Содержание
- 2. 1953 - В.Массхофф and В.Кнапп detected of the pathogen P.Т. at a mesadenitis for man (
- 3. Etiology: The pathogen has 0.8 - 2 microns of length and 0.6 – 0.8 microns of
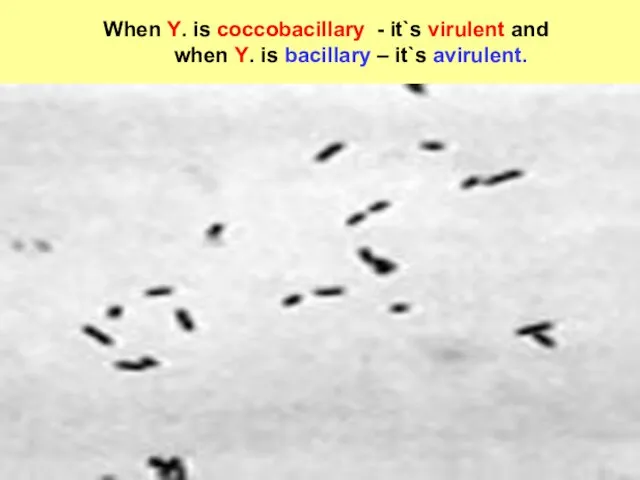
- 4. When Y. is coccobacillary - it`s virulent and when Y. is bacillary – it`s avirulent.
- 5. They have O , Н ,V and W antigenes. On O antigene all pathogens are distributed
- 6. Toxinoformation – the endotoxin become frees only at bacteria destraction. The endotoxin Y. - has expressed
- 7. The mechanism of infection - faecal-oral Transmission has usually traced to contact with infected animals (
- 9. Susceptibility general, but children are sick more often especially in the closed collectives ( have common
- 10. 2. Y. reach a terminal portion of a small intestine, pass through an epithelium up to
- 11. 4. Diarrhea, which frequently develops at Y. has secretory character, being by a consequence of activation
- 12. 7. At an incompetence of immunity Y. will penetrate in blood- stream and are carried on
- 13. 8. The long-lived finding in a blood and tissues Y. results in various autoimmune processes, frequently
- 14. More probably all Y. is "caused" by these diaseases, enlarging autoantibodyformation! 9. The liberation of an
- 15. The clinical forms of manifestation of diseases: PT Y - gastrointestinal Seldom + - abdominal +
- 16. Clinicalal manifestations gastrointestinal form: For Y. and PT. is characteristic cyclic of current and polymorphism of
- 17. - bring down or absence of appetite - weakness, malaise, headache and muscle pains, insomnia, OBJECTIVE:
- 19. - there is a punctate rash on a skin flexions of extremities and side part of
- 21. - at a palpation of a abdomen- murmur both painfulness in mesogastrium and hypogastrium (on the
- 23. The abdominal: - pain in the right half of abdomen - moderate watery diarrhea up to
- 24. Appendicular: Differs from clinic acute catarrhal of an appendicitis with signs of an acute mesadenitis a
- 25. arthralgial The main clinic signs this form are a damage of a locomotory apparatus ( arthralgia
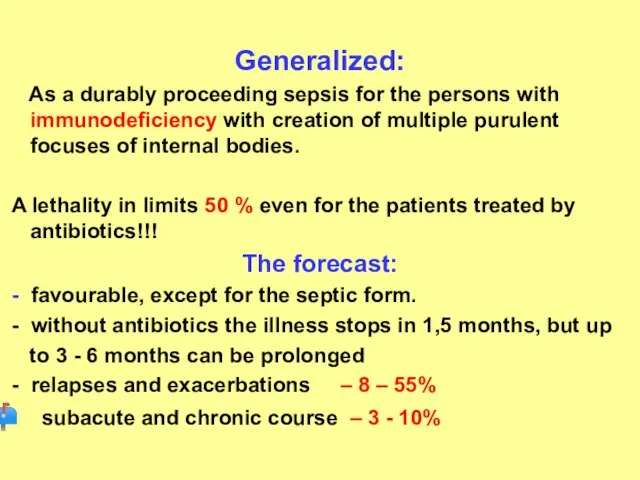
- 26. Generalized: As a durably proceeding sepsis for the persons with immunodeficiency with creation of multiple purulent
- 27. Complications: myocarditis hepatitis cholecystitis pancreatitis appendicitis Intestinal obstruction Intestinal perforation peritonitis glomerulonephritis meningoencephalitis etc.
