Содержание
- 2. Enum
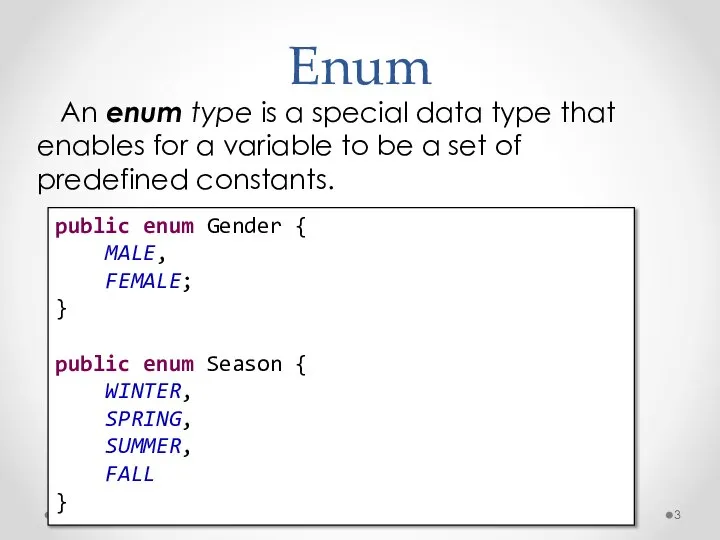
- 3. Enum An enum type is a special data type that enables for a variable to be
- 4. The enum class body can include methods and other fields. public enum Planet { MERCURY(3.303e+23, 2.4397e6),
- 5. Enum example public enum Direction { NORTH(0, 1), EAST(1, 0), SOUTH(0, -1), WEST(-1, 0); private final
- 6. Enum All enums implicitly extend java.lang.Enum. All enum constants implicitly have public static final modifier You
- 7. Enum Non static methods of enum: ordinal() - Returns the ordinal of this enumeration constant (its
- 8. Annotation Annotation is a form of metadata, provide data about a program that is not part
- 9. Predefined Annotation Types @Deprecated @Override @SuppressWarnings /** * @deprecated explanation of why it was deprecated */
- 10. Number
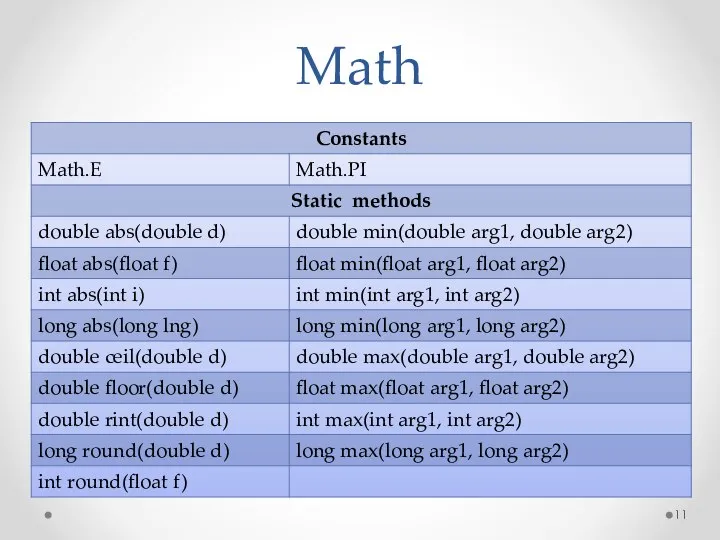
- 11. Math
- 12. Math
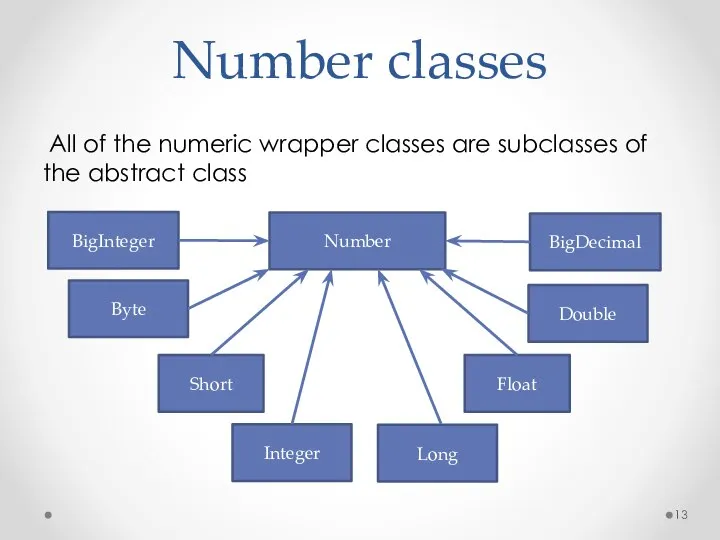
- 13. Number classes All of the numeric wrapper classes are subclasses of the abstract class Number BigInteger
- 14. Numbers There are three reasons that you might use a Number object rather than a primitive:
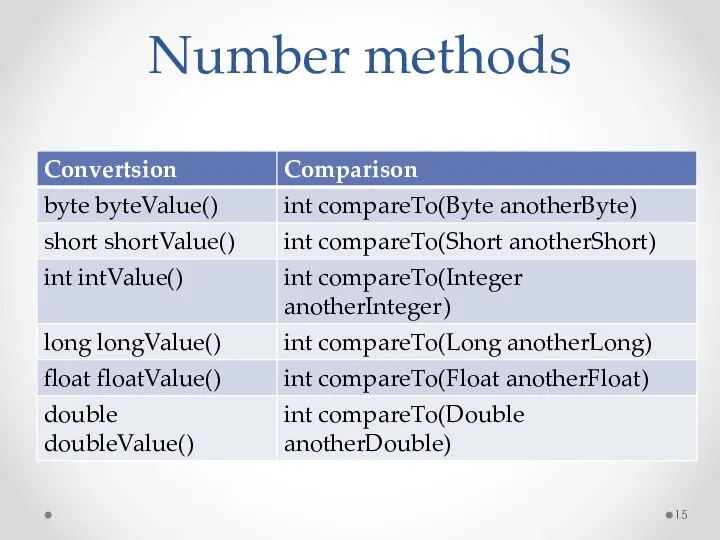
- 15. Number methods
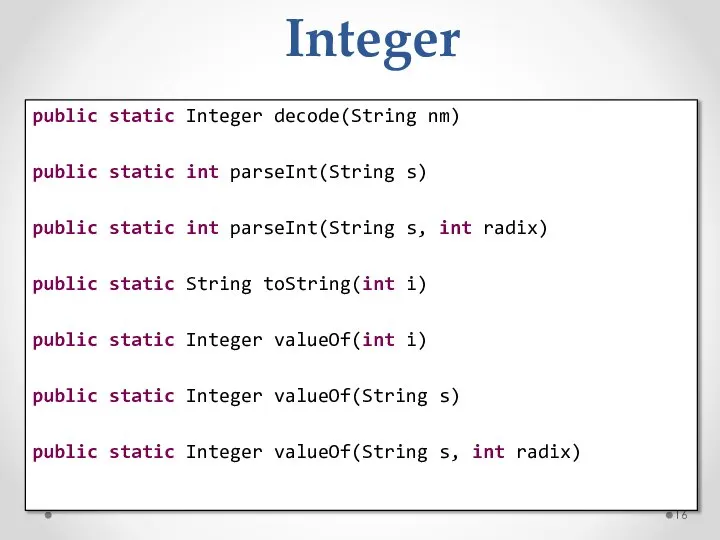
