Содержание
- 2. Objectives Describe quality of life and list some measures used to describe quality of life. List
- 3. Quality of Life General Sense of Happiness and Satisfaction And Contentment Hard to Measure Personal sense
- 4. How To Lead Flourishing Lives? Scarcity/Poverty: Can cause increased health risks, high levels of stress, tunneling
- 5. To Increase Life Expectancy and Quality of Life…People Need Knowledge Motivation Opportunities Resources Life expectancy is
- 6. Mortality Number of deaths that occur at a specific time, in a specific group, from a
- 7. Morbidity Number of people with a specific disease, during a specific period, in a specific location.
- 8. Rates Formula that divides the number of events (cases) occurring in a population by the number
- 9. Health Disparities Differences in the health of people that is not due to biological or genetic
- 10. Disparities Due to Gender Longer Life Expectancy Lower Death Rates Lower Rates of Intentional Injuries Higher
- 11. Disparities Due to Race/Ethnicity African Americans Hispanics Infant Mortality Complications of Heart Disease Diabetes Prostate Cancer
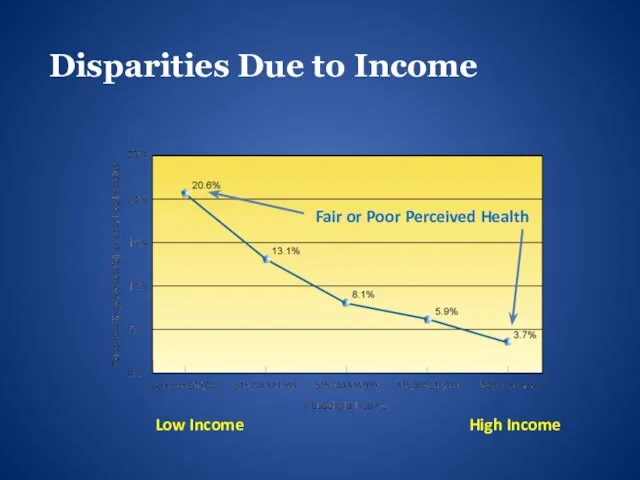
- 12. Disparities Due to Income Fair or Poor Perceived Health Low Income High Income
- 13. Relationship Between Education and Income Over a 30 year career the increase in salary between a
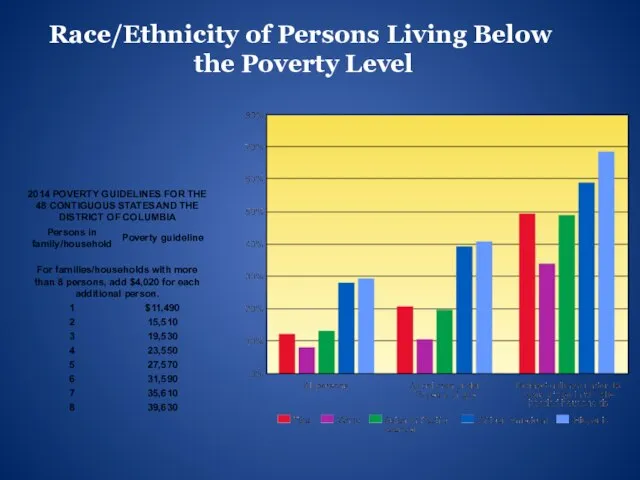
- 14. Race/Ethnicity of Persons Living Below the Poverty Level
- 15. Educational Attainment by Race/Ethnicity
- 16. Disparities Due to Disabilities Activity Limitations Weight Control Access to Health Care
- 18. Скачать презентацию













 Патофизиология обмена веществ
Патофизиология обмена веществ Гипоталамо-гипофизарная система
Гипоталамо-гипофизарная система UWF Campus Alcohol Coalition
UWF Campus Alcohol Coalition Параметрические методы оценки результатов статистического исследования. Лекция №7
Параметрические методы оценки результатов статистического исследования. Лекция №7 Хирургические инфекции при повреждениях и заболеваниях конечностей
Хирургические инфекции при повреждениях и заболеваниях конечностей Медицинский дискурс
Медицинский дискурс Введение в рентгенанатомию
