Содержание
- 2. An adjective is a word which describes or gives more information about a noun or pronoun.
- 3. Functions in the sentence Functions of an attribute When an adjective is placed before its noun,
- 4. Functions of predicative When it follows a linking verb, it is used predicatively. The bush is
- 5. Functions of postpositive Sometimes an adjective occurs immediately after a noun. Postposition is obligatory, when the
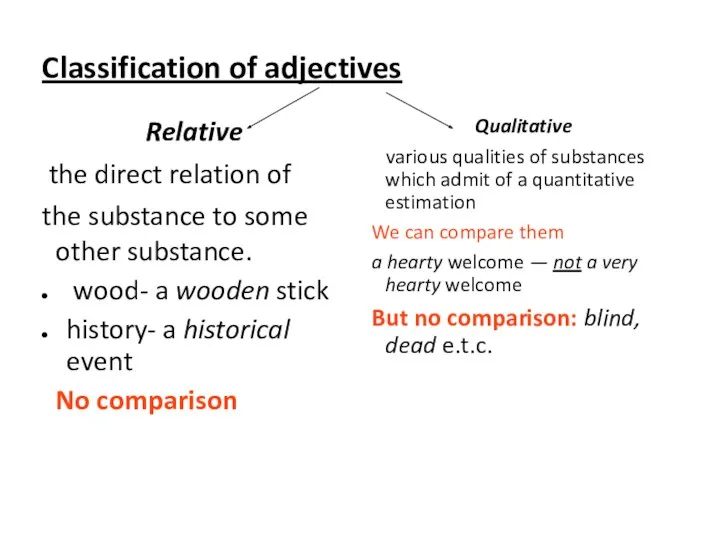
- 6. Classification of adjectives Relative the direct relation of the substance to some other substance. wood- a
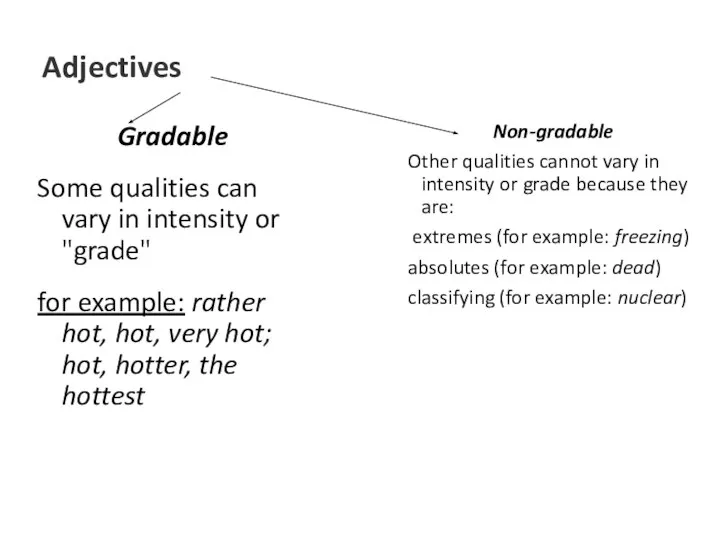
- 7. Adjectives Gradable Some qualities can vary in intensity or "grade" for example: rather hot, hot, very
- 8. Two kinds of adjectives: Gradable: You can be very cold or a bit cold. Gradable adjectives
- 10. The nounal forms of adjectives (adjectivids) fall into two main grammatical subgroups: pluralia tantum (the English,
- 11. The synthetical forms of comparison positive degree The boy is strong comparative degree He is stronger
- 12. The analytical forms of comparison. Auxiliaries more and most. two-syllable words with the stress on the
- 13. Most-combination can take the indefinite article, meaning “very” - It was a most dangerous trip (elative
- 14. Auxiliaries less and least. Negative degree, semantically analogous to combinations of more/most positive degree – The
- 16. Скачать презентацию











 Галерея изображений женского русского народного костюма
Галерея изображений женского русского народного костюма Урок 2_Ист. города 7
Урок 2_Ист. города 7 Коренное население Америки и его культура
Коренное население Америки и его культура Заболевания органов дыхания. Острая пневмония.
