Содержание
- 2. China’s Health Care System Public Health in China I will discuss…
- 3. Basic Statistics/Economic status System overview Who pay for health services? Government’s health policies China and its
- 4. Area: 9.6 million km2 Total population: 1.27 billion (2000) Population in rural areas: 63.8% Administrative Region:
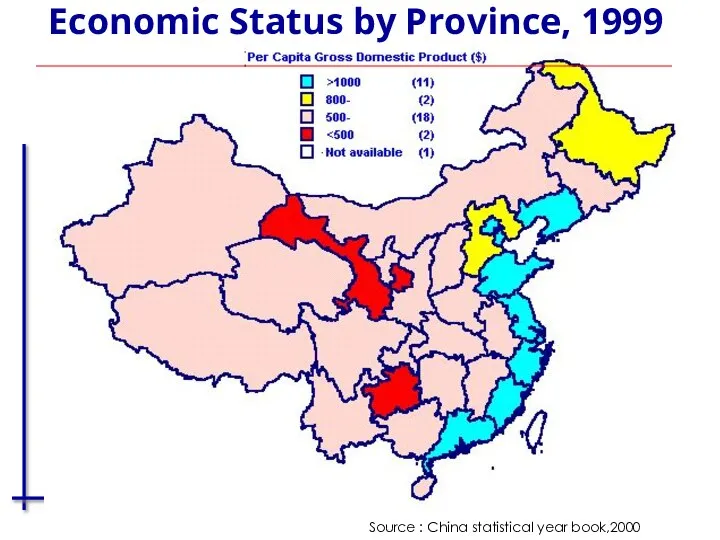
- 5. Economic Status by Province, 1999 Source : China statistical year book,2000
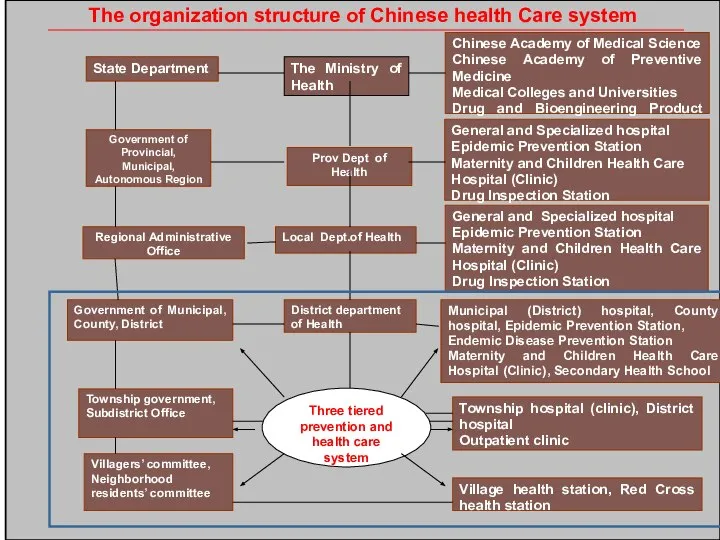
- 6. Health Care System
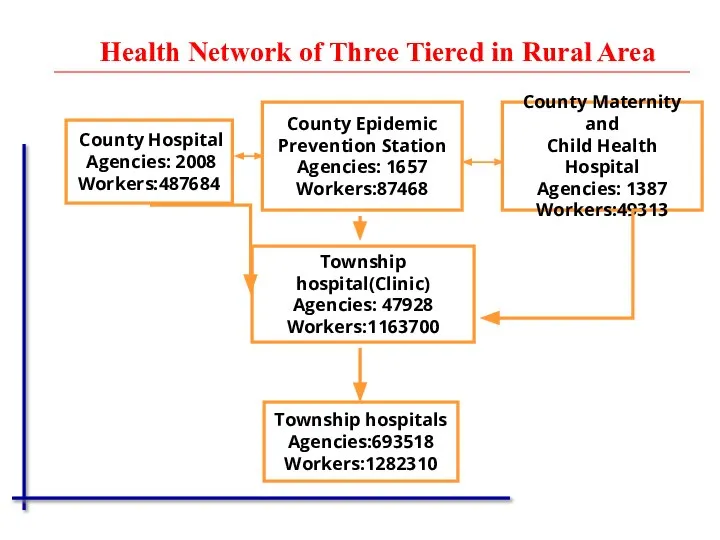
- 7. County Hospital Agencies: 2008 Workers:487684 Township hospital(Clinic) Agencies: 47928 Workers:1163700 County Maternity and Child Health Hospital
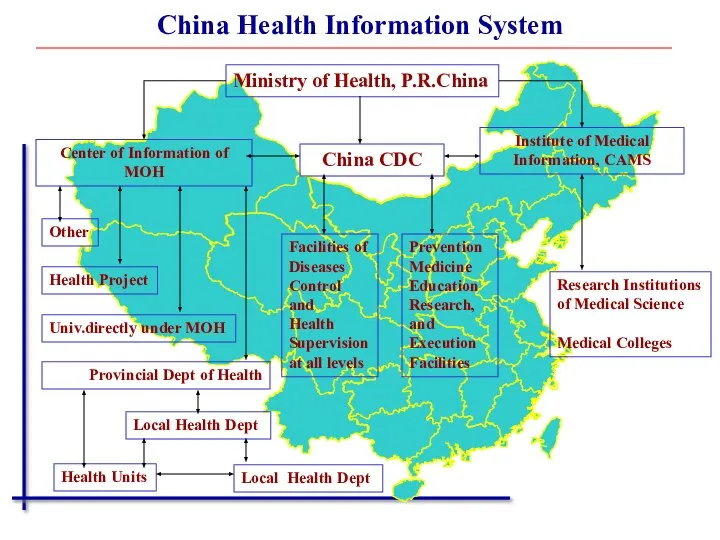
- 8. China Health Information System Ministry of Health, P.R.China China CDC Center of Information of MOH Institute
- 9. Who pay for health services ? 1949-1977 free health services for the entire urban population, government
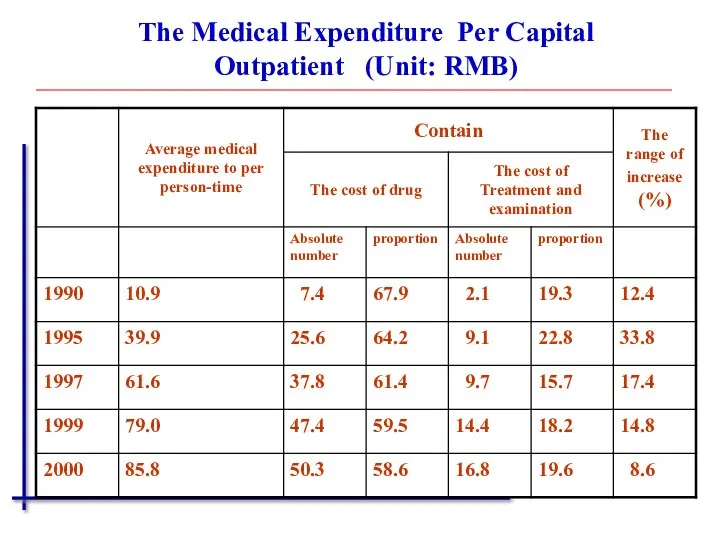
- 10. The Medical Expenditure Per Capital Outpatient (Unit: RMB)
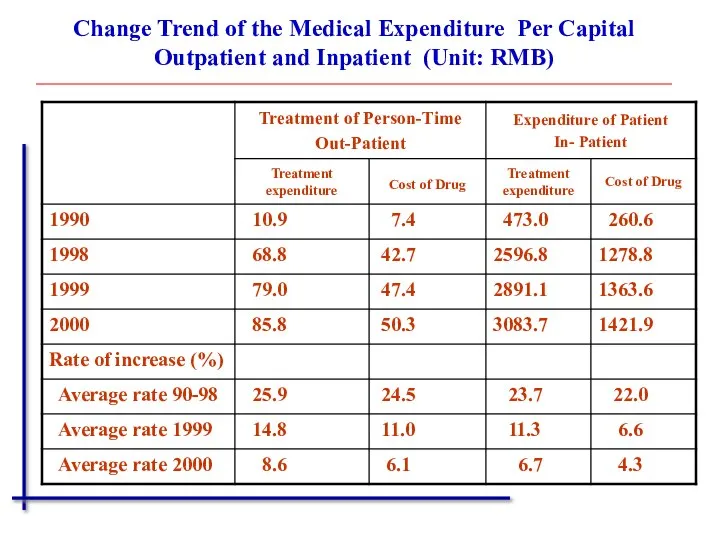
- 11. Change Trend of the Medical Expenditure Per Capital Outpatient and Inpatient (Unit: RMB)