- 16. Integer public static Integer decode(String nm) public static int parseInt(String s) public static int parseInt(String s,
- 17. Double
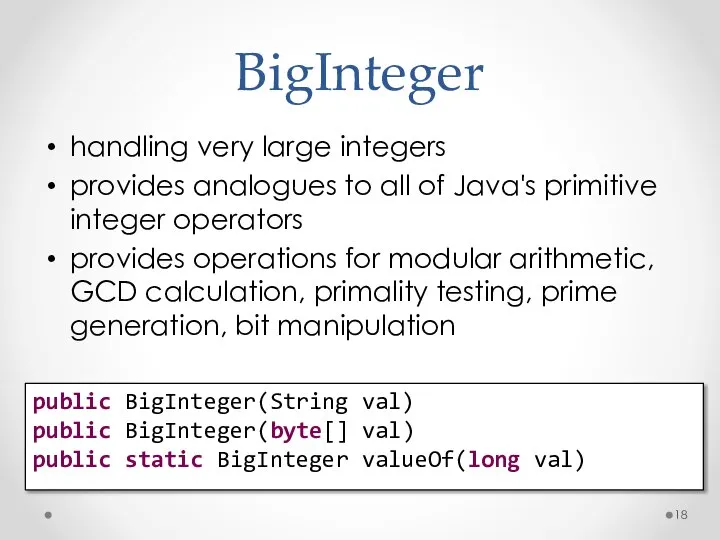
- 18. BigInteger handling very large integers provides analogues to all of Java's primitive integer operators provides operations
- 19. BigInteger methods public BigInteger add(BigInteger val) public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) public BigInteger
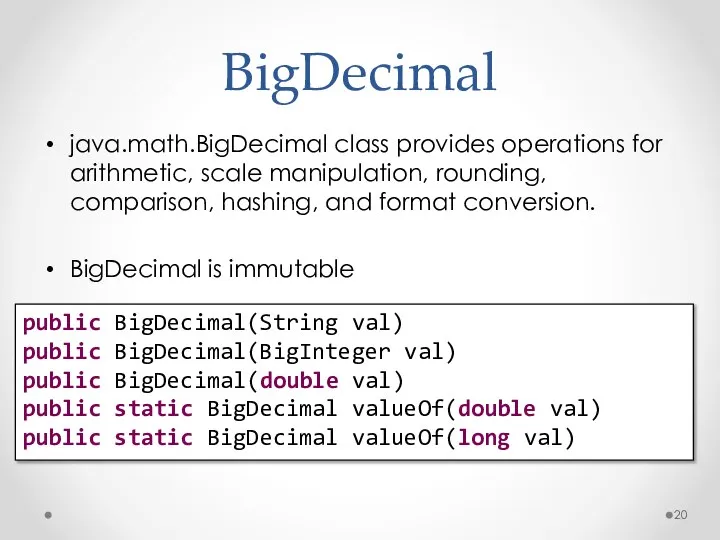
- 20. BigDecimal java.math.BigDecimal class provides operations for arithmetic, scale manipulation, rounding, comparison, hashing, and format conversion. BigDecimal
- 21. BigDecimal methods public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend) public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend) public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand, MathContext mc)
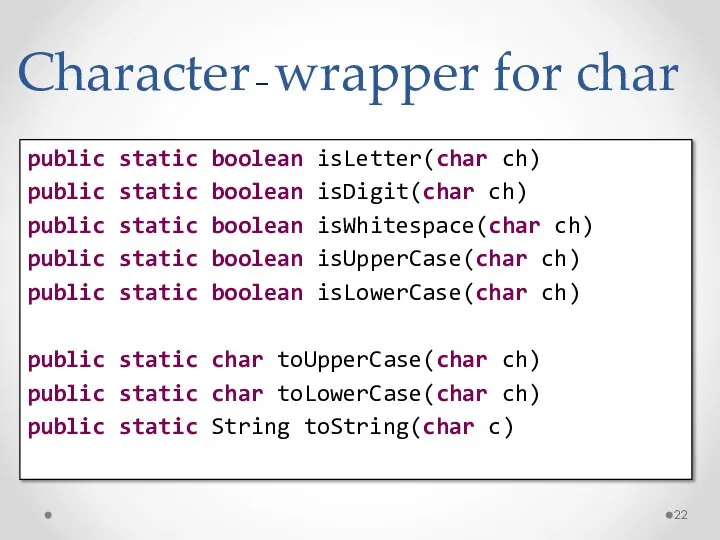
- 22. Character – wrapper for char public static boolean isLetter(char ch) public static boolean isDigit(char ch) public
- 23. Autoboxing Autoboxing is the automatic conversion that the Java compiler makes between the primitive types and
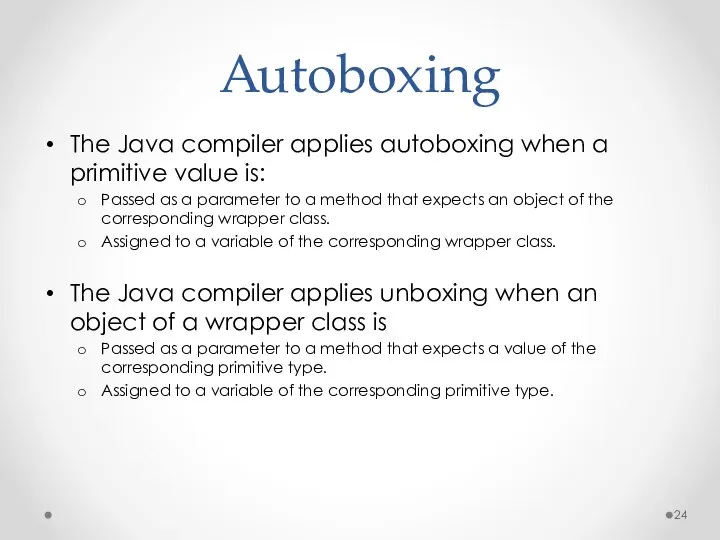
- 24. Autoboxing The Java compiler applies autoboxing when a primitive value is: Passed as a parameter to
