Содержание
- 2. Basics of lighting - Contents Introduction Selection parameters Overview of building lighting Overview of home lighting
- 3. Why this module? With the world focusing on how to reduce the energy bill With professionals
- 4. Lighting & energy consumption Lighting alone is responsible for 19% of the world's electricity demand Lighting
- 5. Buildings Lighting = 25 to 50% (average 40%) of electricity bill Offices, hotels, shops & supermarkets
- 6. Industry & Housing Lighting = 10 to 15% of the electricity bill Power plant, heavy industry,
- 7. On the market today Two main technologies Incandescent lamps Gas discharge lamps Several types of applications
- 8. Technologies on the market Incandescent bulbs "GLS"*: Most common bulbs LV & ELV* halogen Gas discharge
- 9. Applications / Lights: Buildings Fluorescent tubes Metal halide "MH, HQI, MIB" Lights for homes, small shops
- 10. Lighting - Selection parameters Lighting needs in relation to end-use Required brightness (lighting power level) Environment
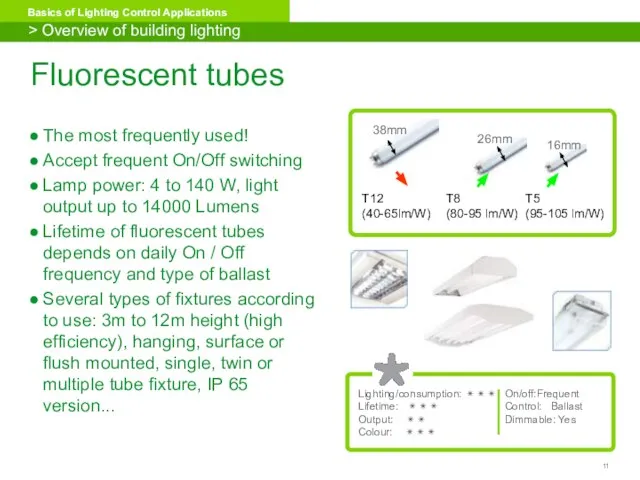
- 11. Fluorescent tubes The most frequently used! Accept frequent On/Off switching Lamp power: 4 to 140 W,
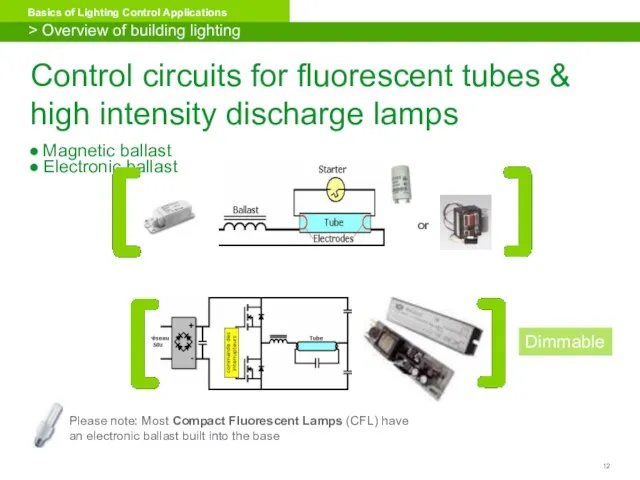
- 12. Control circuits for fluorescent tubes & high intensity discharge lamps Electronic ballast Magnetic ballast > Overview
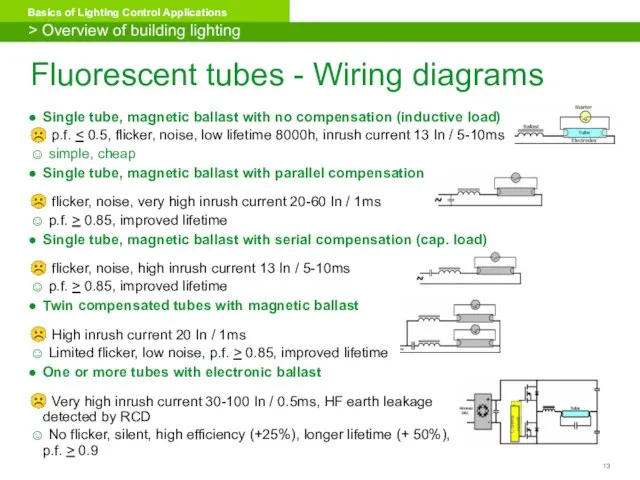
- 13. Fluorescent tubes - Wiring diagrams Single tube, magnetic ballast with no compensation (inductive load) ☹ p.f.
