Содержание
- 2. What is Ion Scattering Spectroscopy? Ion scattering spectroscopy (ISS), is a surface-sensitive analytical technique used to
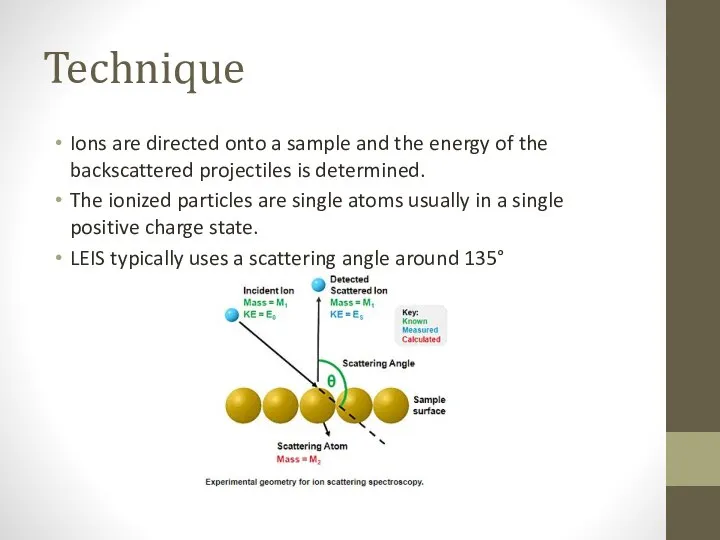
- 3. Technique Ions are directed onto a sample and the energy of the backscattered projectiles is determined.
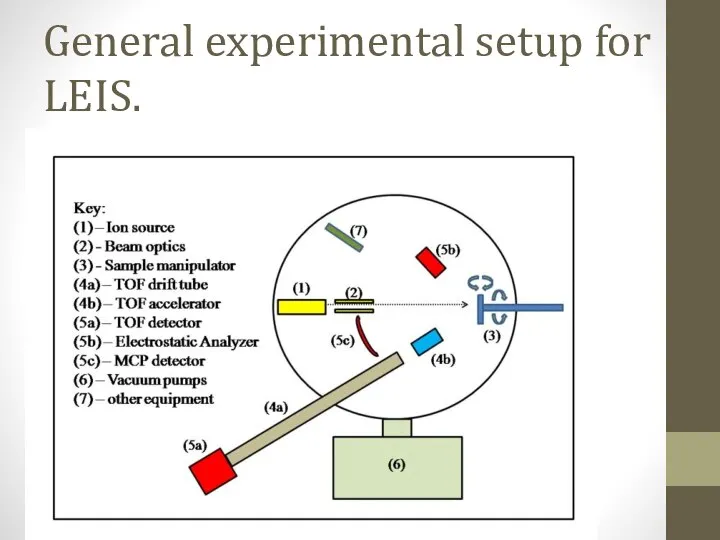
- 4. General experimental setup for LEIS.
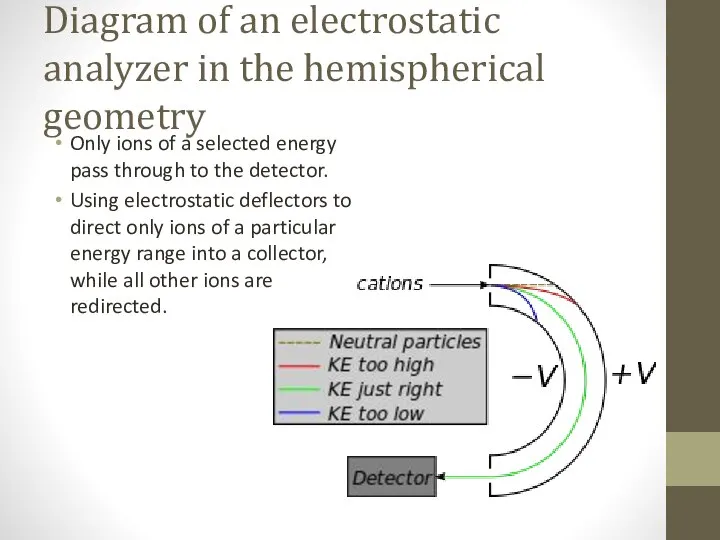
- 5. Diagram of an electrostatic analyzer in the hemispherical geometry Only ions of a selected energy pass
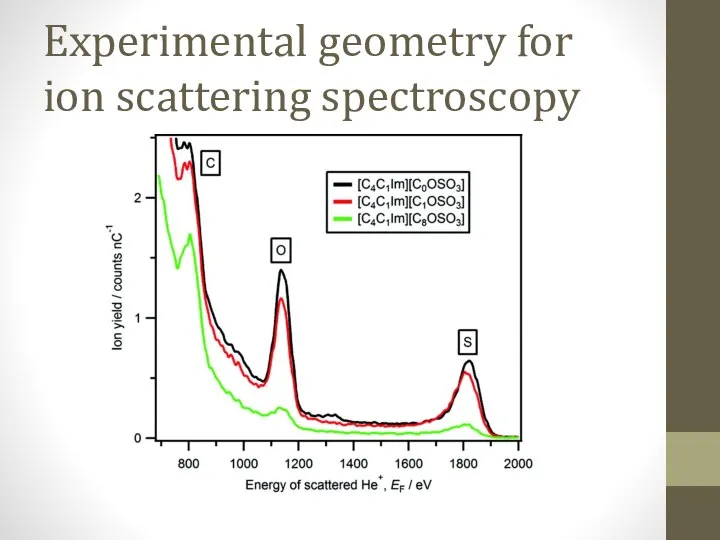
- 6. Experimental geometry for ion scattering spectroscopy
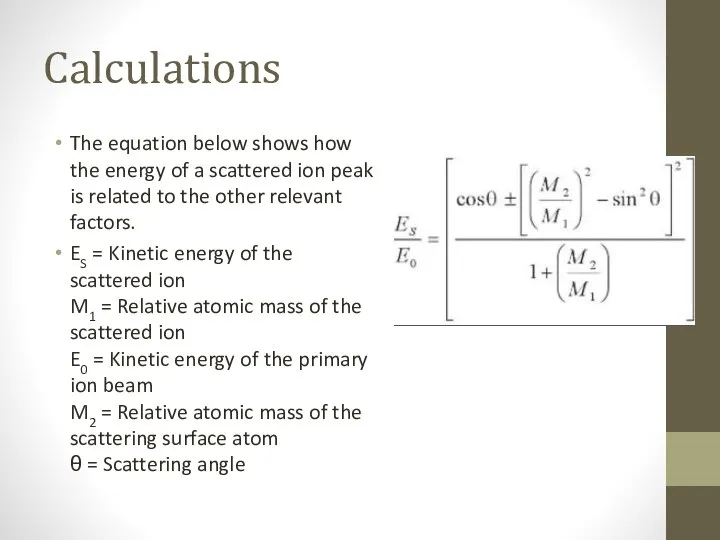
- 7. Calculations The equation below shows how the energy of a scattered ion peak is related to
- 9. Скачать презентацию

 Программирование алгоритмов обработки сложных данных
Программирование алгоритмов обработки сложных данных Волшебный мастер - презентация для начальной школы
Волшебный мастер - презентация для начальной школы Православный храм. Облачение священника
Православный храм. Облачение священника Презентация "Сервисология. Введение" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Сервисология. Введение" - скачать презентации по Экономике Этические правила служебного поведения и проф. служебной деятельности гос. гражданских служащих РФ
Этические правила служебного поведения и проф. служебной деятельности гос. гражданских служащих РФ Презентация на тему "Режим дня ученика младших классов" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Режим дня ученика младших классов" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Деревянное зодчество Древней Руси
Деревянное зодчество Древней Руси Права и свободы человека и гражданина
Права и свободы человека и гражданина Чтение чертежа общего вида
Чтение чертежа общего вида Философия Гегеля
Философия Гегеля Отечественная война 1812 года глазами художников-баталистов
Отечественная война 1812 года глазами художников-баталистов Устройство автомобиля. Кривошипно-шатунный механизм
