Содержание
- 2. Importance of Vaccine Safety Decreases in disease risks and increased attention on vaccine risks Public confidence
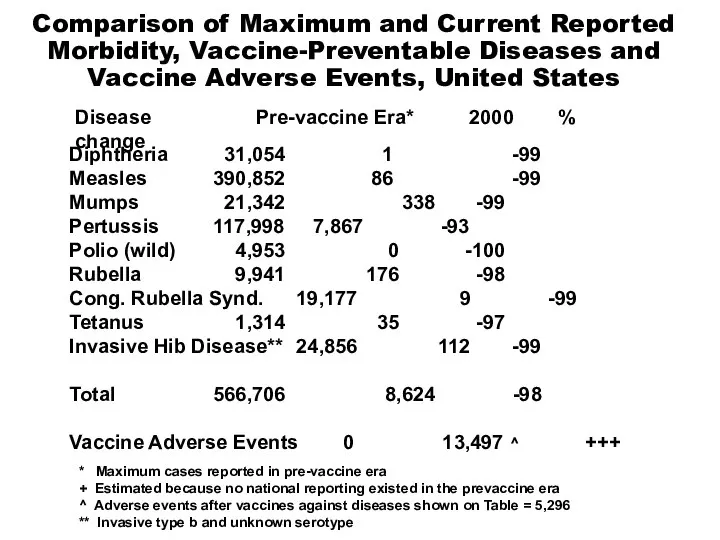
- 3. * Maximum cases reported in pre-vaccine era + Estimated because no national reporting existed in the
- 4. Importance of Vaccine Safety Ongoing safety monitoring needed for the development of sound policies and recommendations
- 5. Prelicensure Vaccine Safety Studies Laboratory Animals Humans
- 6. Prelicensure Human Studies Phases I, II, III trials Common reactions are identified Vaccines are tested in
- 7. Postlicensure Surveillance Identify rare reactions Monitor increases in known reactions Identify risk factors for reactions Identify
- 8. Postlicensure Vaccine Safety Activities Phase IV Trials ~10,000 participants better but still limited Large-Linked Databases Clinical
- 9. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) National reporting system Jointly administered by CDC and FDA Passive
- 10. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) Detects new or rare events increases in rates of known
- 11. Adverse Event Classification Vaccine-induced Vaccine-potentiated Programmatic error Coincidental
- 12. Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) Large-linked database Links vaccination and health records “Active surveillance” 8 HMOs ~2%
- 13. Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment (CISA) Network Improve understanding of vaccine safety issues at individual level Evaluate
- 14. Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) Established by National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act (1986) “No fault” program
- 15. The Provider’s Role Immunization providers can help to ensure the safety and efficacy of vaccines through
- 16. The Provider’s Role Immunization providers can help to ensure the safety and efficacy of vaccines through
- 17. Contraindication A condition in a recipient that increases the chance of a serious adverse reaction
- 18. Precaution A condition in a recipient that might Increase the chance or severity of an adverse
- 19. Invalid Contraindications to Vaccination Minor illness Mild/moderate local reaction or fever following a prior dose Antimicrobial
- 20. Benefit and Risk Communication Opportunities for questions should be provided before each vaccination Vaccine Information Statements
- 22. Скачать презентацию


















 Повышение эффективности взаимодействия транспортных средств и погрузочно-разгрузочных машин и механизмов на примере ООО ПЭК
Повышение эффективности взаимодействия транспортных средств и погрузочно-разгрузочных машин и механизмов на примере ООО ПЭК Простейший ремонт сантехнического оборудования
Простейший ремонт сантехнического оборудования Технология ремонта унитаза
Технология ремонта унитаза Sidorenko_Alina_Sergiyivna
Sidorenko_Alina_Sergiyivna Картошечка с грибочками
Картошечка с грибочками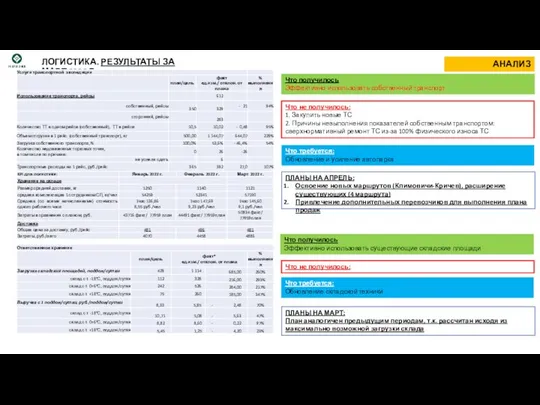 Логистика. Результаты за март 2022 г
Логистика. Результаты за март 2022 г Bumper ads in UAC The Value & Power of 6 Seconds
Bumper ads in UAC The Value & Power of 6 Seconds Материнская плата
Материнская плата M5Lesson5
M5Lesson5 ЦНППМ: внутренние и внешние ресурсы эффективной деятельности (Чаcть 1)
ЦНППМ: внутренние и внешние ресурсы эффективной деятельности (Чаcть 1) Общие понятия о лесозаготовительном производстве. Лекция 1. Основные понятия о лесозаготовительных предприятиях
Общие понятия о лесозаготовительном производстве. Лекция 1. Основные понятия о лесозаготовительных предприятиях Санитарный и противоэпидемиологический контроль
Санитарный и противоэпидемиологический контроль Бег как средство укрепления здоровья
Бег как средство укрепления здоровья Ознакомление с окружающим миром - Деревья и кусты
Ознакомление с окружающим миром - Деревья и кусты День Святого Валентина
День Святого Валентина Основы религиозных культур и светской этики
Основы религиозных культур и светской этики 20160308_prezentatsiya1
20160308_prezentatsiya1 Наша семья
Наша семья Направления повышения эффективности деятельности ООО ГБЦ
Направления повышения эффективности деятельности ООО ГБЦ Модернизация шлифовального станка
Модернизация шлифовального станка Профессия Лесопатолог
Профессия Лесопатолог Фазовые равновесия с участием фаялитных шлаков в процессах кислородно-факельной плавки
Фазовые равновесия с участием фаялитных шлаков в процессах кислородно-факельной плавки Декоративно-прикладное искусство моей семьи
Декоративно-прикладное искусство моей семьи Реконструкция игры властилин замка
Реконструкция игры властилин замка Шаблон презентации исследования
Шаблон презентации исследования Безопасность автоматизированных систем в финансовобанковской сфере
Безопасность автоматизированных систем в финансовобанковской сфере Благотворительная просветительская акция. Рождество приходит к каждому
Благотворительная просветительская акция. Рождество приходит к каждому 20111108_zagadki_o_lete_chast_4
20111108_zagadki_o_lete_chast_4