- 25. Wrapper classes
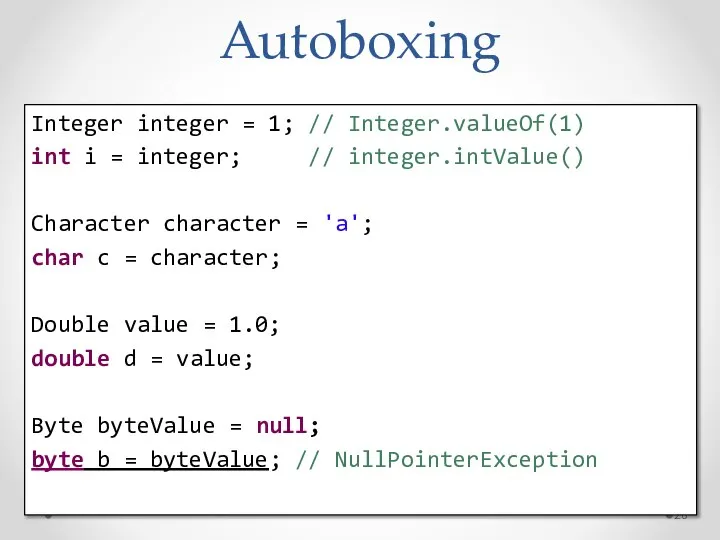
- 26. Autoboxing Integer integer = 1; // Integer.valueOf(1) int i = integer; // integer.intValue() Character character =
- 27. Autoboxing public static List asList(final int[] a) { return new AbstractList () { public Integer get(int
- 28. String
- 29. String Строка – объект класса String String creation public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable ,
- 30. Working with strings Длина строки String concatenation String s = "Some text"; s.length(); "Text".length(); s =
- 31. Converting string to number Wrapper classes Primitive types Integer value = Integer.valueOf("1"); Double value = Double.valueOf("1.0");
- 32. Converting number to string String Number classes String.valueOf(1); String.valueOf(1.0); Integer.toString(1); Double.toString(1.0);
- 33. Getting Characters and Substrings by Index String text = "Niagara. O roar again!"; char aChar =
- 34. String methods public String[] split(String regex) public String[] split(String regex, int limit) public CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex,
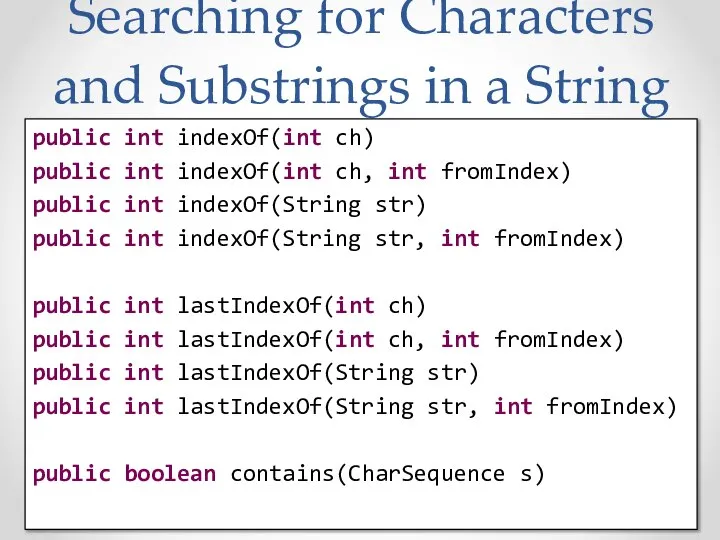
- 35. Searching for Characters and Substrings in a String public int indexOf(int ch) public int indexOf(int ch,