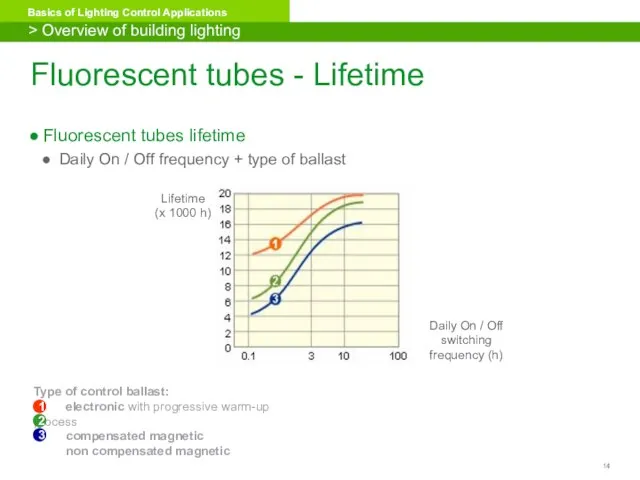
- 14. Fluorescent tubes - Lifetime Fluorescent tubes lifetime Daily On / Off frequency + type of ballast
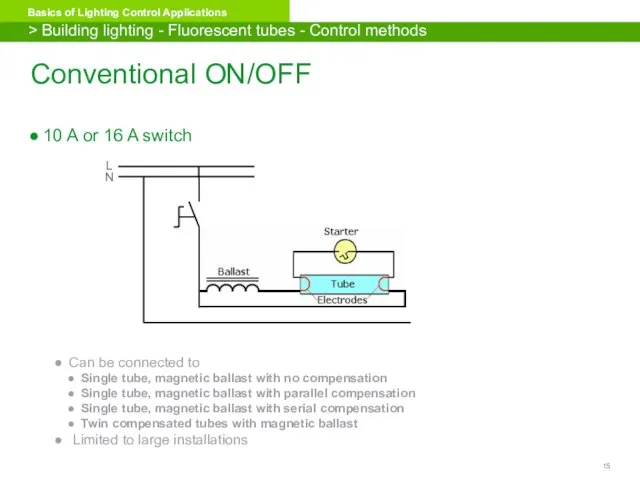
- 15. Conventional ON/OFF 10 A or 16 A switch Can be connected to Single tube, magnetic ballast
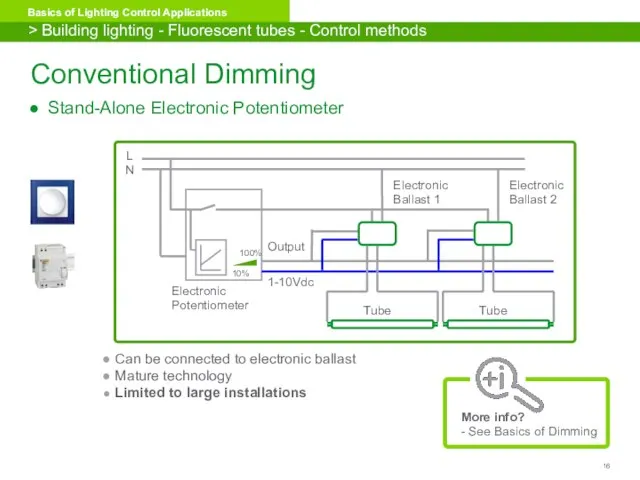
- 16. Conventional Dimming Stand-Alone Electronic Potentiometer Can be connected to electronic ballast Mature technology Limited to large
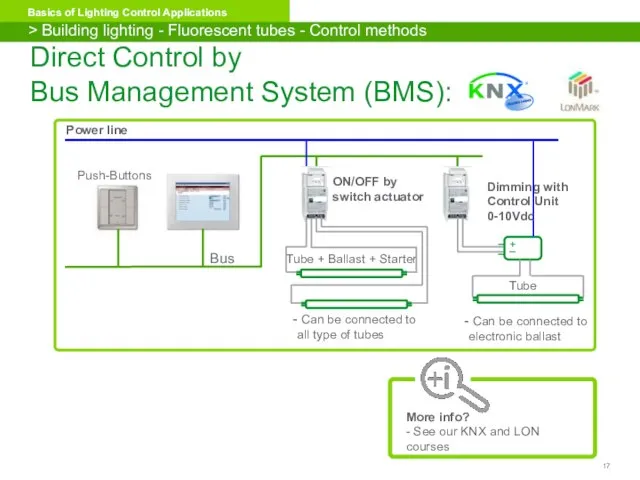
- 17. Power line Bus Push-Buttons Can be connected to electronic ballast Tube + Ballast + Starter +
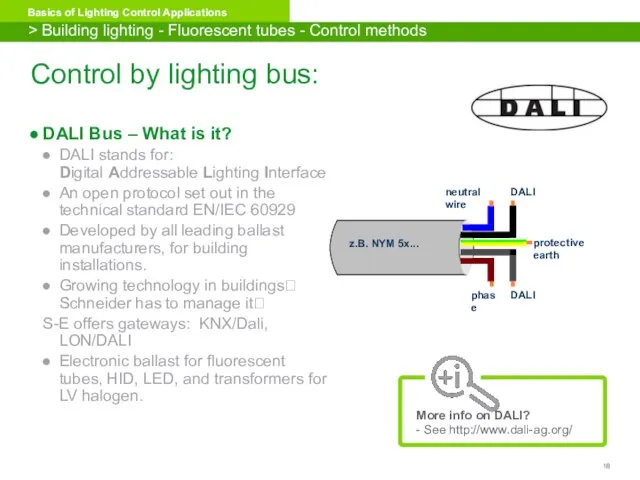
- 18. Control by lighting bus: DALI Bus – What is it? DALI stands for: Digital Addressable Lighting
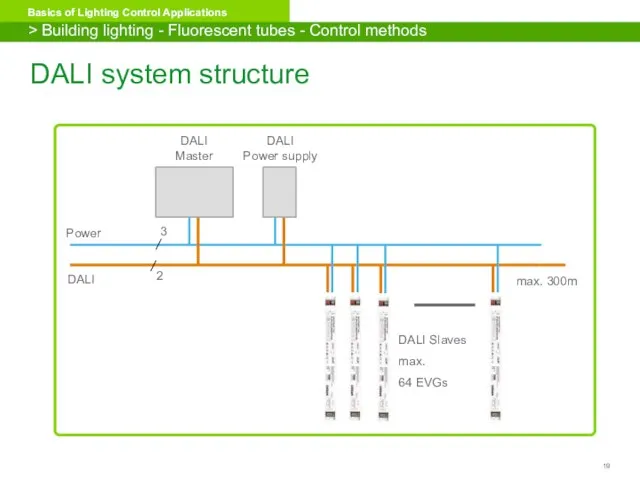
- 19. DALI system structure > Building lighting - Fluorescent tubes - Control methods DALI Power max. 300m
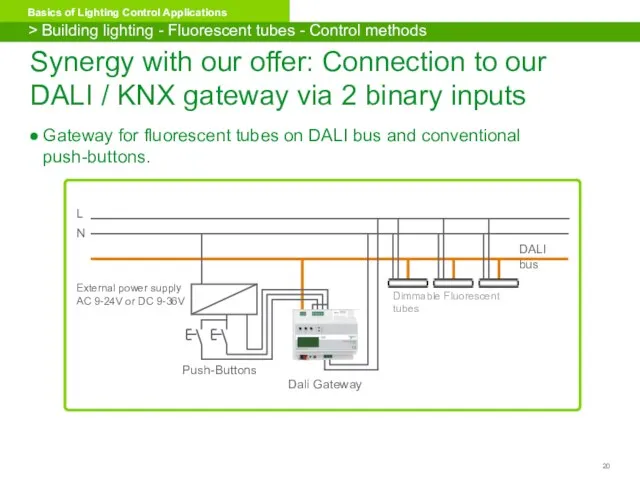
