Содержание
- 2. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Reference Book “Modern Control Engineering”, Katsuhiko
- 3. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 How is it important? Good Improved
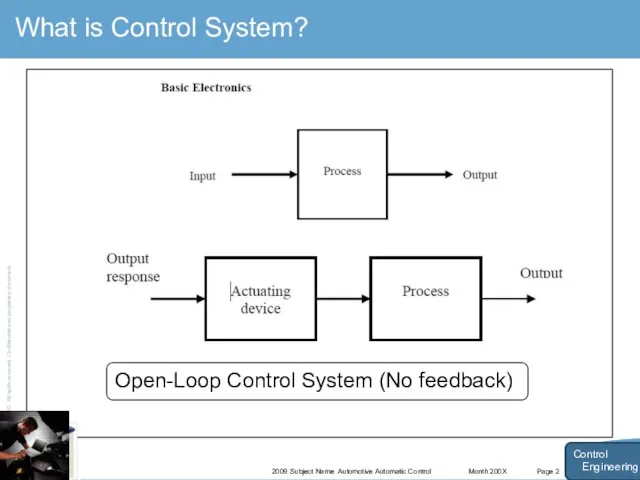
- 4. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 What is Control System? Control Engineering
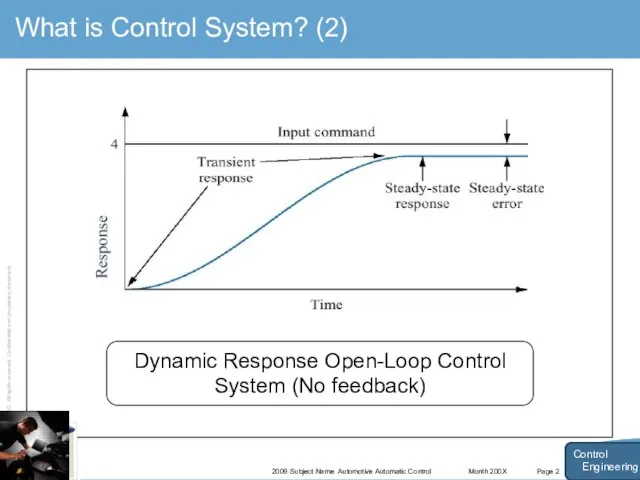
- 5. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 What is Control System? (2) Control
- 6. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 What is Control System? (3) Control