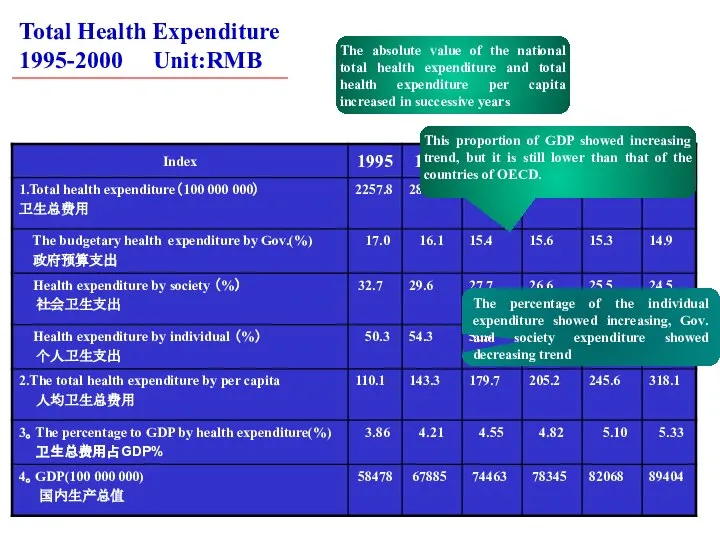
- 12. Total Health Expenditure 1995-2000 Unit:RMB The absolute value of the national total health expenditure and total
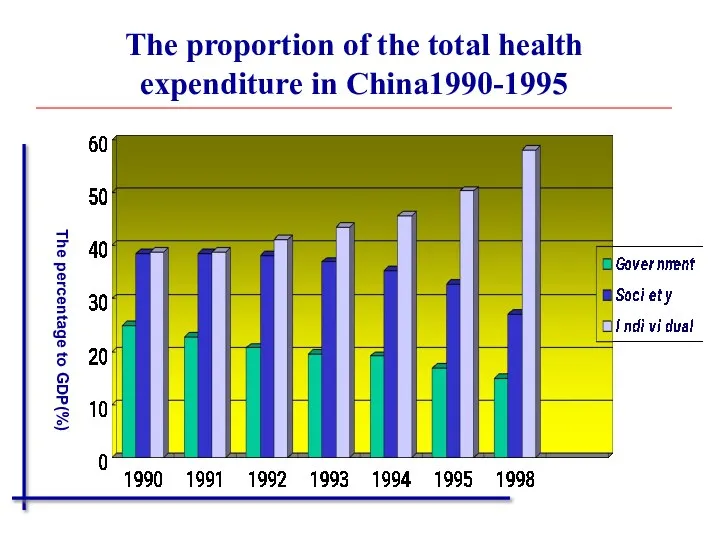
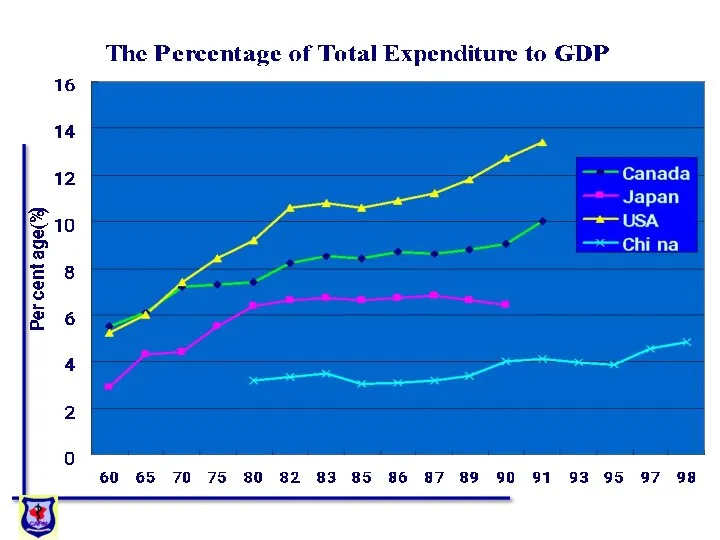
- 13. The proportion of the total health expenditure in China1990-1995 The percentage to GDP(%)
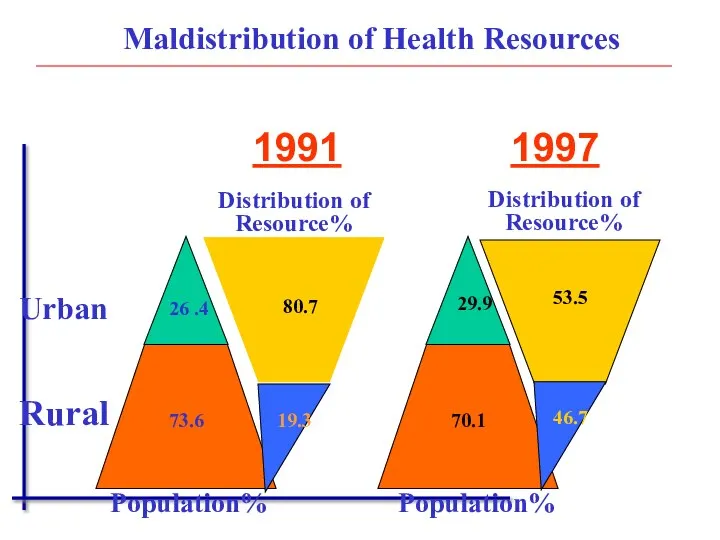
- 14. Maldistribution of Health Resources
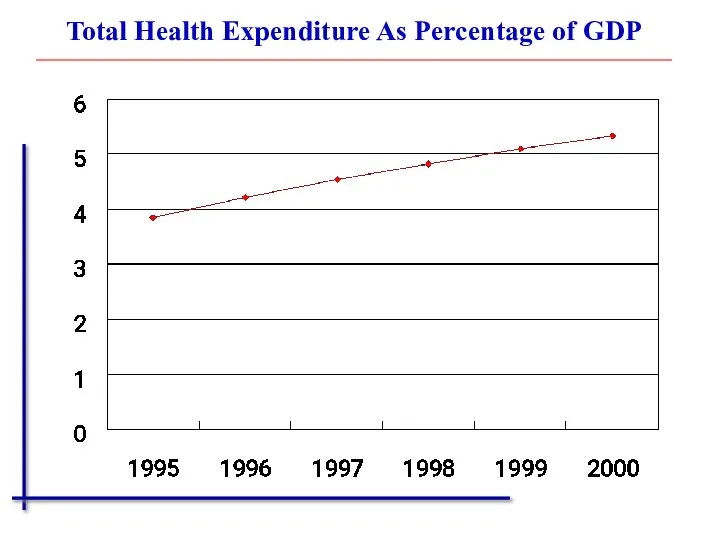
- 15. Total Health Expenditure As Percentage of GDP
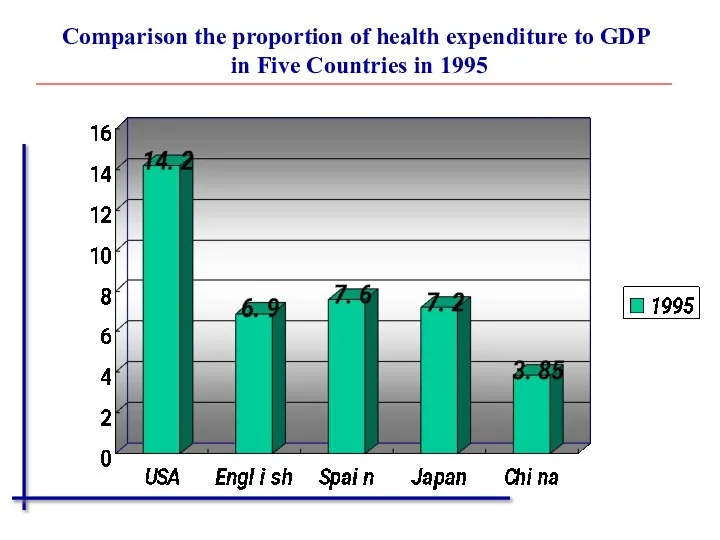
- 17. Comparison the proportion of health expenditure to GDP in Five Countries in 1995
- 18. Health Policy in China(1950s) Meet health needs of the workers, peasants and soldiers Put the prevention
- 19. Health Policy in China(1980s) Put the prevention first Rely on the advanced scientific progress Mobilize the
- 20. Health Policy in China(2000s) --The 1996 Health Meeting of China’s Central Gov. Emphasize on the health
- 21. History of Public Health Public Health Achievements Public Health Challenges Public Health in China