- 20. Gateway for fluorescent tubes on DALI bus and conventional push-buttons. Synergy with our offer: Connection to
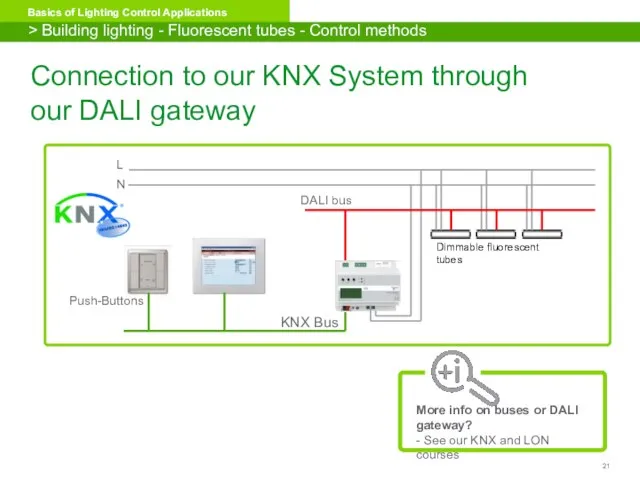
- 21. DALI bus Dimmable fluorescent tubes L N KNX Bus Push-Buttons Connection to our KNX System through
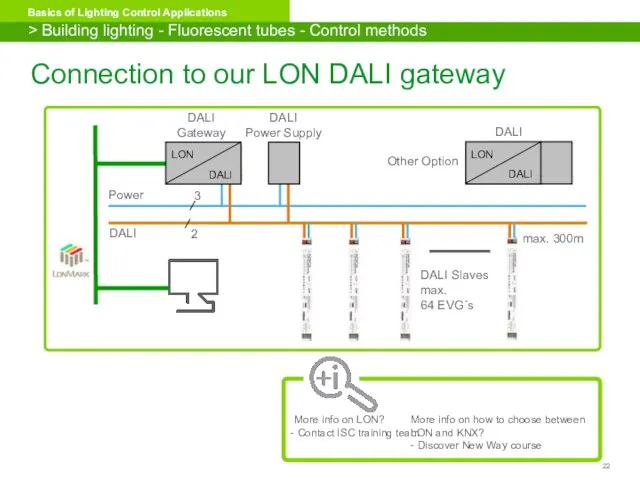
- 22. Connection to our LON DALI gateway > Building lighting - Fluorescent tubes - Control methods DALI
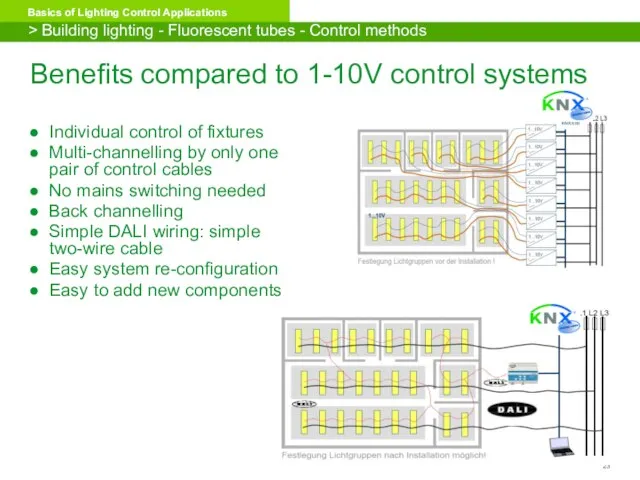
- 23. Benefits compared to 1-10V control systems Individual control of fixtures Multi-channelling by only one pair of
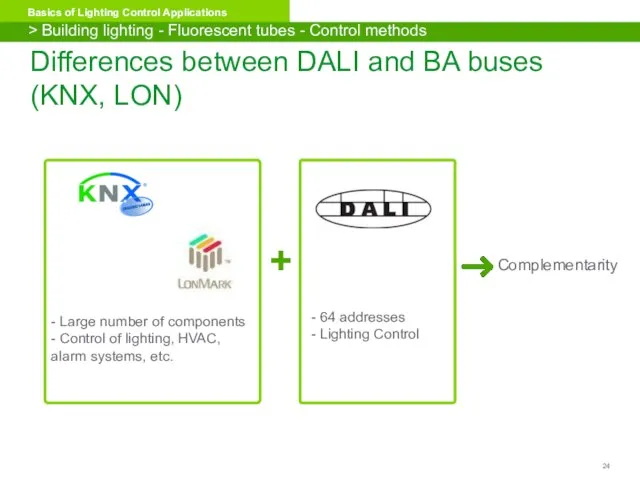
- 24. Differences between DALI and BA buses (KNX, LON) 64 addresses Lighting Control - Large number of
- 25. DSI for Digital Serial Protocol 1991 Proprietary system from Tridonic-Atco (Zumtobel) An "intelligent" central unit +
- 26. Introduction to home lighting Energy efficient lighting in homes Lighting may account for up to a
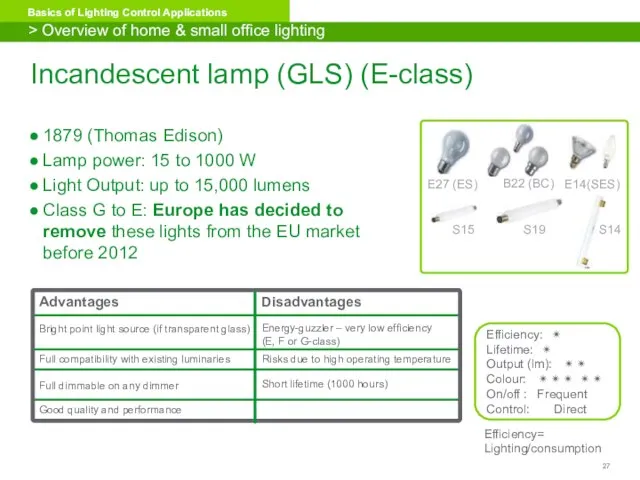
- 27. Incandescent lamp (GLS) (E-class) 1879 (Thomas Edison) Lamp power: 15 to 1000 W Light Output: up
