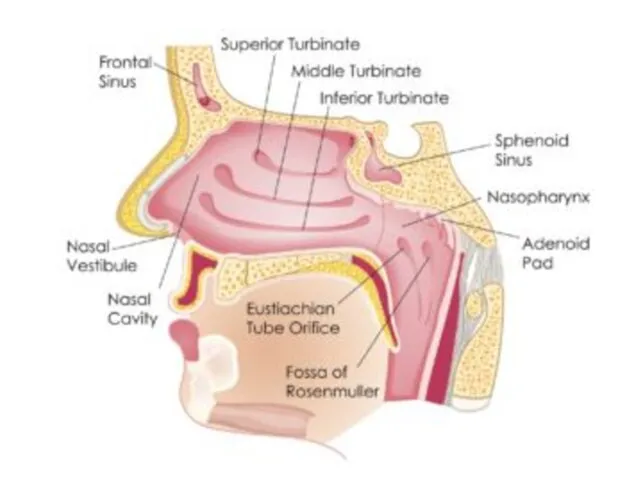
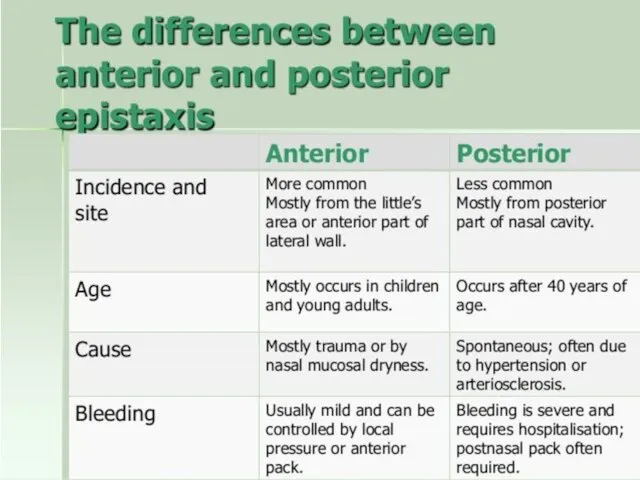
- 7. By location: Anterior epistaxis Posterior epstaxis unilateral bleeding bilateral bleeding
- 9. By mechanism of manifestation: Capillary (with damage to shallow surface vessels); Venous (with ruptured veins of
- 10. By quantity of lost blood: slight bleeding, blood volume at which is not more than 70-100
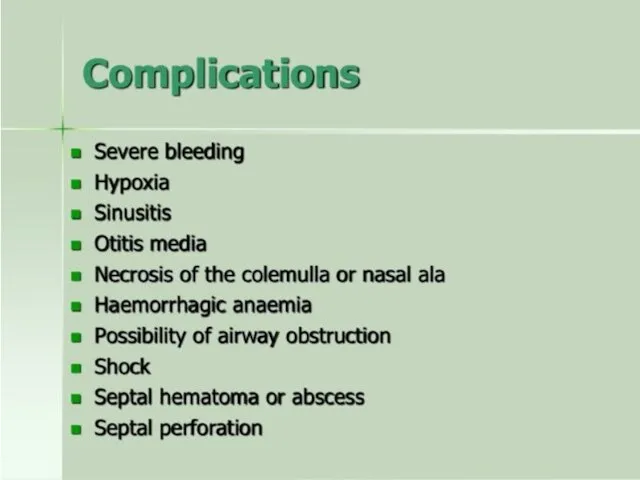
- 27. Differential diagnosis: Disseminated intravascular coagulation; Hemophilia; Von Willebrand disease; Toxicity (aspirin, warfarin, cocaine, coumarine poisoning); Nasal
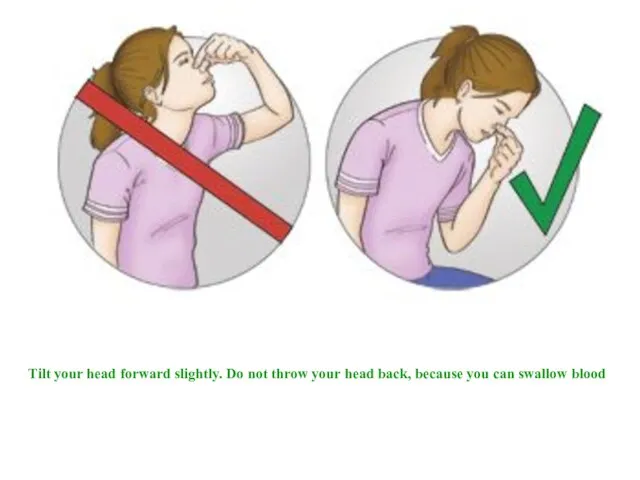
- 29. Tilt your head forward slightly. Do not throw your head back, because you can swallow blood
- 30. Conclusion: In conclusion, epistaxis or the common nosebleed may look frightening and may even cause a
- 32. Скачать презентацию






















 Современные принципы терапии дисфункциональных расстройств билиарного тракта
Современные принципы терапии дисфункциональных расстройств билиарного тракта Факторы, влияющие на здоровье человека
Факторы, влияющие на здоровье человека Дифференциальный диагноз заболеваний, сопровождающихся синдромом экзантемы
Дифференциальный диагноз заболеваний, сопровождающихся синдромом экзантемы Основные патоморфологические аспекты развития миксомы сердца
Основные патоморфологические аспекты развития миксомы сердца Противотуберкулезные и противосифилитические препараты
Противотуберкулезные и противосифилитические препараты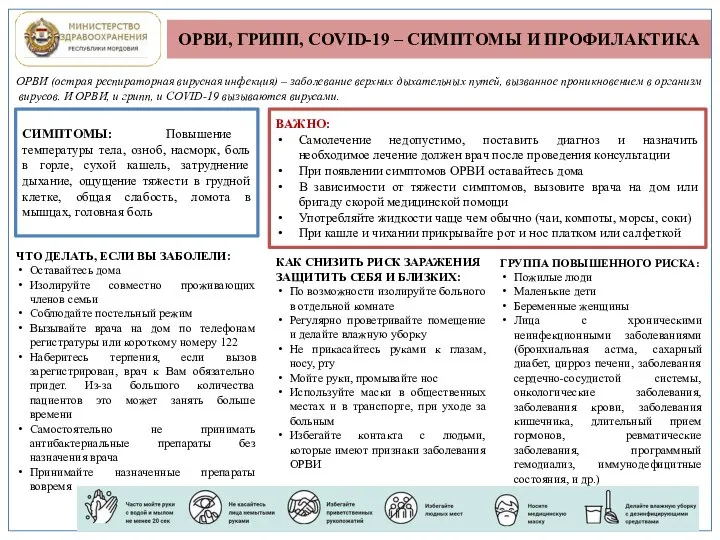 ОРВИ, грипп, covid-19 – симптомы и профилактика
ОРВИ, грипп, covid-19 – симптомы и профилактика Паразиты в организме человека
Паразиты в организме человека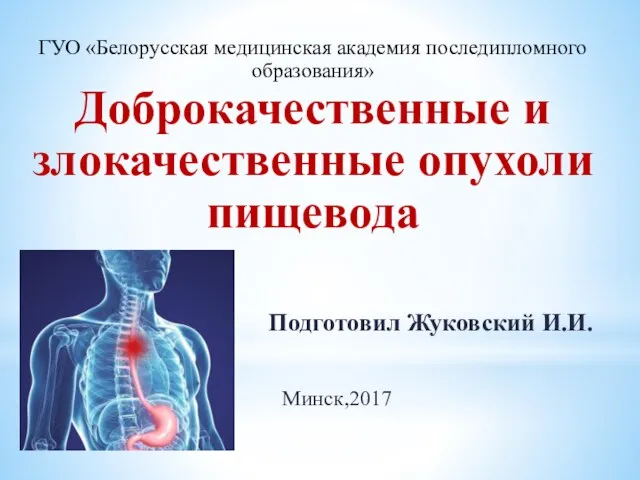 Опухоли пищевода