- 22. Brief History of PH in China Before the Eighteenth Century The Eighteenth –Nineteenth Century The 20s-30s
- 23. Brief History of PH in China --before of the eighteenth century The Yellow Emperor’ s Canon
- 24. Book on epidemic febrile diseases Experience of diagnosing and treating Western(modern) medicine into China in 1830s,
- 25. The western medical hospital in China, represented by Peking Union Medical College Hospital The first Department
- 26. Coping the public health system of the former Soviet Union in 1950s Setting up an anti-epidemic
- 27. The great sanitary awakening Preventing acute infectious diseases Health education Free basic immunization Established three-tiered PHC
- 28. The rapid development of public health in China reform and open policy development of science and
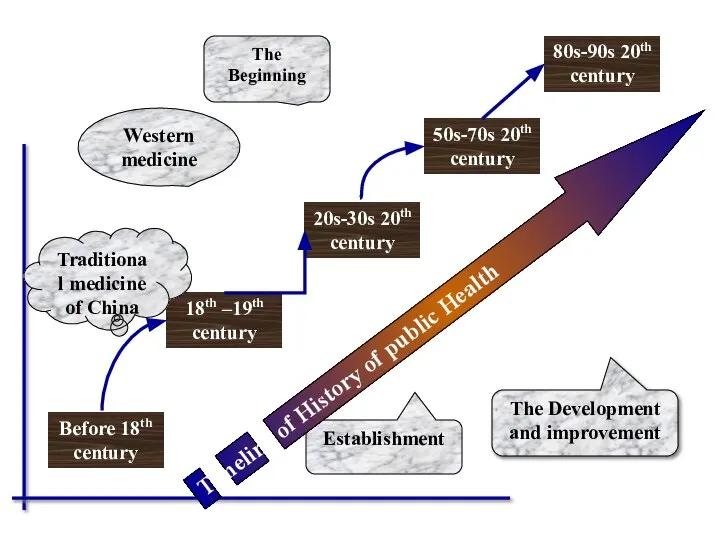
- 29. The Development and improvement Establishment Before 18th century 18th –19th century 20s-30s 20th century 50s-70s 20th
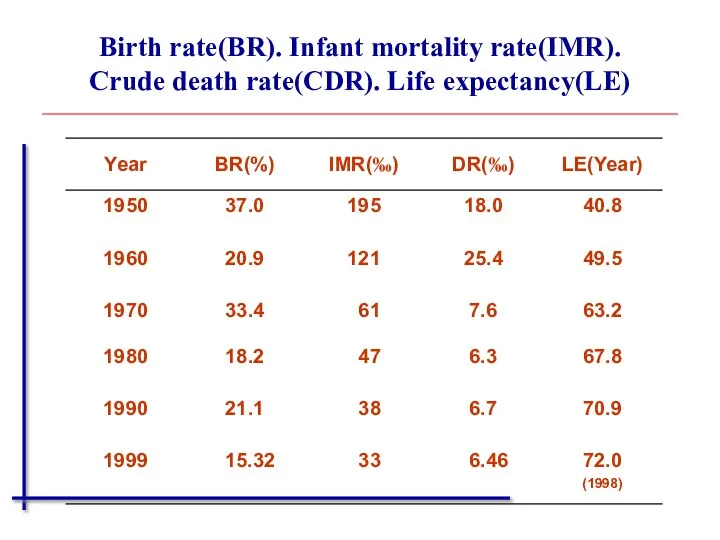
- 30. Birth rate(BR). Infant mortality rate(IMR). Crude death rate(CDR). Life expectancy(LE)
- 31. Leading Causes of Death
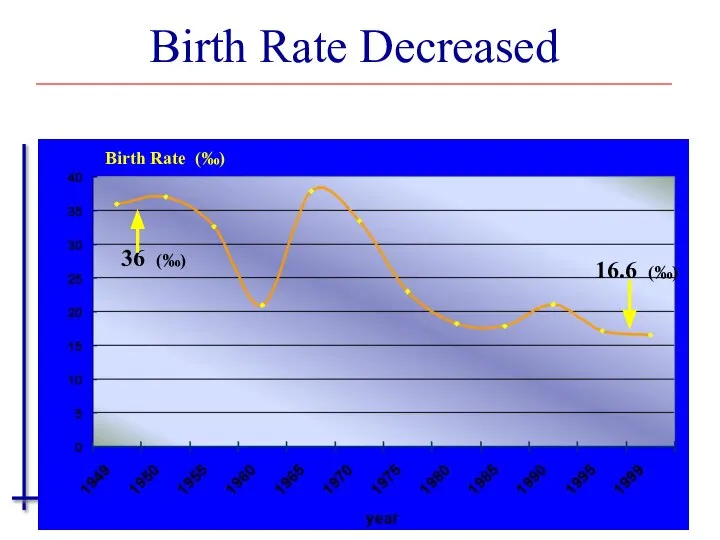
- 32. Birth Rate (‰) Birth Rate Decreased