- 36. Replacing Characters and Substrings into a String public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) public String replace(CharSequence
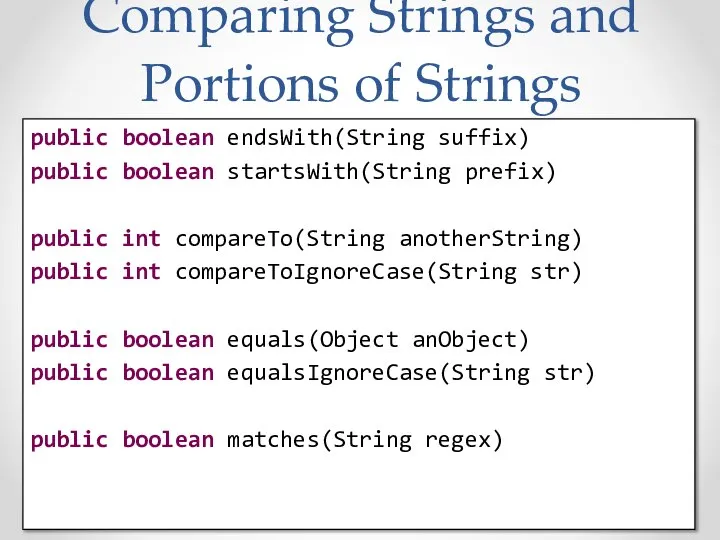
- 37. Comparing Strings and Portions of Strings public boolean endsWith(String suffix) public boolean startsWith(String prefix) public int
- 38. String immutability String objects are immutable String is not changed: Currently “s” refers to new String
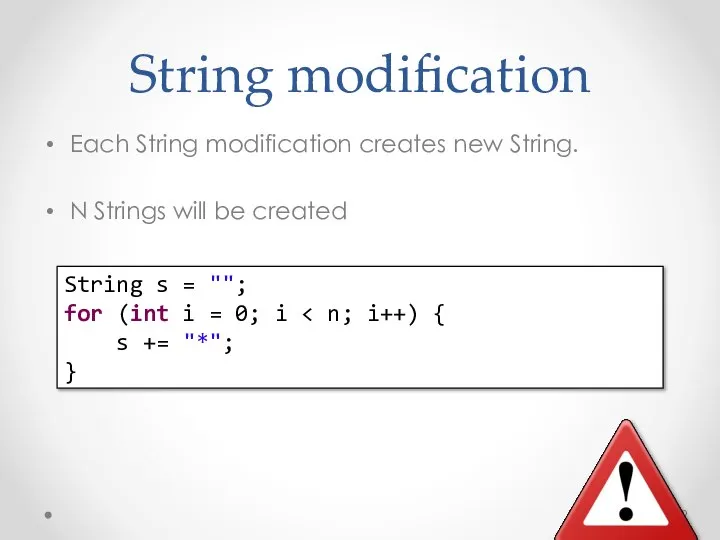
- 39. String modification Each String modification creates new String. N Strings will be created String s =
- 40. StringBuilder Like String objects, except that they can be modified. Strings should always be used unless
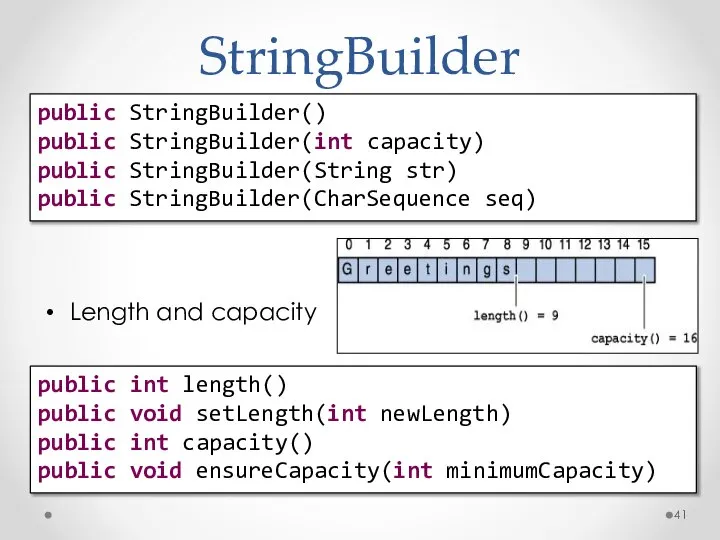
- 41. StringBuilder Конструкторы Length and capacity public StringBuilder() public StringBuilder(int capacity) public StringBuilder(String str) public StringBuilder(CharSequence seq)
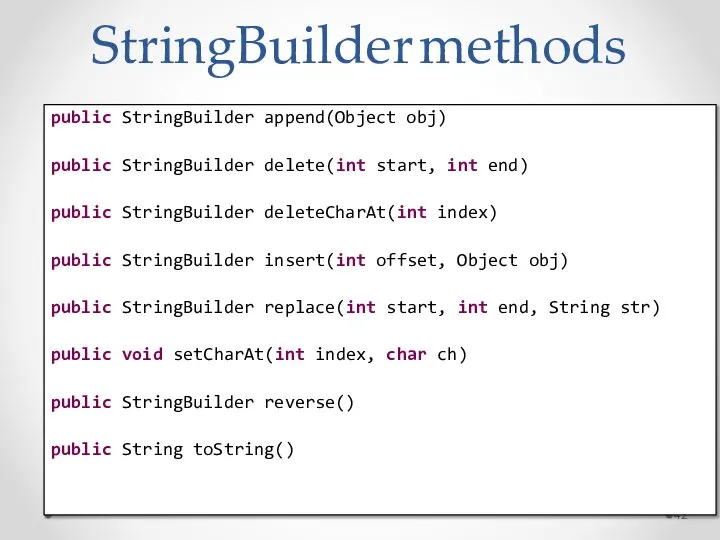
- 42. StringBuilder methods public StringBuilder append(Object obj) public StringBuilder delete(int start, int end) public StringBuilder deleteCharAt(int index)
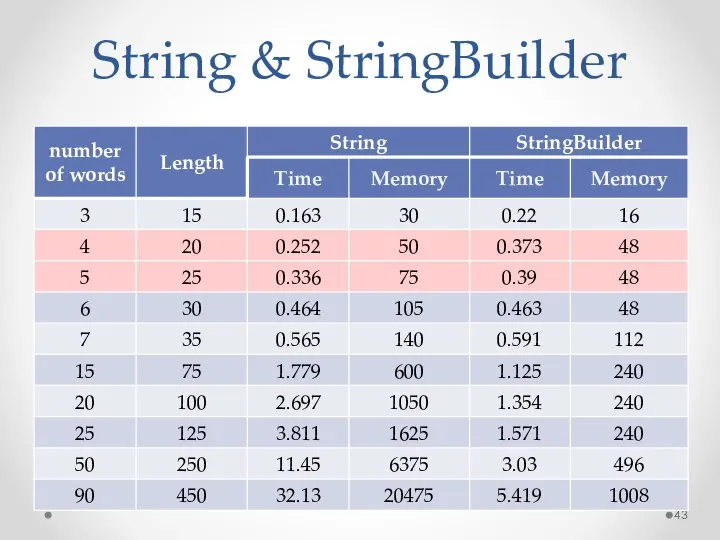
- 43. String & StringBuilder
- 44. Date
