Содержание
- 2. ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: “Nomoi” meaning natural laws “Ergon” meaning work Hence,
- 3. History As early as 18th century doctors noted that workers who required to maintain body positions
- 4. Static work: musculoskeletal effort required to hold a certain position, even a comfortable one. Example: sit
- 5. Elements at work (cont) Force: amount of tension our muscles generate Example: tilting your head forward
- 6. 3 Main Ergonomic Principles: Work activities should permit worker to adopt several different healthy and safe
- 7. The average person working at a keyboard can perform 50,000 to 200,000 keystrokes a day Overexertion,
- 8. A Bit of Anatomy !! Overuse and small repetitive movements ie: CTD, RSI, MSD disturb balance
- 9. What causes Nerve Compression or Entrapment? Repeated motions Tight muscles Inflammation of surrounding tissues Misalignment of
- 10. What are 4 Common Nerve injuries? Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: brachial plexus compression d/t muscle tightness side
- 11. Nerve injuries (cont) Radial tunnel syndrome: compressed radial nerve @ outside of elbow d/t repetitive wrist
- 12. Nerve injuries (cont) Cubital tunnel syndrome: ulnar nerve compression inside of the elbow d/t repetitive bending
- 13. Nerve injuries (cont) Carpal tunnel syndrome: compression of median nerve at level of carpal tunnel Where
- 14. Tendons and Tendonitis Tendons are connective tissue that attach muscle to bone; have little stretch or
- 15. What to do ?? Warm up & stretch before activities that are repetitive, static or prolonged
- 16. Maintain erect position of back & neck w/ shoulders relaxed Position equipment & work directly in
- 17. Avoid bending neck forward for prolonged periods of time (*remember quadruple the force); use a copy
- 18. Modify Tasks: Alternate activities frequently; rotate heavy &/or repetitive tasks w/ lighter less repetitive ones. If
- 19. Use the largest joints & muscles to do the job Use 2 hands to lift rather
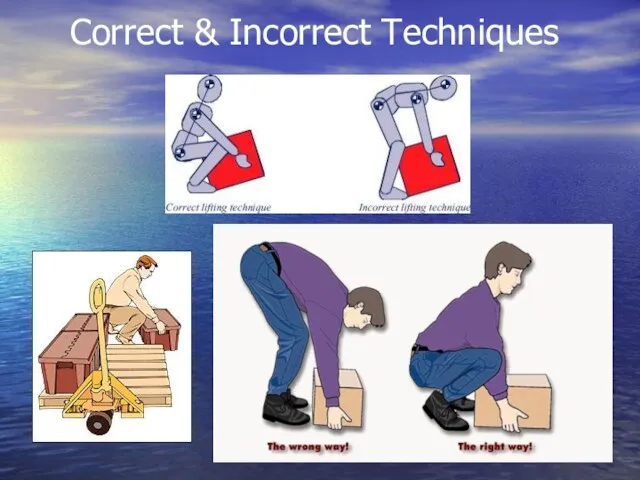
- 20. Correct & Incorrect Techniques
- 21. Good and Bad of “ TILT”
- 22. ERGO REMINDERS from Stretchbreak.com
- 23. Practice Wellness at Work and Home ! Exercise Nutrition Relaxation Body Mind Spirit
- 24. MOVE BRE AT HE STRETCH
- 26. Скачать презентацию






















 Виготовлення яблучного соку (освітленого)
Виготовлення яблучного соку (освітленого) Организация ТО и ремонта на универсальных и специализированных постах
Организация ТО и ремонта на универсальных и специализированных постах Сыныптар арасында
Сыныптар арасында In Harmony With Nature
In Harmony With Nature Организация технического обслуживания и ремонт электрооборудования радиально-сверлильных станков
Организация технического обслуживания и ремонт электрооборудования радиально-сверлильных станков Будущее Земли. Какое будущее ожидает Землю
Будущее Земли. Какое будущее ожидает Землю Удивительная природа
Удивительная природа 2. CSS Buttons
2. CSS Buttons ETO_ZYuMYa
ETO_ZYuMYa Времена года
Времена года Пространственная разметка
Пространственная разметка Правка и гибка металла
Правка и гибка металла ASP.NET Core лекція 01 (2)
ASP.NET Core лекція 01 (2) Описание работ по ГРП по скважине 7162Г к 12 Сыморьяхского месторождения
Описание работ по ГРП по скважине 7162Г к 12 Сыморьяхского месторождения Игротехника
Игротехника Ремонт трубопроводов и арматуры котельной установки
Ремонт трубопроводов и арматуры котельной установки 产品介绍. 产品编号
产品介绍. 产品编号 Определение площадей зданий. Экспликация (тема 4.5)
Определение площадей зданий. Экспликация (тема 4.5) Материнство
Материнство 20140528_m.m._bakhtin
20140528_m.m._bakhtin Лазерная сварка алюминия и его сплавов
Лазерная сварка алюминия и его сплавов Линейка 2015
Линейка 2015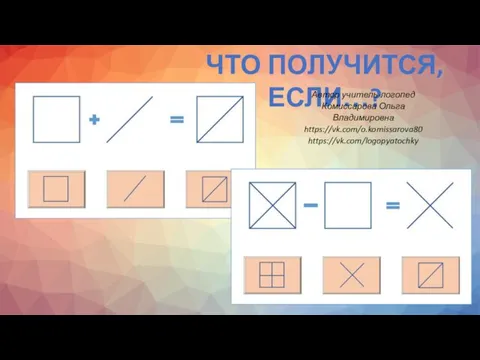 СЛОЖЕНИЕ И ВЫЧИТАНИЕ фигуры
СЛОЖЕНИЕ И ВЫЧИТАНИЕ фигуры X- full version. Awsome Layout pirtures
X- full version. Awsome Layout pirtures 20131126_kazanina_yu.yu_
20131126_kazanina_yu.yu_ К.Г. Паустовский Растрёпанный воробей
К.Г. Паустовский Растрёпанный воробей 20161109_domostroy
20161109_domostroy Национальные идеи: ресурсы успеха
Национальные идеи: ресурсы успеха