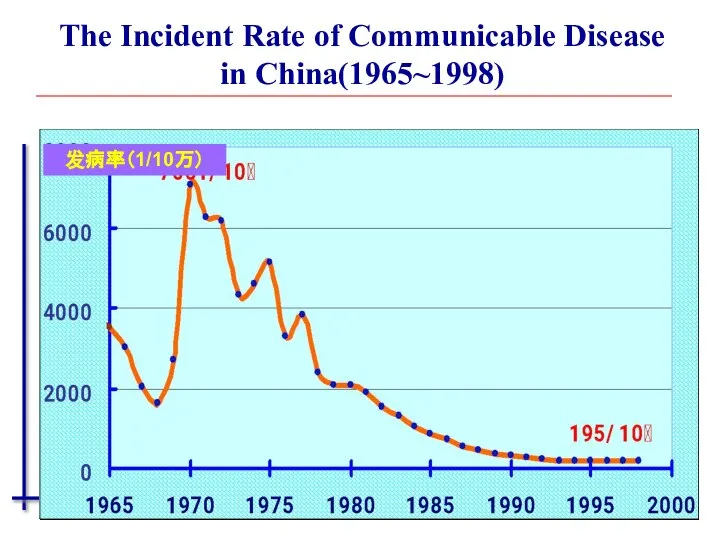
- 33. The Incident Rate of Communicable Disease in China(1965~1998) 发病率(1/10万)
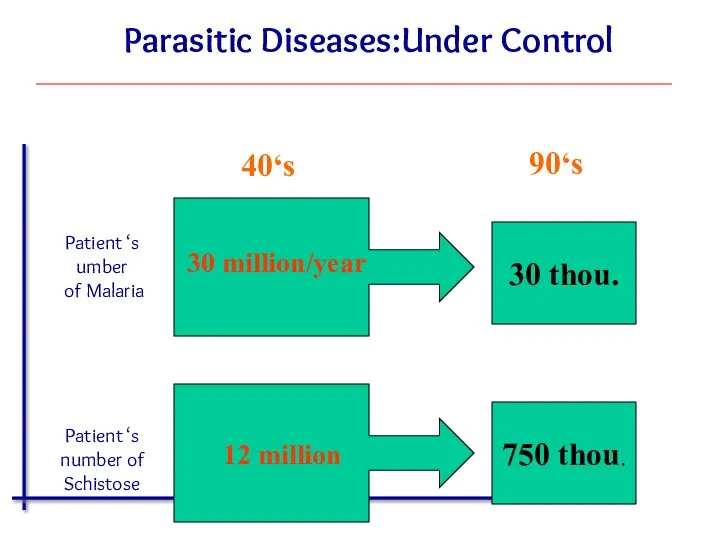
- 34. Parasitic Diseases:Under Control
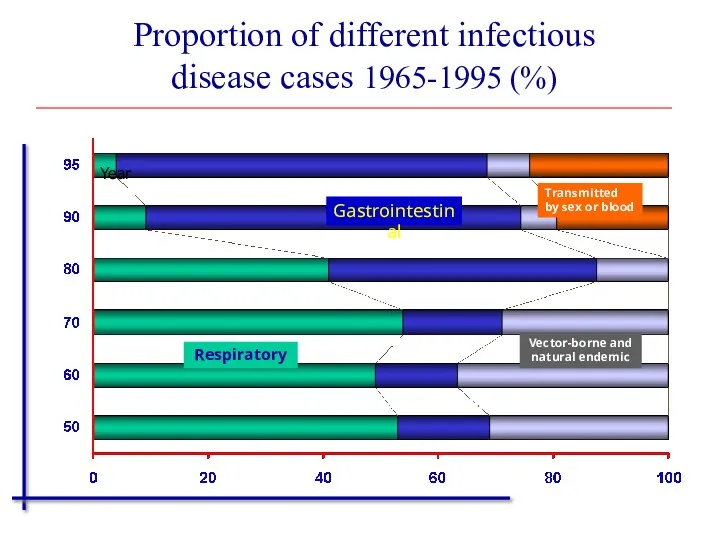
- 35. Proportion of different infectious disease cases 1965-1995 (%) Transmitted by sex or blood Respiratory Gastrointestinal Vector-borne
- 36. Patriotic Sanitation Campaign
- 37. Strengthening Health legislation - issued 9 laws, 24 rule of laws and more than 400 regulations
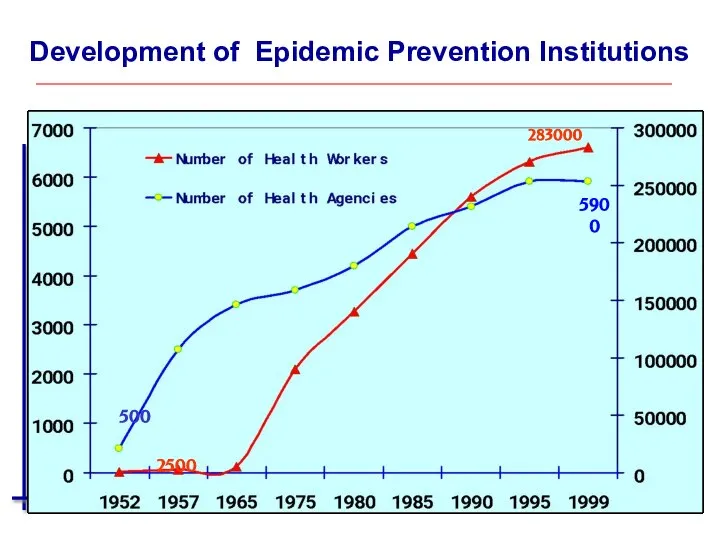
- 38. Development of Epidemic Prevention Institutions 283000 5900 2500 500
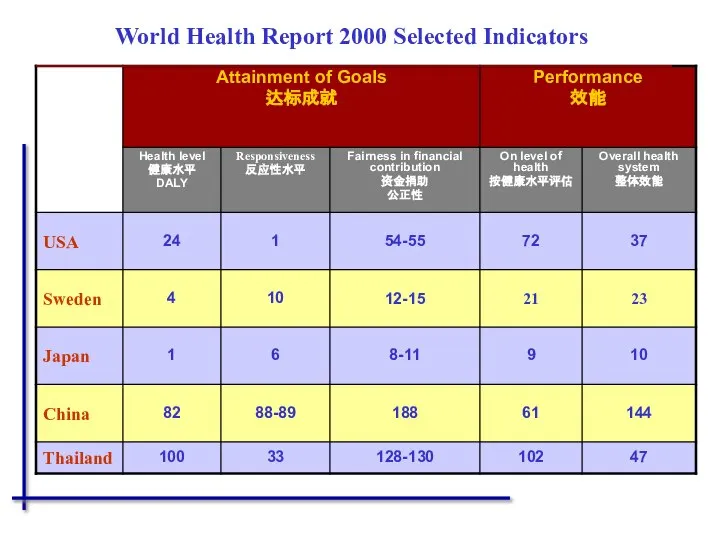
- 39. World Health Report 2000 Selected Indicators
- 40. The Experts of the World Bank Evaluate Primary Health Care in China: “Truly, Declare of Alma-Ata
- 41. Change of Population Urbanization and industrialization Double burdens of diseases Behavioral and Environmental Unreasonable of allocation
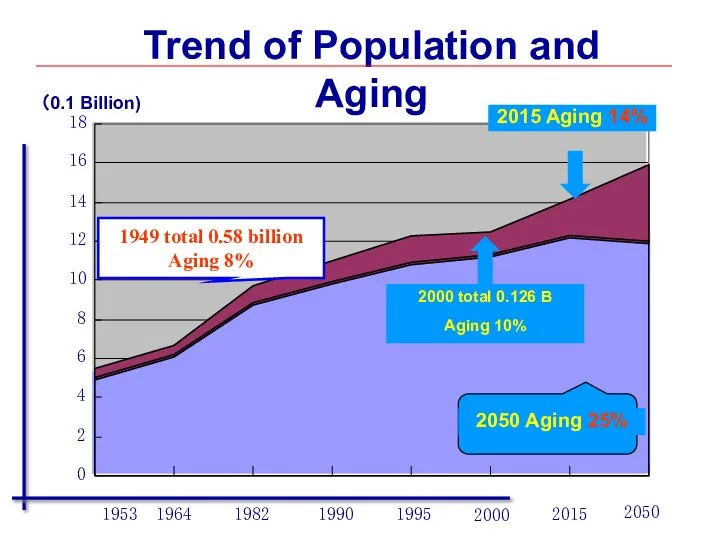
- 42. Trend of Age Composition Change 1999 year China: 0.126 billion Asia: 0.314 billion World: 0.593 billion
- 43. 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 1953 1964 1982 1990 1995 2000