- 45. Working with dates Main classes java.util.Date java.util.Calendar For Database java.sql.Timestamp java.sql.Date java.sql.Time
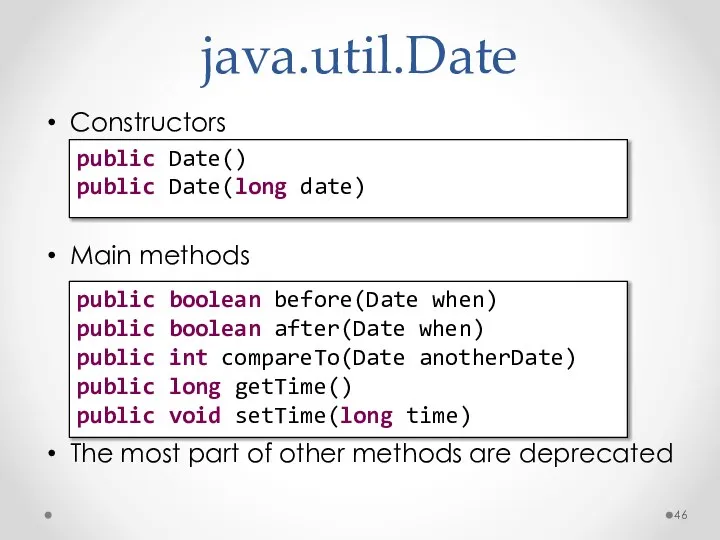
- 46. java.util.Date Constructors Main methods The most part of other methods are deprecated public Date() public Date(long
- 47. Calendar Main methods Constants: ERA, YEAR, MONTH, WEEK_OF_YEAR, WEEK_OF_MONTH, DAY_OF_MONTH, DAY_OF_YEAR, DAY_OF_WEEK, AM_PM, HOUR, HOUR_OF_DAY, MINUTE,
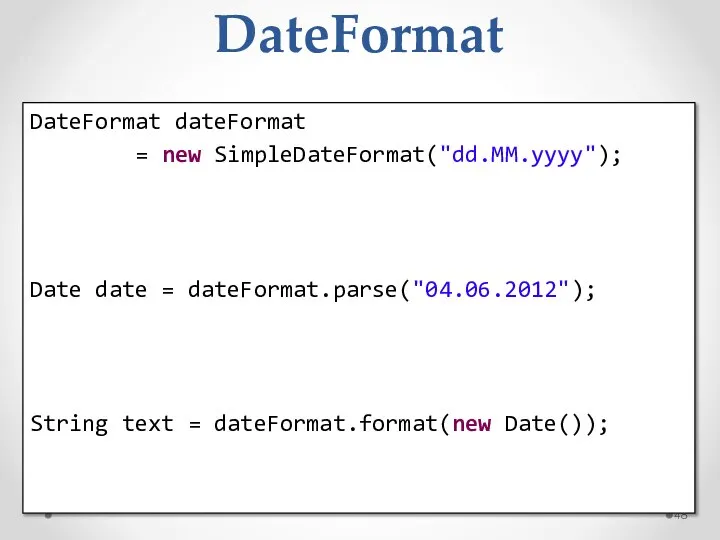
- 48. DateFormat DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd.MM.yyyy"); Date date = dateFormat.parse("04.06.2012"); String text = dateFormat.format(new Date());
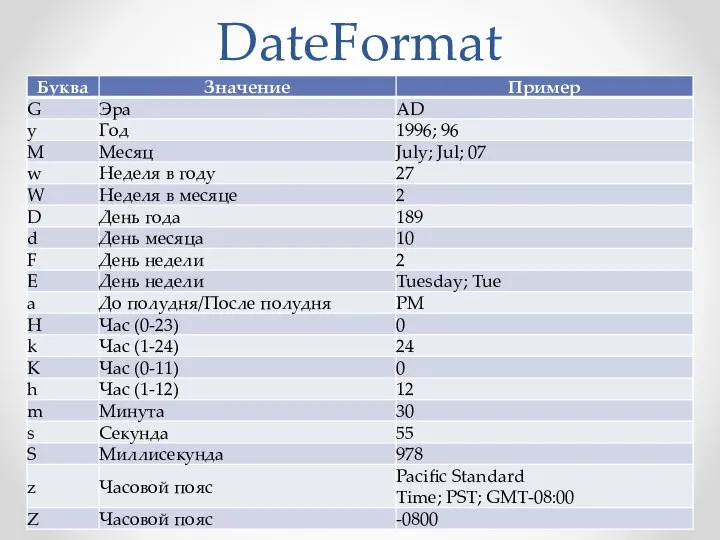
- 49. DateFormat
- 51. Task№3 – Общие требования Общие требования: Код должен быть отформатирован и соответствовать Java Code Convention. Решение
- 52. Task№3 – Задание №1 В Учебном Центре компании проходят обучение студенты. Каждый студент проходит обучение по
- 53. Task№3 – список данных о студентах: STUDENT: Ivanov Ivan CURRICULUM: J2EE Developer START_DATE: COURSE DURATION (hrs)
- 54. Task№3 – список данных о студентах: STUDENT: Ivanov Ivan CURRICULUM: J2EE Developer START_DATE: COURSE DURATION (hrs)
- 55. Task№3 – Задание 1 Условия: Учебными считаются все дни недели при условии 8-ми часового учебного дня