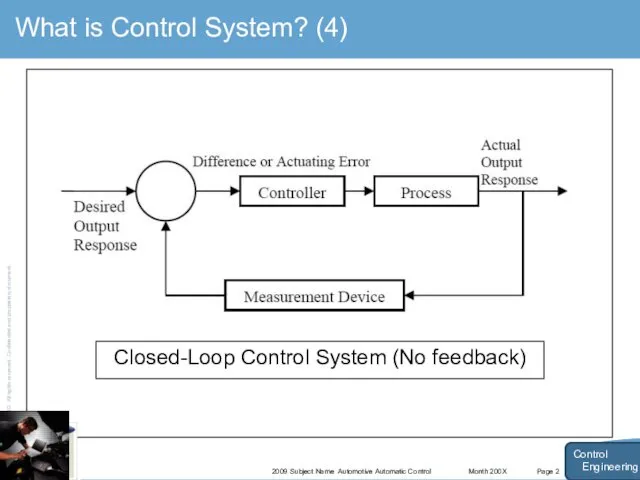
- 7. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 What is Control System? (4) Control
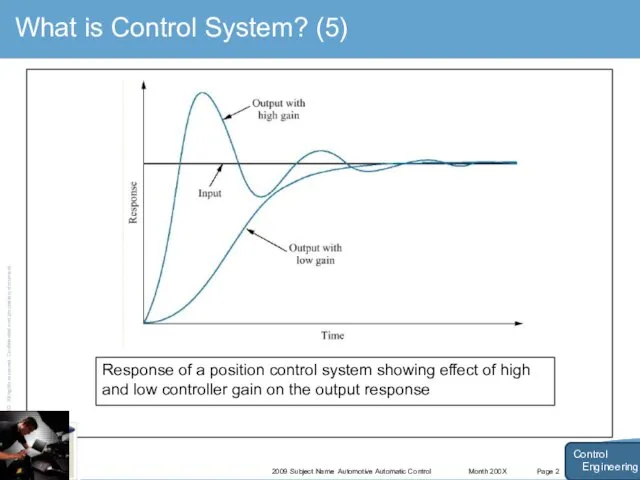
- 8. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 What is Control System? (5) Control
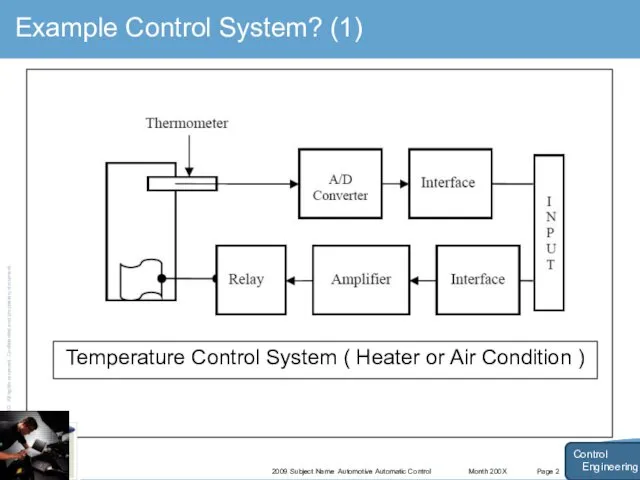
- 9. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Example Control System? (1) Control Engineering
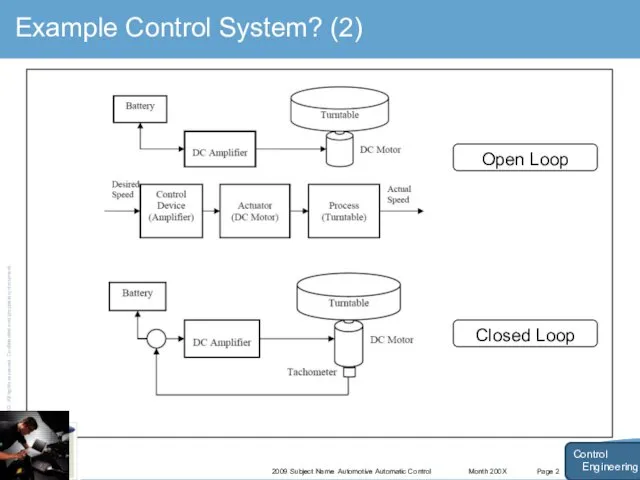
- 10. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Example Control System? (2) Control Engineering