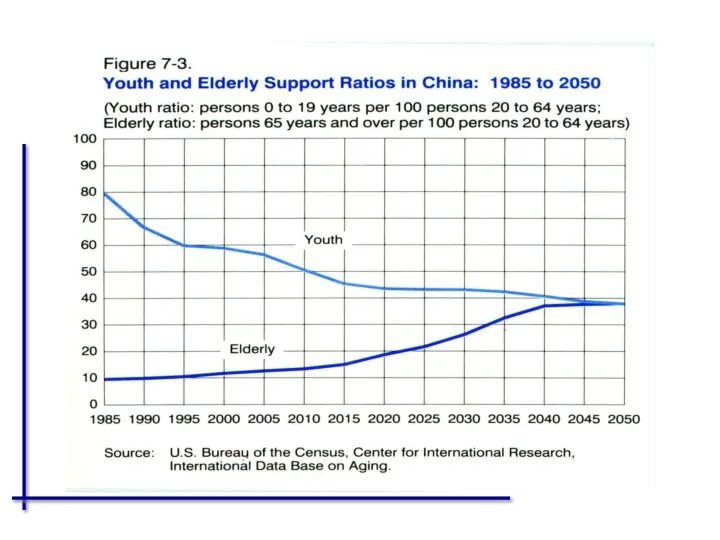
- 44. The change trends of the structure of population, dependency ratio and medical vulnerable population in China
- 46. Urbanization and Industrialization Environmental pollution Life and work stress Injury Immigrant
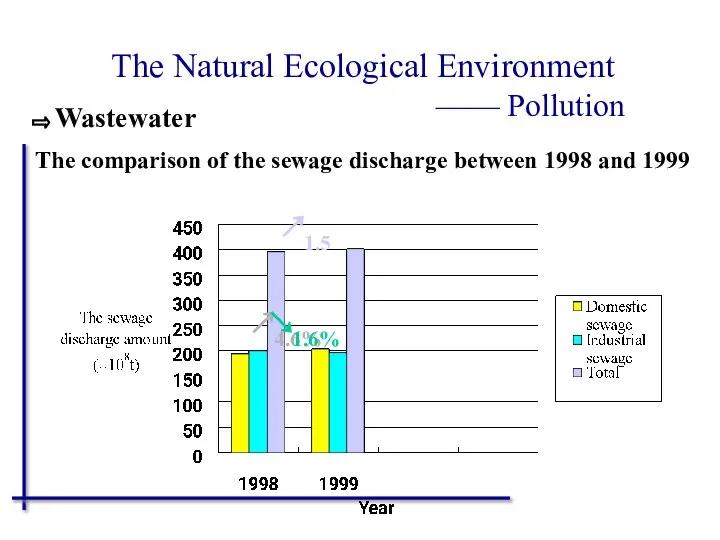
- 47. The Natural Ecological Environment —— Pollution The comparison of the sewage discharge between 1998 and 1999
- 48. The amount of urban refuse in China Beijing In 1996 the amount of urban refuse cleared
- 49. In 1999, the coal smoke type was still the main type of air pollution in China
- 50. Double Burdens of Disease Threats of communicable disease and parasitic disease still exists Chronic and non-communicable
- 51. Threats of Infectious Disease and Parasitic Disease Still Exists Threats from old infectious diseases such as
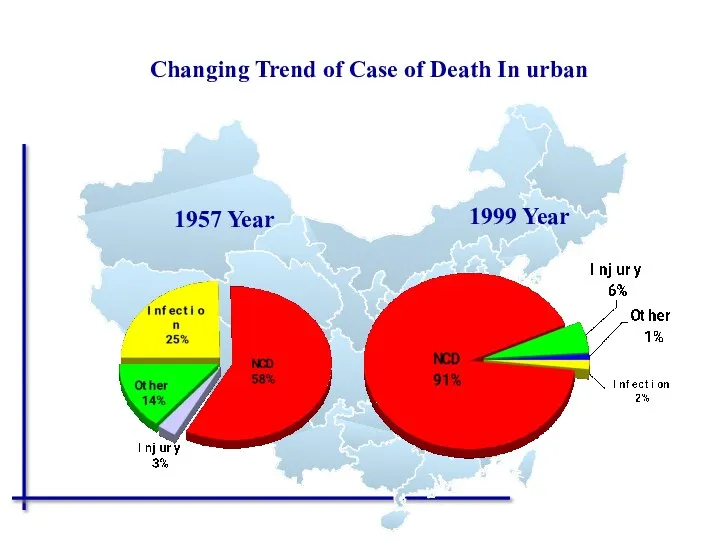
- 52. 1957 Year 1999 Year Changing Trend of Case of Death In urban
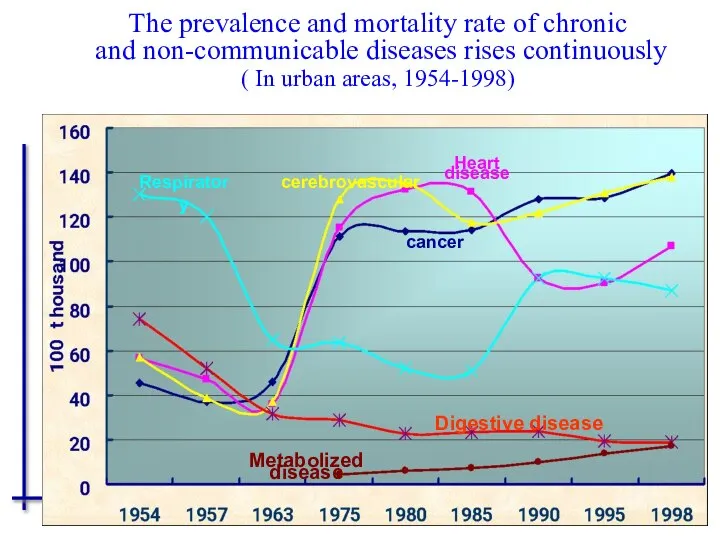
- 53. Respiratory Heart disease cerebrovascular cancer Metabolized disease Digestive disease The prevalence and mortality rate of chronic
- 54. Behavioral Risk Factors Smoking Drinking Dirt