- 56. Task№3 – Задание 1 Условия: Учебными считаются все дни недели при условии 8-ми часового учебного дня
- 57. Task№3 – Задание 1 2. Вывести подробный отчет по обучению: ФИО, рабочее время (с 10 до
- 58. Task№3 – Дополнительное задание Реализовать template generator. Например, есть шаблон: “Hello, ${name}” , и значение name=”Reader”
- 60. Скачать презентацию















![Autoboxing public static List asList(final int[] a) { return new AbstractList](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1373872/slide-26.jpg)






![String methods public String[] split(String regex) public String[] split(String regex, int](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1373872/slide-33.jpg)















 Магматические породы
Магматические породы Поиск работы: этапы, способы, приемы
Поиск работы: этапы, способы, приемы Презентация "Дали художник сюрреализма" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Дали художник сюрреализма" - скачать презентации по МХК Техника трюков на BMX
Техника трюков на BMX Основы алгоритмизации и программирование
Основы алгоритмизации и программирование Процесс производства ПО: методы, технология и инструментальные средства
Процесс производства ПО: методы, технология и инструментальные средства Введение в воинскую специальность
Введение в воинскую специальность  ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ ВОЗДЕЛЫВАНИЯ ОВСА
ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ ВОЗДЕЛЫВАНИЯ ОВСА Первое Соборное послание святого апостола Петра. Глава 2
Первое Соборное послание святого апостола Петра. Глава 2 Архитектура 20 – 30 гг. Подготовила – САМБУР ВЕРА 11 «А»
Архитектура 20 – 30 гг. Подготовила – САМБУР ВЕРА 11 «А» ATA — параллельный интерфейс подключения накопителей к компьютеру
ATA — параллельный интерфейс подключения накопителей к компьютеру Фарфор фаянс ыдыс аяқ түрлері
Фарфор фаянс ыдыс аяқ түрлері Качество как объект управления
Качество как объект управления Женские шляпки
Женские шляпки Гражданское общество и политическая власть. Подготовили Ерченко А. и Гордеева К.
Гражданское общество и политическая власть. Подготовили Ерченко А. и Гордеева К. Коммуникации Церкви в кризисных ситуациях Что говорить когда у нас проблемы? - презентация
Коммуникации Церкви в кризисных ситуациях Что говорить когда у нас проблемы? - презентация Способы и области применения герметических мастик
Способы и области применения герметических мастик Стандарты финансовой отчетности