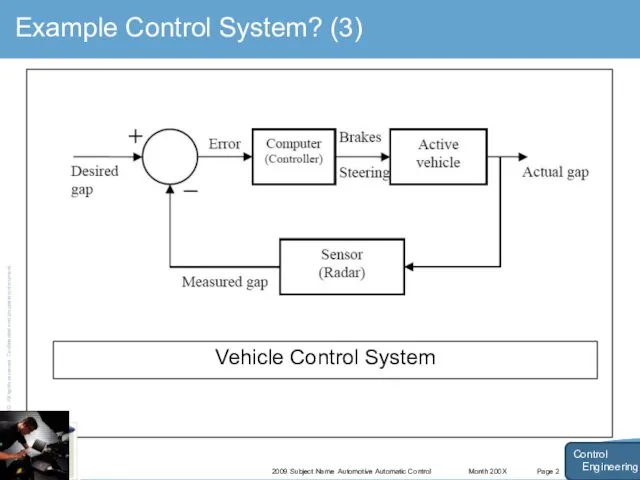
- 11. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Example Control System? (3) Control Engineering
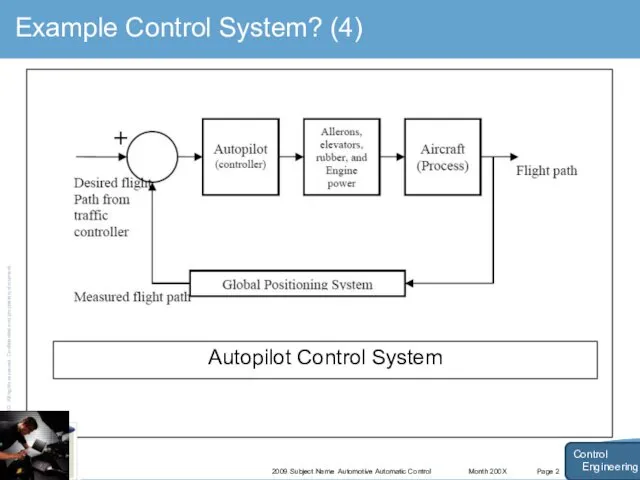
- 12. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Example Control System? (4) Control Engineering
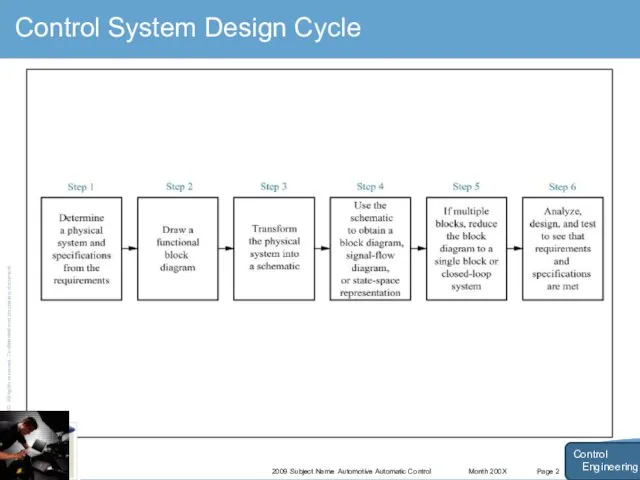
- 13. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Control System Design Cycle Control Engineering
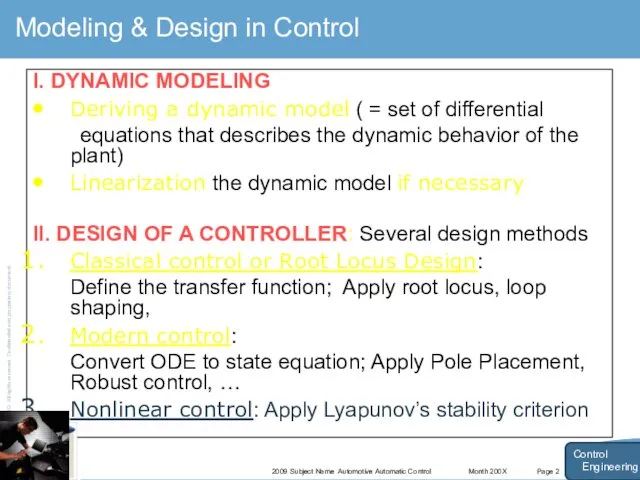
- 14. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Modeling & Design in Control I.
