Содержание
- 2. Table of Contents Printing to the Console Printing Strings and Numbers Reading from the Console Reading
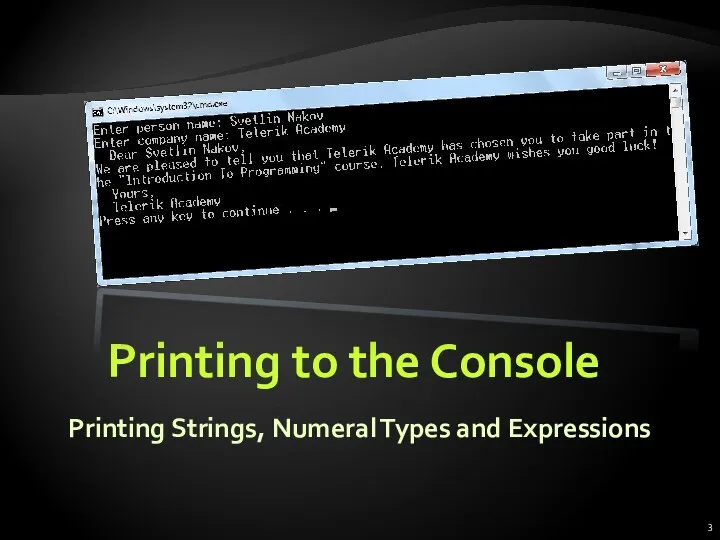
- 3. Printing to the Console Printing Strings, Numeral Types and Expressions
- 4. Printing to the Console Console is used to display information in a text window Can display
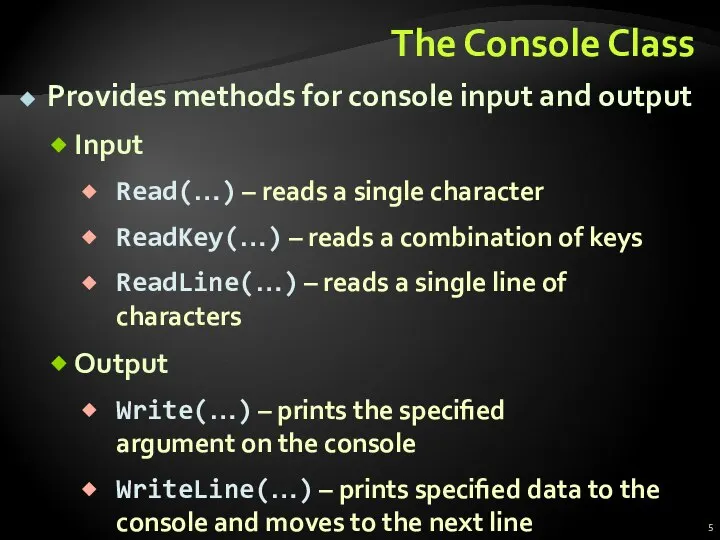
- 5. The Console Class Provides methods for console input and output Input Read(…) – reads a single
- 6. Console.Write(…) Printing more than one variable using a formatting string int a = 15; ... Console.Write(a);
- 7. Console.WriteLine(…) Printing more than one variable using a formatting string string str = "Hello C#!"; ...
- 8. Printing to the Console – Example static void Main() { string name = "Peter"; int age
- 9. Using Parameters – Example static void Main() { int a=2, b=3; Console.Write("{0} + {1} =", a,
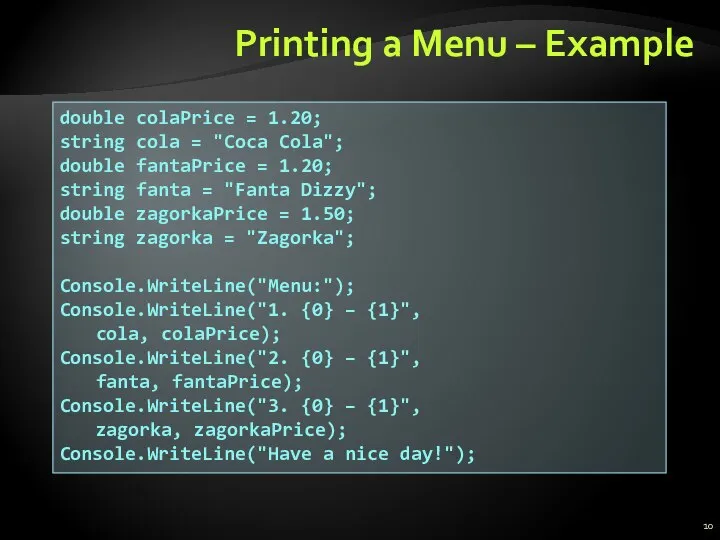
- 10. Printing a Menu – Example double colaPrice = 1.20; string cola = "Coca Cola"; double fantaPrice
- 11. Printing to the Console Live Demo
- 12. Reading from the Console Reading Strings and Numeral Types
- 13. Reading from the Console We use the console to read information from the command line We
- 14. Console.Read() Gets a single character from the console (after [Enter] is pressed) Returns a result of
- 15. Reading Characters from the Console Live Demo
- 16. Console.ReadKey() Waits until a combination of keys is pressed Reads a single character from console or
- 17. Reading Keys from the Console Live Demo
- 18. Console.ReadLine() Gets a line of characters Returns a string value Returns null if the end of
- 19. Reading Strings from the Console Live Demo
- 20. Reading Numeral Types Numeral types can not be read directly from the console To read a
- 21. Converting Strings to Numbers Numeral types have a method Parse(…) for extracting the numeral value from
- 22. Reading Numbers from the Console – Example static void Main() { int a = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); int
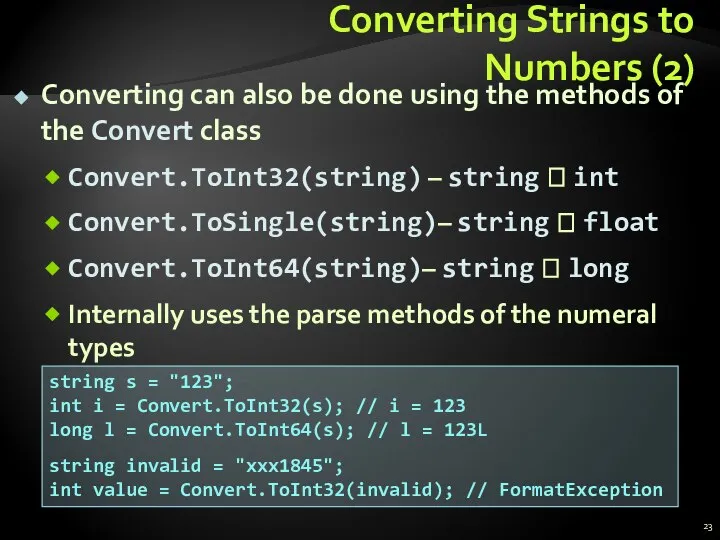
- 23. Converting Strings to Numbers (2) Converting can also be done using the methods of the Convert
- 24. Reading Numbers from the Console Live Demo
- 25. Error Handling when Parsing Sometimes we want to handle the errors when parsing a number Two
- 26. Parsing with TryParse() Live Demo
- 27. Reading and Printing to the Console Various Examples Examples
- 28. Printing a Letter – Example Console.Write("Enter person name: "); string person = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("Enter company name:
- 29. Printing a Letter Live Demo
- 30. Calculating Area – Example Console.WriteLine("This program calculates " + "the area of a rectangle or a
- 31. Calculating Area Live Demo
- 32. Summary We have discussed the basic input and output methods of the class Console Write(…) and
- 33. Exercises Write a program that reads 3 integer numbers from the console and prints their sum.
- 34. Exercises (2) Write a program that reads two positive integer numbers and prints how many numbers
- 36. Скачать презентацию