Опухоли пищевода Болезни, передаваемые половым путём. Меры профилактики. СПИД и его профилактика
Болезни, передаваемые половым путём. Меры профилактики. СПИД и его профилактика Сердечно-легочная реанимация
Сердечно-легочная реанимация Обморок. Коллапс. Шок
Обморок. Коллапс. Шок Оперативті хирургиялық техниканың заманауи инструменттерінің негіздері
Оперативті хирургиялық техниканың заманауи инструменттерінің негіздері Травмы костей черепа и грудной клетки
Травмы костей черепа и грудной клетки Переношенная беременность
Переношенная беременность Адреногенитальный синдром
Адреногенитальный синдром Шытырман есеп: «Жақ остеомилиті»
Шытырман есеп: «Жақ остеомилиті» Реабилитация и социальная защита инвалидов
Реабилитация и социальная защита инвалидов Основы психологического анализа конфликтов
Основы психологического анализа конфликтов Molisan Лосьон
Molisan Лосьон Paura kauls os parietale
Paura kauls os parietale Общая характеристика нарушений опорно-двигательного аппарата. Детский церебральный паралич
Общая характеристика нарушений опорно-двигательного аппарата. Детский церебральный паралич Кожа – самый большой орган нашего организма
Кожа – самый большой орган нашего организма Микроэлементозы человека. Биогеохимические провинции. Эндемические заболевания центрального черноземья
Микроэлементозы человека. Биогеохимические провинции. Эндемические заболевания центрального черноземья Экстрапирамидная система
Экстрапирамидная система Врачевание эпохи европейского Возрождения ( XIV –XVII вв.)
Врачевание эпохи европейского Возрождения ( XIV –XVII вв.) Чистота залог здоровья
Чистота залог здоровья Регенерация как общее свойство живых организмов
Регенерация как общее свойство живых организмов Средства, влияющие на сердечно - сосудистую систему. Лекция №13
Средства, влияющие на сердечно - сосудистую систему. Лекция №13