- 55. Smoking At present China has turned into the biggest country of tobacco consumption in the world
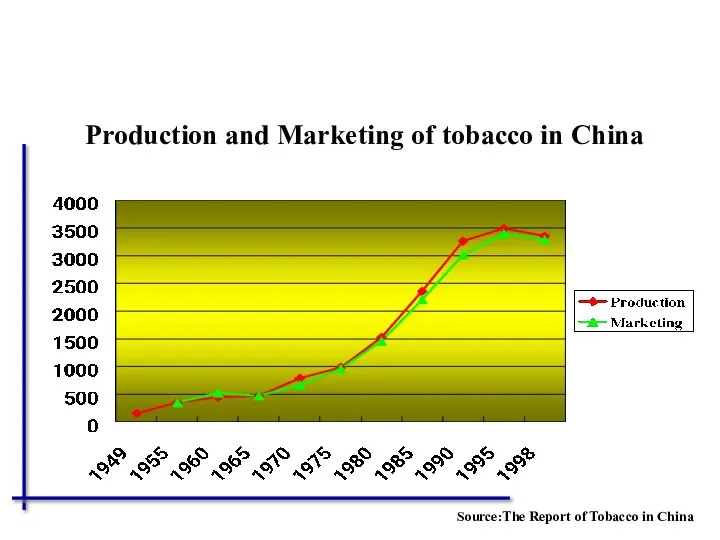
- 56. Production and Marketing of tobacco in China Source:The Report of Tobacco in China
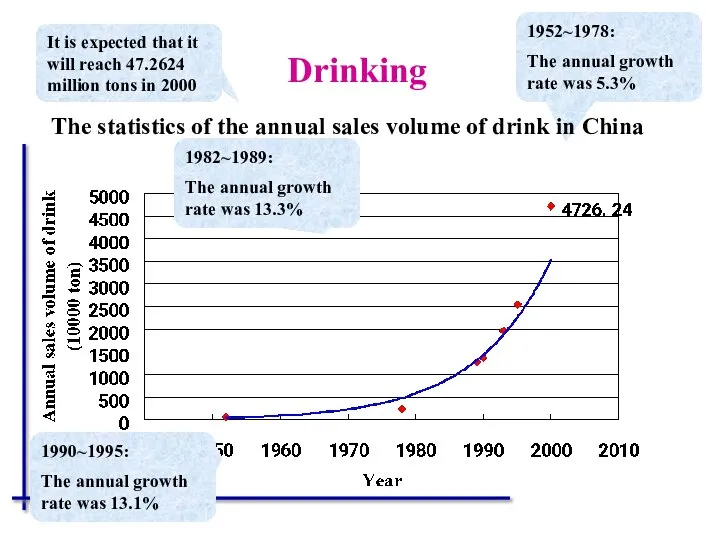
- 57. It is expected that it will reach 47.2624 million tons in 2000 1952~1978: The annual growth
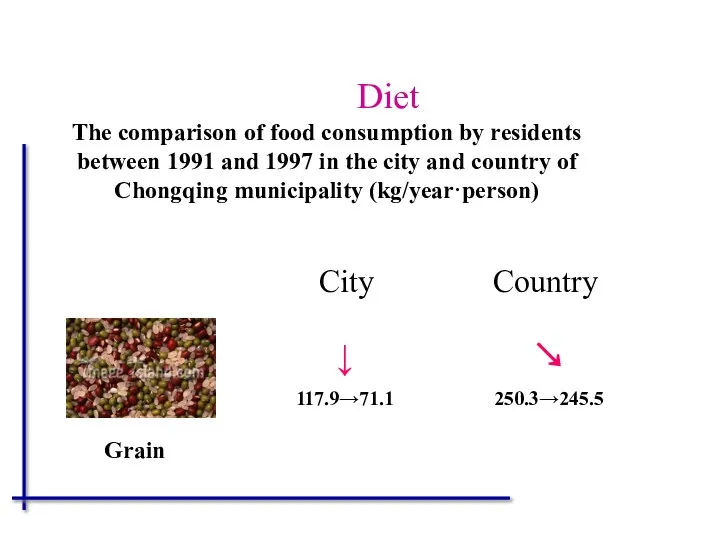
- 58. Diet The comparison of food consumption by residents between 1991 and 1997 in the city and
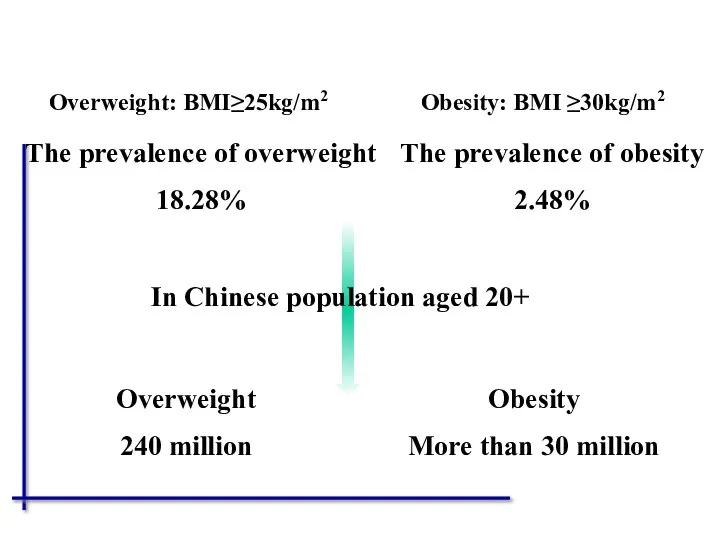
- 59. The prevalence of overweight 18.28% The prevalence of obesity 2.48% In Chinese population aged 20+ Overweight
- 60. Social population environment Natural ecological environment Working environment Living environment Environments Risk Factors
- 62. Скачать презентацию






























 Современные принципы терапии дисфункциональных расстройств билиарного тракта
Современные принципы терапии дисфункциональных расстройств билиарного тракта Факторы, влияющие на здоровье человека
Факторы, влияющие на здоровье человека Дифференциальный диагноз заболеваний, сопровождающихся синдромом экзантемы