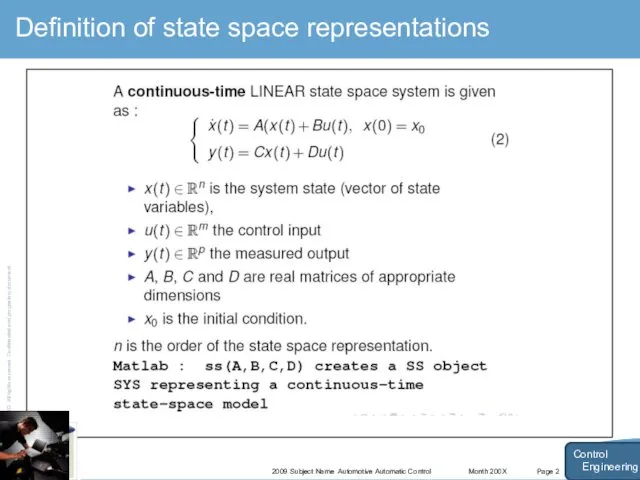
- 15. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Definition of state space representations Control
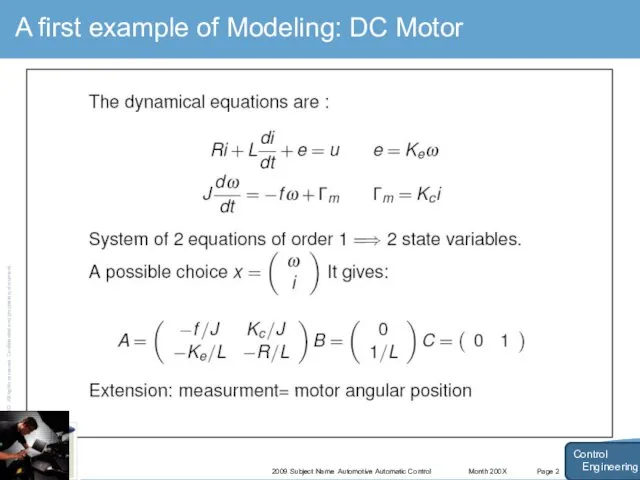
- 16. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 A first example of Modeling: DC
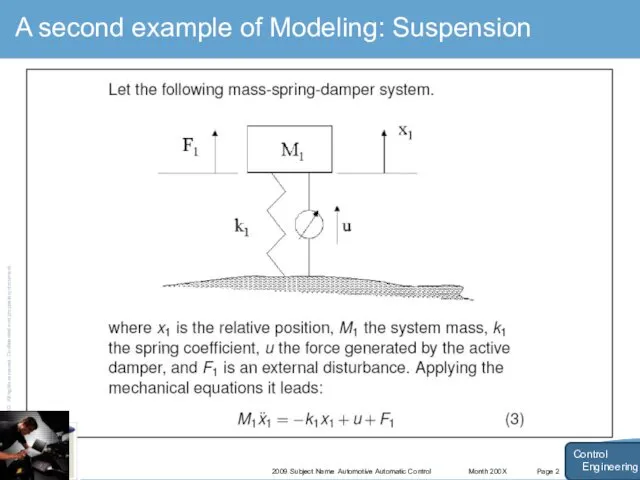
- 17. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 A second example of Modeling: Suspension
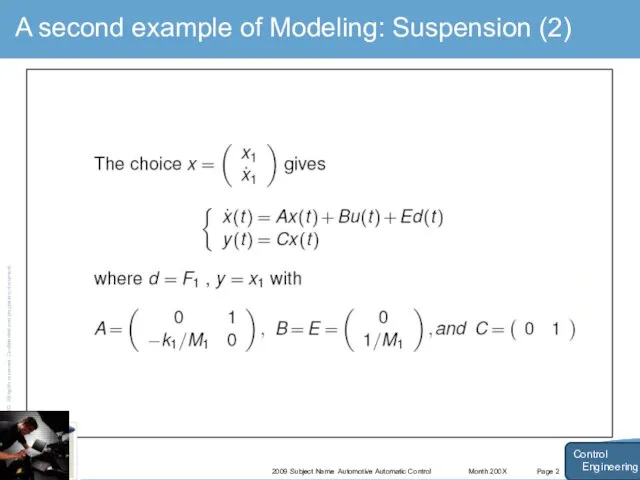
- 18. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 A second example of Modeling: Suspension
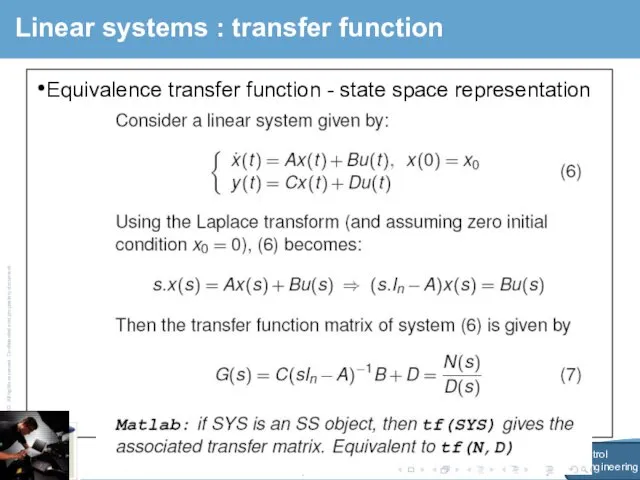
- 19. Month 200X 2009 Subject Name Automotive Automatic Control Page 2 Linear systems : transfer function Equivalence
- 21. Скачать презентацию



 20170216_tayny_simf_ork
20170216_tayny_simf_ork Афиша, плакат к спектаклю
Афиша, плакат к спектаклю Сканер
Сканер Графика Петровского времени
Графика Петровского времени Основы развивающего обучения в работе с детьми раннего и дошкольного возраста
Основы развивающего обучения в работе с детьми раннего и дошкольного возраста Панель управления гостиничным комплексом
Панель управления гостиничным комплексом Правка и гибка металла
Правка и гибка металла Геотехнологии горного дела. Технологические схемы выемки угля в длинных очистных забоях на крутых пластах. (лекция 6)