Стандарты финансовой отчетности  МОУ «Средняя общеобразовательная школа №37»г.Рязань Шемонаева Лилия Александровна – учитель информатики, экономики
МОУ «Средняя общеобразовательная школа №37»г.Рязань Шемонаева Лилия Александровна – учитель информатики, экономики Преобразование графиков тригонометрических функций - презентация по Алгебре
Преобразование графиков тригонометрических функций - презентация по Алгебре Корпускулярно-волновой дуализм
Корпускулярно-волновой дуализм  ASEL ASAN BIOCH
ASEL ASAN BIOCH ИТ для людей со специальными возможностями
ИТ для людей со специальными возможностями Жұдырықша механизмдегі негізгі өлшемдері және параметрлері
Жұдырықша механизмдегі негізгі өлшемдері және параметрлері Исследовательская работа « Изучение влияния корма на продолжительность жизни мух». Выполнила учащаяся 5 класса Дружинина Анна Сер
Исследовательская работа « Изучение влияния корма на продолжительность жизни мух». Выполнила учащаяся 5 класса Дружинина Анна Сер КАЗКА “ПРИГОДИ БЕРЕЗОВОГО ЛИСТОЧКА”
КАЗКА “ПРИГОДИ БЕРЕЗОВОГО ЛИСТОЧКА” Терроризм – глобальная проблема современности
Терроризм – глобальная проблема современности Розвиток міжнародного захисту прав національних меншин в системі ООН. Принцип недискримінації
Розвиток міжнародного захисту прав національних меншин в системі ООН. Принцип недискримінації