- 28. Conventional halogen lamps (D or E-class) 1980s 230Vac lamps or 12Vdc lamps (+ transformer) Improved incandescent
- 29. 12Vdc lamps (+ transformer) Lamp power: 5 to 500 W, Light Output: up to 12,000 lumens
- 30. Halogen lamps with xenon gas filling (C-class) Recent technology With xenon gas filling, about 25% less
- 31. Halogen lamps with infrared coating (B-class) Recent technology Infrared coating added to the wall of halogen
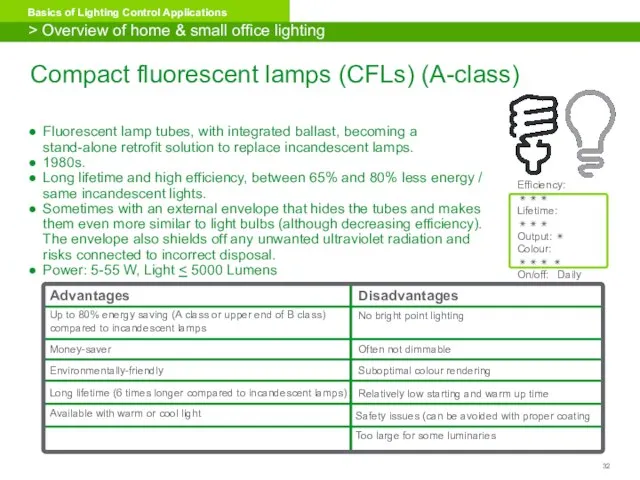
- 32. Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) (A-class) Fluorescent lamp tubes, with integrated ballast, becoming a stand-alone retrofit solution
- 33. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Very long lifetime Quickly emerging technology with recent progress in efficiency For room
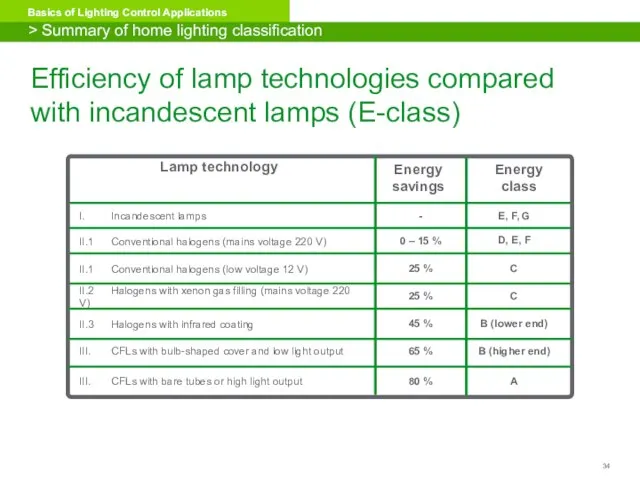
- 34. Efficiency of lamp technologies compared with incandescent lamps (E-class) Lamp technology I. Incandescent lamps Energy savings