![Console.Read() Gets a single character from the console (after [Enter] is](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1359925/slide-13.jpg)



















 Каким должен быть кабинет психолога (идеальная модель)
Каким должен быть кабинет психолога (идеальная модель) Изучение машин и оборудования для организации рельефа и производства дорожных работ
Изучение машин и оборудования для организации рельефа и производства дорожных работ Технология ремонта и проверки стационарной ССМ № 3
Технология ремонта и проверки стационарной ССМ № 3 Презентация на тему "моя воспитательная концепция" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "моя воспитательная концепция" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Структура экономической деятельности таможенных органов Выполнили студентки экономического факультета третьего курса группы э1
Структура экономической деятельности таможенных органов Выполнили студентки экономического факультета третьего курса группы э1 Таможенная экспертиза меда
Таможенная экспертиза меда Винсент Виллем ван Гог Слободяник Артём
Винсент Виллем ван Гог Слободяник Артём Договор личного страхования
Договор личного страхования Релейная защита
Релейная защита Растворы ВМС
Растворы ВМС Международные отношения России и Китая
Международные отношения России и Китая Исследование качества жизни подростков 14-17
Исследование качества жизни подростков 14-17 Основы алгоритмизации и быстрое введение в язык Си
Основы алгоритмизации и быстрое введение в язык Си игра правописание гласных 3 класс - презентация для начальной школы
игра правописание гласных 3 класс - презентация для начальной школы Современные компьютерные устройства
Современные компьютерные устройства Политологический анализ демократии
Политологический анализ демократии Тромбоцитопении у детей
Тромбоцитопении у детей Кластер (градостроительство)
Кластер (градостроительство) «Организация процесса самообразования в педагогической деятельности учителя» Автор: заместитель директора по методической раб
«Организация процесса самообразования в педагогической деятельности учителя» Автор: заместитель директора по методической раб b2c32ee31b7d73ec283cb7b321ca54
b2c32ee31b7d73ec283cb7b321ca54 Физиология сердечно- сосудистой системы
Физиология сердечно- сосудистой системы Презентация "Проблема стиля и стилизации в изобразительном искусстве. Рисуем собаку" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Проблема стиля и стилизации в изобразительном искусстве. Рисуем собаку" - скачать презентации по МХК Основы менеджмента
Основы менеджмента Идеология антикоррупционной политики в России
Идеология антикоррупционной политики в России ООП на Delphi – 5: Элементы ввода и вывода информации. Обработка исключений
ООП на Delphi – 5: Элементы ввода и вывода информации. Обработка исключений Особенности проектирования тепловых сетей в районах с вечномерзлыми грунтами
Особенности проектирования тепловых сетей в районах с вечномерзлыми грунтами Быт знатных людей в древней Руси
Быт знатных людей в древней Руси Трёхсторонний диалог. Инструмент закрытия сделки
Трёхсторонний диалог. Инструмент закрытия сделки