It is blocked into the allotments
Monochronic cultures = one thing at
a time
They do not value interruptions.
They take time commitments very seriously.
Monochronic time
If you live in the United States, Canada, or Northern Europe, you live in a monochronic culture. If you live in Latin America, the Arab part of the Middle East, or sub-Sahara Africa, you live in a polychronic culture.
Polychronic time
Polychronic cultures = multiple things at the same time,
They change plans often and easily but have a tendency to build lifetime relationships.
5. Polychronic and monochronic time cultures.








 Презентація_Обстеження_обєктів_Михайло_Жужа_Віктор_Носенко_09_06
Презентація_Обстеження_обєктів_Михайло_Жужа_Віктор_Носенко_09_06 Метаболизм – основа существования клетки
Метаболизм – основа существования клетки Производство электроэнергии в России
Производство электроэнергии в России 20161106_ryby_0
20161106_ryby_0 Презентация к 5 заданию
Презентация к 5 заданию Презентация 17
Презентация 17 Типовая должностная инструкция приемосдатчика груза и багажа: основные обязанности
Типовая должностная инструкция приемосдатчика груза и багажа: основные обязанности волшебник недоучка
волшебник недоучка 20131222_russkaya_ikona
20131222_russkaya_ikona Реконструкция линий связи К60 на ЦСП МС04-DSL-3U
Реконструкция линий связи К60 на ЦСП МС04-DSL-3U Минеральные вяжущие материалы и изделия
Минеральные вяжущие материалы и изделия Презентация2 (3) (2)
Презентация2 (3) (2) the political party Yabloko
the political party Yabloko Устройство и оборудование водопроводных сетей зданий
Устройство и оборудование водопроводных сетей зданий Хозяйство России
Хозяйство России Міжнародна система безпеки
Міжнародна система безпеки Общество с ограниченной ответственностью ДонПорта
Общество с ограниченной ответственностью ДонПорта Архитектура микропроцессора и микропроцессорной системы
Архитектура микропроцессора и микропроцессорной системы Основы радиотехнических цепей и сигналов
Основы радиотехнических цепей и сигналов Учебный план
Учебный план Логопсихология наблюдение
Логопсихология наблюдение Җиңү көне белән!
Җиңү көне белән! 20130407_detskie_igrushki
20130407_detskie_igrushki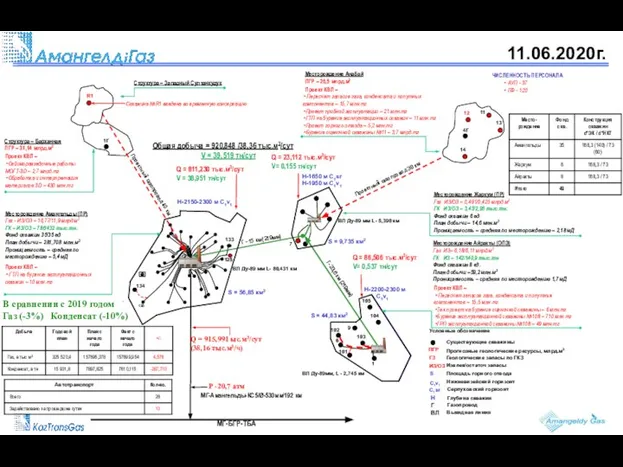 АмангелдiГаз. Отчет о работе месторождений
АмангелдiГаз. Отчет о работе месторождений Установки непрерывного действия для приготовления абс
Установки непрерывного действия для приготовления абс Гидроизоляция
Гидроизоляция Новая форма социальной поддержки малоимущих семей и одиноких граждан
Новая форма социальной поддержки малоимущих семей и одиноких граждан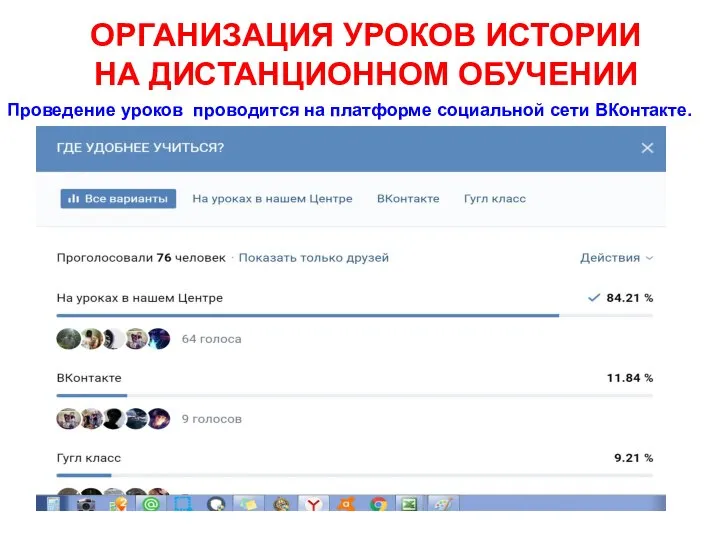 Организация уроков истории на дистанционном обучении
Организация уроков истории на дистанционном обучении