- 35. Wiring Devices for essential lighting applications Control for advanced lighting applications Schneider products to control this
- 36. High Intensity Discharge lamps (HID) Produce light by means of an electric arc. Several types: Mercury
- 37. Main use: Public lighting, industry, shelters, docks, with high bay fixtures Technical characteristics: The oldest HID
- 38. Main use: Outdoors only, road & security lighting, with high bay fixtures Technical characteristics: Most efficient,
- 39. Main use: Streets, monuments, tunnels, airports, docks, car parks, parks, shopping malls, warehouses, halls, etc. with
- 40. Main use: streets, car parks, shopping malls, shops, halls, gymnasiums, factories, workshops, warehouses, garden lights, etc.
- 41. Main use: areas with difficult access or requiring high service continuity: High ceilings, tunnels, airports, uninterruptable
- 42. Schneider products to control this type of lighting Time switches IH, IHP Twilight switches IC 2000,
- 43. In the same set of basics Module 1: Basics of Lighting Module 2: Basic of Lighting
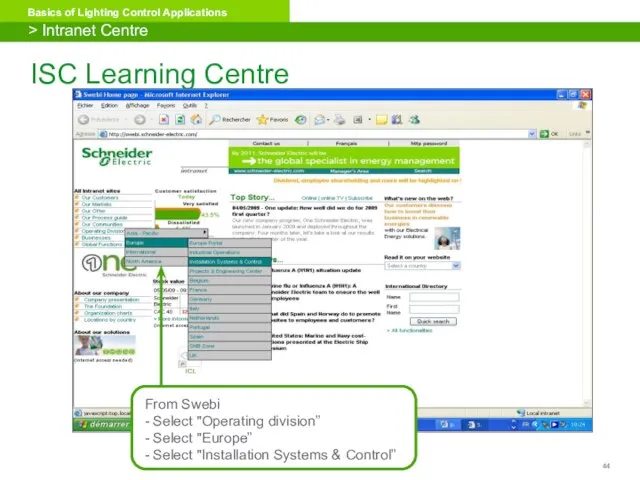
- 44. ISC Learning Centre From Swebi - Select "Operating division” - Select "Europe” - Select "Installation Systems
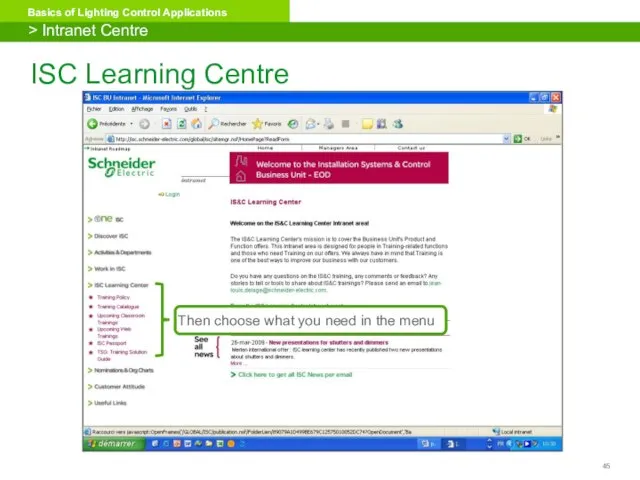
- 45. ISC Learning Centre > Intranet Centre
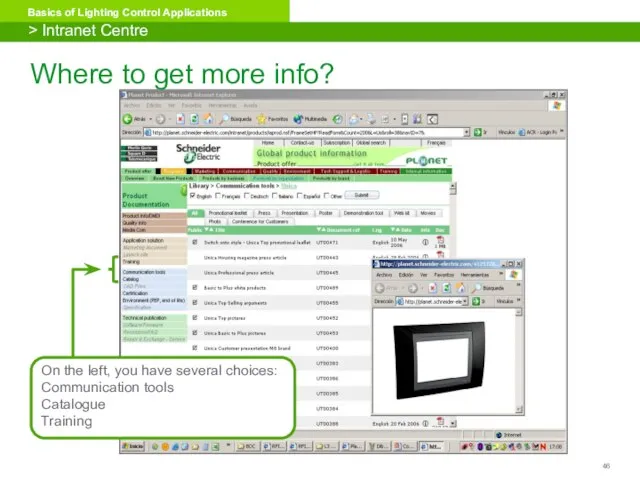
- 46. On the left, you have several choices: Communication tools Catalogue Training Where to get more info?
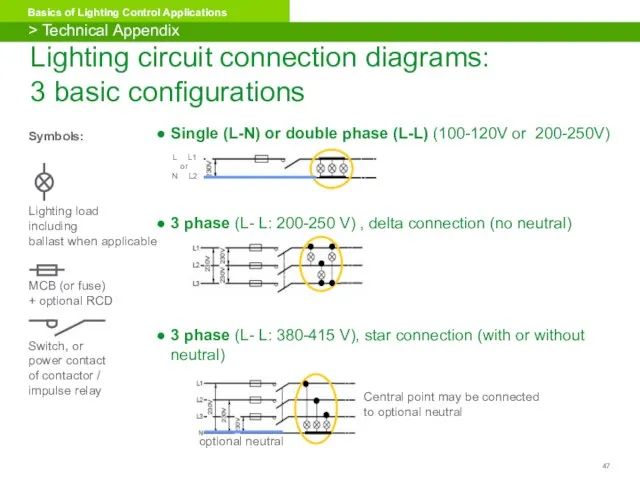
- 47. Lighting circuit connection diagrams: 3 basic configurations Single (L-N) or double phase (L-L) (100-120V or 200-250V)
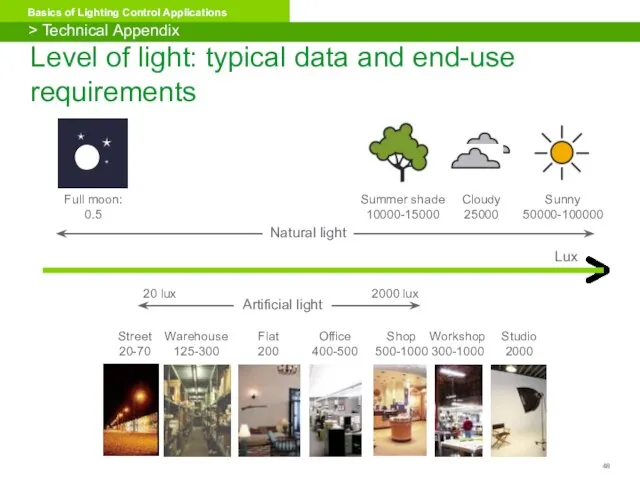
- 48. Level of light: typical data and end-use requirements Summer shade 10000-15000 Full moon: 0.5 Cloudy 25000
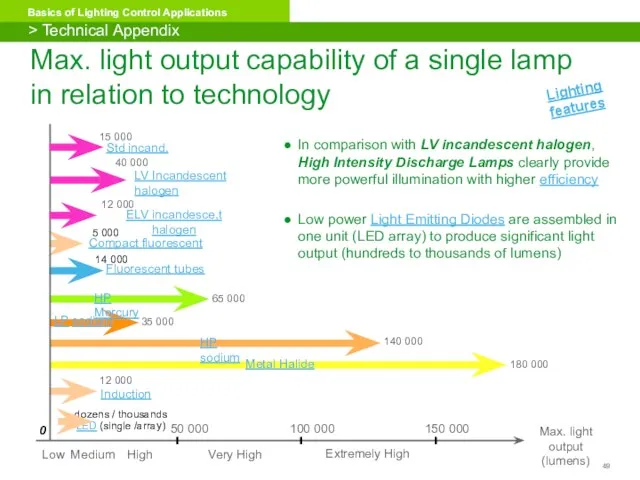
- 49. Max. light output capability of a single lamp in relation to technology 150 000 0 Max.
- 51. Скачать презентацию

