Устройство автомобиля. Кривошипно-шатунный механизм Ave Maria
Ave Maria Презентация на тему "Мориамин" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "Мориамин" - скачать презентации по Медицине Презентация "Сотворение мира" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Сотворение мира" - скачать презентации по МХК Электронная почта и другие сервисы компьютерных сетей
Электронная почта и другие сервисы компьютерных сетей Внешняя политика США в Южной Африке
Внешняя политика США в Южной Африке Химия элементов d- элементы 3-4
Химия элементов d- элементы 3-4 Игорь Петрович Иванов (1923 – 1992). Экспедиции по Макаренковским местам Украины и России
Игорь Петрович Иванов (1923 – 1992). Экспедиции по Макаренковским местам Украины и России Булевы функции
Булевы функции Многими достопримечательностями, культурными и научными достижениями славится город Воронеж
Многими достопримечательностями, культурными и научными достижениями славится город Воронеж Методы исследования истории политики. (Тема 5)
Методы исследования истории политики. (Тема 5) Инновационная политика КрасГМУ. Красноярский биомедицинский кластер проф. А.Б.Салмина, проректор по инновационному развитию
Инновационная политика КрасГМУ. Красноярский биомедицинский кластер проф. А.Б.Салмина, проректор по инновационному развитию  Резьба по дереву
Резьба по дереву Программа тренировок для развития взрывной силы и силовой выносливости «НОРД»
Программа тренировок для развития взрывной силы и силовой выносливости «НОРД» Особенности формирования имущественных налогов на базе кадастровой стоимости в Самарской области
Особенности формирования имущественных налогов на базе кадастровой стоимости в Самарской области Презентация Служба в органах ОВД РФ
Презентация Служба в органах ОВД РФ Проектирование и монтаж станка-качалки для оборудования скважины с дебитом Q = 20 м3 /сутки и глубиной подвески насоса 1100 м
Проектирование и монтаж станка-качалки для оборудования скважины с дебитом Q = 20 м3 /сутки и глубиной подвески насоса 1100 м