Дифференциальный диагноз заболеваний, сопровождающихся синдромом экзантемы Основные патоморфологические аспекты развития миксомы сердца
Основные патоморфологические аспекты развития миксомы сердца Противотуберкулезные и противосифилитические препараты
Противотуберкулезные и противосифилитические препараты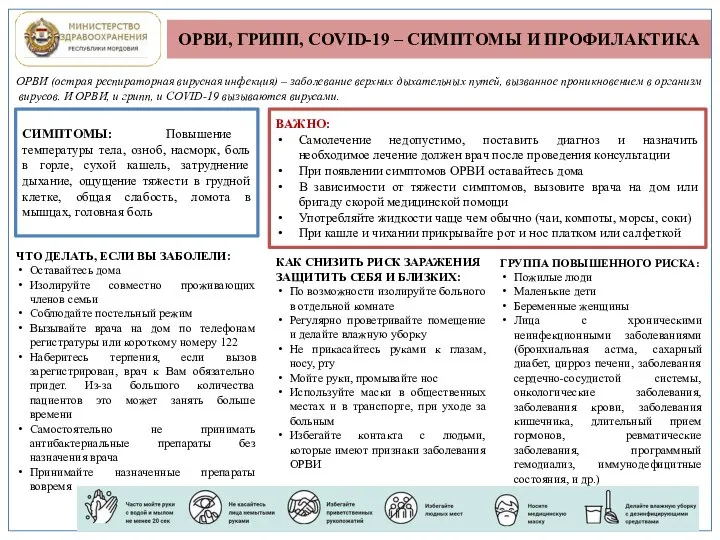 ОРВИ, грипп, covid-19 – симптомы и профилактика
ОРВИ, грипп, covid-19 – симптомы и профилактика Паразиты в организме человека
Паразиты в организме человека Опухоли пищевода
Опухоли пищевода Болезни, передаваемые половым путём. Меры профилактики. СПИД и его профилактика
Болезни, передаваемые половым путём. Меры профилактики. СПИД и его профилактика Сердечно-легочная реанимация
Сердечно-легочная реанимация Обморок. Коллапс. Шок
Обморок. Коллапс. Шок Оперативті хирургиялық техниканың заманауи инструменттерінің негіздері
Оперативті хирургиялық техниканың заманауи инструменттерінің негіздері Травмы костей черепа и грудной клетки
Травмы костей черепа и грудной клетки Переношенная беременность
Переношенная беременность Адреногенитальный синдром
Адреногенитальный синдром Шытырман есеп: «Жақ остеомилиті»
Шытырман есеп: «Жақ остеомилиті» Реабилитация и социальная защита инвалидов
Реабилитация и социальная защита инвалидов Основы психологического анализа конфликтов
Основы психологического анализа конфликтов Molisan Лосьон
Molisan Лосьон Paura kauls os parietale
Paura kauls os parietale Общая характеристика нарушений опорно-двигательного аппарата. Детский церебральный паралич
Общая характеристика нарушений опорно-двигательного аппарата. Детский церебральный паралич Кожа – самый большой орган нашего организма
Кожа – самый большой орган нашего организма Микроэлементозы человека. Биогеохимические провинции. Эндемические заболевания центрального черноземья
Микроэлементозы человека. Биогеохимические провинции. Эндемические заболевания центрального черноземья Экстрапирамидная система
Экстрапирамидная система Врачевание эпохи европейского Возрождения ( XIV –XVII вв.)
Врачевание эпохи европейского Возрождения ( XIV –XVII вв.) Чистота залог здоровья
Чистота залог здоровья Регенерация как общее свойство живых организмов
Регенерация как общее свойство живых организмов Средства, влияющие на сердечно - сосудистую систему. Лекция №13
Средства, влияющие на сердечно - сосудистую систему. Лекция №13