Введение в рентгенанатомию Базовые диагностические услуги многопрофильных медицинских Центров Москвы. Обзор медицинского рынка ЦФО и Москвы
Базовые диагностические услуги многопрофильных медицинских Центров Москвы. Обзор медицинского рынка ЦФО и Москвы Физиология выделения. Физиология почек и водно-солевого обмена
Физиология выделения. Физиология почек и водно-солевого обмена Анализ телерентгенограммы
Анализ телерентгенограммы Туа біткен кардиттер. Эластофиброз
Туа біткен кардиттер. Эластофиброз 20 искусственных объектов для улучшения и поддержания здоровья, усовершенствования тела человека
20 искусственных объектов для улучшения и поддержания здоровья, усовершенствования тела человека Психогигиена
Психогигиена Черепно-мозговая травма: сотрясение головного мозга
Черепно-мозговая травма: сотрясение головного мозга Конфликты в межличностных отношениях
Конфликты в межличностных отношениях Острые лейкозы. Лабораторная диагностика гемобластозов
Острые лейкозы. Лабораторная диагностика гемобластозов Треугольник Гиппократа
Треугольник Гиппократа Науқас пен оның туыстарымен денсаулық сақтау саласында жұмыс істейтін қызметкерлер мен тиімді қарым-қатынасқа түсудің
Науқас пен оның туыстарымен денсаулық сақтау саласында жұмыс істейтін қызметкерлер мен тиімді қарым-қатынасқа түсудің СПИД. ВИЧ
СПИД. ВИЧ 20131010_pervaya_pomoshch_pri_ukusakh_zhivotnykh
20131010_pervaya_pomoshch_pri_ukusakh_zhivotnykh Психология воздействия в следственной практике
Психология воздействия в следственной практике Интенсивная терапия алкогольного абстинентного синдрома
Интенсивная терапия алкогольного абстинентного синдрома Панкреонекроз
Панкреонекроз Дифференциальная диагностика кратковременной потери сознании (синкопе)
Дифференциальная диагностика кратковременной потери сознании (синкопе) Системы регуляции жизнедеятельности
Системы регуляции жизнедеятельности Психологические особенности проявления синдрома эмоционального выгорания у сотрудников уголовно-исполнительной системы
Психологические особенности проявления синдрома эмоционального выгорания у сотрудников уголовно-исполнительной системы Руководство по забору проб для лабораторных исследований
Руководство по забору проб для лабораторных исследований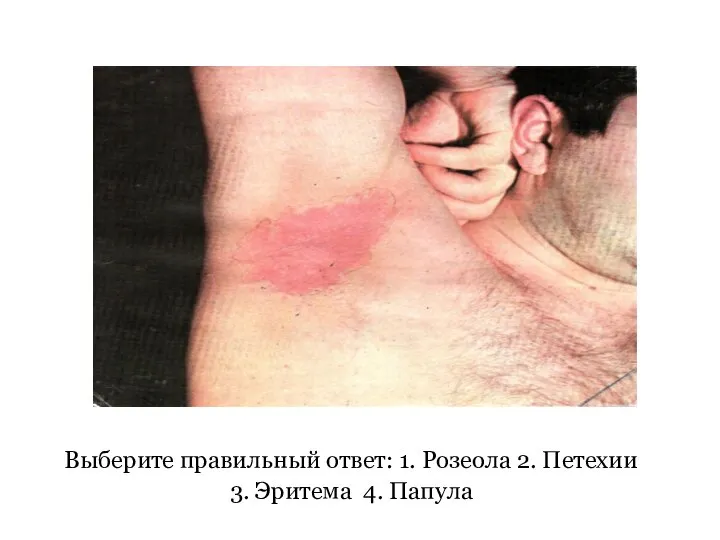 Дерматологический статус. Задачи
Дерматологический статус. Задачи