Заболевания органов дыхания. Острая пневмония.  Направление работы кадрового резерва: Здравоохранение
Направление работы кадрового резерва: Здравоохранение Курсовий проект з дисципліни "Програмування" на тему: напівпровідникові прилади
Курсовий проект з дисципліни "Програмування" на тему: напівпровідникові прилади Презентация Принятие христианства на Руси
Презентация Принятие христианства на Руси Основы теории устойчивости систем
Основы теории устойчивости систем Презентация "Рафаэль Санти" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Рафаэль Санти" - скачать презентации по МХК Чемпионат по мини-футболу среди команд предприятий и структурных подразделений дивизиона «Северсталь Российская сталь»
Чемпионат по мини-футболу среди команд предприятий и структурных подразделений дивизиона «Северсталь Российская сталь» Азбука Морзе
Азбука Морзе Лекция 9 (C/C++). Стиль программирования. Структуры в Си. Объединения - union
Лекция 9 (C/C++). Стиль программирования. Структуры в Си. Объединения - union Этапы развития метрологии
Этапы развития метрологии  История возникновения и развития хоккея на Южном Урале
История возникновения и развития хоккея на Южном Урале Участие прокурора в рассмотрении дел судами. Лекция № 6:
Участие прокурора в рассмотрении дел судами. Лекция № 6: Развертки поверхностей
Развертки поверхностей Сергей Викторович Лавров
Сергей Викторович Лавров  Информационный портал «Будущее России. Национальные проекты»
Информационный портал «Будущее России. Национальные проекты» Жанры фольклора
Жанры фольклора Презентация "Производство и издержки" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Производство и издержки" - скачать презентации по Экономике Подарки в деловых отношениях
Подарки в деловых отношениях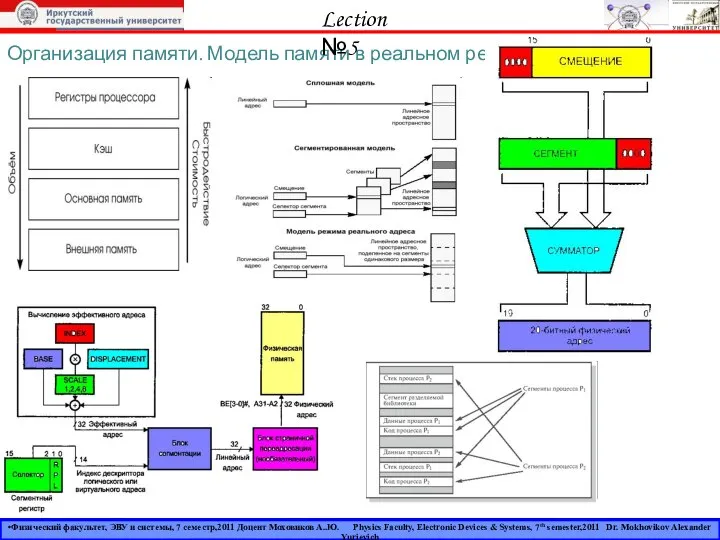 Организация памяти
Организация памяти Волейбол, правила игры
Волейбол, правила игры Федерация ездового спорта Саратовской области. Питомник сибирских хаски «DogWinter»
Федерация ездового спорта Саратовской области. Питомник сибирских хаски «DogWinter» Герби України
Герби України Презентация Сущность понятия «научное исследование» Выполнили: Никонов Владислав Рыбалко Владислав Группа 1309
Презентация Сущность понятия «научное исследование» Выполнили: Никонов Владислав Рыбалко Владислав Группа 1309 Предельные деформации бетона
Предельные деформации бетона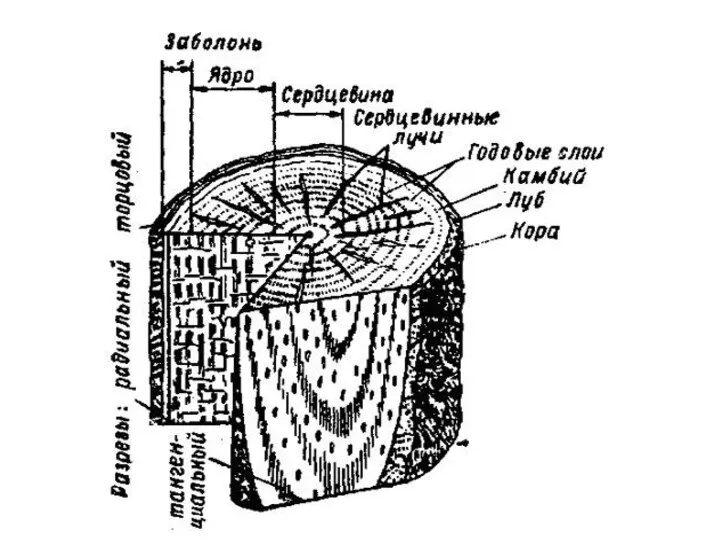 Микроструктура древесины сосны
Микроструктура древесины сосны