Геотехнологии горного дела. Технологические схемы выемки угля в длинных очистных забоях на крутых пластах. (лекция 6) 20161221_literaturnyy_auktsion
20161221_literaturnyy_auktsion Neighborhood
Neighborhood Геоинформационные технологии
Геоинформационные технологии ТОС НА НАБЕРЕЖНОЙ
ТОС НА НАБЕРЕЖНОЙ Воспитатель Житарь Виктория Николаевна
Воспитатель Житарь Виктория Николаевна Web-сайт кафедри біомедичної інженерії
Web-сайт кафедри біомедичної інженерії Видеокамеры
Видеокамеры Фильтрующие устройства для масел
Фильтрующие устройства для масел Буква Ш. Звук Ш
Буква Ш. Звук Ш Филимонковское, Верхнее Валуево, уч. 4 НАО
Филимонковское, Верхнее Валуево, уч. 4 НАО Список вечерних дел школьника
Список вечерних дел школьника Листаем творческий альбом!
Листаем творческий альбом! ОДО РВСН и ЖКС (3)
ОДО РВСН и ЖКС (3) Тула самоварная - творческий проект
Тула самоварная - творческий проект Кроссворд ВК
Кроссворд ВК Родословная
Родословная Зимний рисунок
Зимний рисунок Мошенники
Мошенники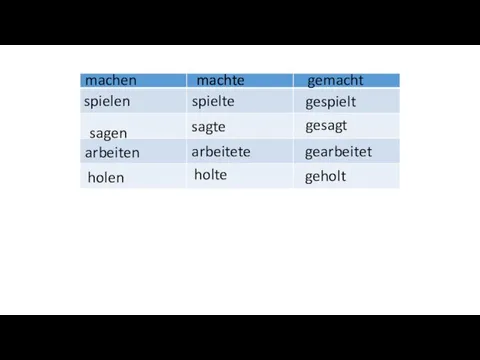 Verbformen
Verbformen Реконструкция СЭС АО Тамбовский завод Комсомолец имени Н.С. Артемова
Реконструкция СЭС АО Тамбовский завод Комсомолец имени Н.С. Артемова