 Акция День экологических знаний
Акция День экологических знаний И.А. Гончаров роман Обломов
И.А. Гончаров роман Обломов День психического здоровья
День психического здоровья Обеспечение жильем детей-сирот
Обеспечение жильем детей-сирот Презентация1
Презентация1 Цели и задача ПЭР это изучение устройства крана затяжки крюка крана КС-55713-5, а именно её назначение, устройство,
Цели и задача ПЭР это изучение устройства крана затяжки крюка крана КС-55713-5, а именно её назначение, устройство, Рождение иконы
Рождение иконы Предложение по букированию промо места под бьюти зону чж
Предложение по букированию промо места под бьюти зону чж Бездомные домашние животные
Бездомные домашние животные Do you have an example to follow?
Do you have an example to follow? 55-юбилей
55-юбилей Оборудование и конструкции малых ГЭС
Оборудование и конструкции малых ГЭС Центральный Банк РФ
Центральный Банк РФ Биологическая дозиметрия
Биологическая дозиметрия задание2 длягруппы№1
задание2 длягруппы№1 Детали
Детали Техника безопасности и организация рабочего места при работе на Пк
Техника безопасности и организация рабочего места при работе на Пк 20180414_pevets_lyubvi_i_nadezhdy
20180414_pevets_lyubvi_i_nadezhdy Урок №1 Экономическая и социальная география России. Введение
Урок №1 Экономическая и социальная география России. Введение Стратегия развития линии выходной – лавна
Стратегия развития линии выходной – лавна 20130331_konspekt_prezentaciya
20130331_konspekt_prezentaciya Логопедическое занятие
Логопедическое занятие prezentatsia_kompanii_novartis
prezentatsia_kompanii_novartis Легированные стали. Лекция 7
Легированные стали. Лекция 7 Оборудование для измельчения пищевых продуктов
Оборудование для измельчения пищевых продуктов Правовые и этические аспекты использования Интернета
Правовые и этические аспекты использования Интернета Производство драже
Производство драже Airmux-5000 Version 3.3 General Availability
Airmux-5000 Version 3.3 General Availability