- 28. Differential diagnosis: Scarlet fever Acute intestinal diseases Acute respiratory diseases Rheumatic disease, polyarthritis, Virus hepatitises Adnexitis,
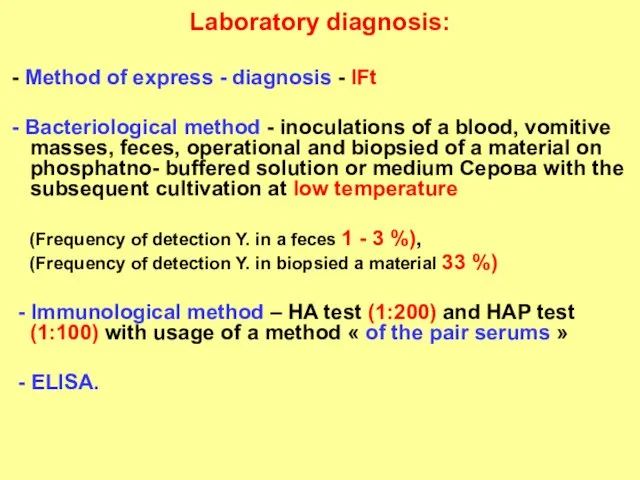
- 29. Laboratory diagnosis: - Method of express - diagnosis - IFt - Bacteriological method - inoculations of
- 30. Treatment: Antiinfectious therapy : - ciprofloxacin 0,5 gr or norfloxacin 0,4 gr PO q12h - doxycycline
- 31. - detoxication therapy - antihistamine drugs - antiinflammatory therapy - surgical treatment + antiinfectious drugs -
- 33. Скачать презентацию



























 Нейровизуализация
Нейровизуализация Современные методы молекулярно-генетической диагностики туберкулёза
Современные методы молекулярно-генетической диагностики туберкулёза Эпидемический паротит. Вирусная инфекция с поражением экзокринных желез
Эпидемический паротит. Вирусная инфекция с поражением экзокринных желез ВИЧ/СПИД
ВИЧ/СПИД Проблема классификация мотивов в психологии
Проблема классификация мотивов в психологии Нейроинфекции. Серозный, гнойный менингиты. Менингококковая инфекция
Нейроинфекции. Серозный, гнойный менингиты. Менингококковая инфекция Коронавирус. Что нужно знать
Коронавирус. Что нужно знать Нарушения ритма сердца и проводимости у детей
Нарушения ритма сердца и проводимости у детей Всемирный день зрения
Всемирный день зрения Компенсаторно-приспособительные процессы
Компенсаторно-приспособительные процессы Семиотика поражений костной системы у детей
Семиотика поражений костной системы у детей Патология щитовидной железы у детей
Патология щитовидной железы у детей Преэклампсия. Факторы риска
Преэклампсия. Факторы риска Ранение сердца - клинический случай
Ранение сердца - клинический случай Понятие первичного образа, образа представления, перцептивного образа, бессознательных умозаключений. Теория восприятия
Понятие первичного образа, образа представления, перцептивного образа, бессознательных умозаключений. Теория восприятия Вредные факторы, влияющие на состояние здоровья людей, работающих за компьютером
Вредные факторы, влияющие на состояние здоровья людей, работающих за компьютером Диабетическая нефропатия
Диабетическая нефропатия Консультирование истерических личностей
Консультирование истерических личностей Синдром Ангельмана
Синдром Ангельмана Предраковые состояния и злокачественные опухоли эпидермиса
Предраковые состояния и злокачественные опухоли эпидермиса Сестринский уход за пациентами после венэктомии
Сестринский уход за пациентами после венэктомии Характеристика бета-адреноблокаторов. Альфа-1-адренергические блокаторы
Характеристика бета-адреноблокаторов. Альфа-1-адренергические блокаторы Поражение почек при алкоголизме
Поражение почек при алкоголизме Синдром Бругада
Синдром Бругада Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии. Современные подходы к диагностике и лечению
Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии. Современные подходы к диагностике и лечению О ВИЧ-инфекции нужно знать
О ВИЧ-инфекции нужно знать Ферментопатии (энзимопатии)
Ферментопатии (энзимопатии) Психологические предпосылки наркотизации подростков
Психологические предпосылки наркотизации подростков