Microsoft official course. Creating methods, handling exceptions, and monitoring applications. (Module 2)
Содержание
- 2. Module Overview Creating and Invoking Methods Creating Overloaded Methods and Using Optional and Output Parameters Handling
- 3. Lesson 1: Creating and Invoking Methods What Is a Method? Creating Methods Invoking Methods Debugging Methods
- 4. What Is a Method? Methods encapsulate operations that protect data .NET Framework applications contain a Main
- 5. Creating Methods Methods comprise two elements: Method specification (return type, name, parameters) Method body Use the
- 6. Invoking Methods To call a method specify: Method name Any arguments to satisfy parameters var upTime
- 7. Debugging Methods Visual Studio provides debug tools that enable you to step through code When debugging
- 8. Demonstration: Creating, Invoking, and Debugging Methods In this demonstration, you will create a method, invoke the
- 9. Text Continuation
- 10. Lesson 2: Creating Overloaded Methods and Using Optional and Output Parameters Creating Overloaded Methods Creating Methods
- 11. Creating Overloaded Methods Overloaded methods share the same method name Overloaded methods have a unique signature
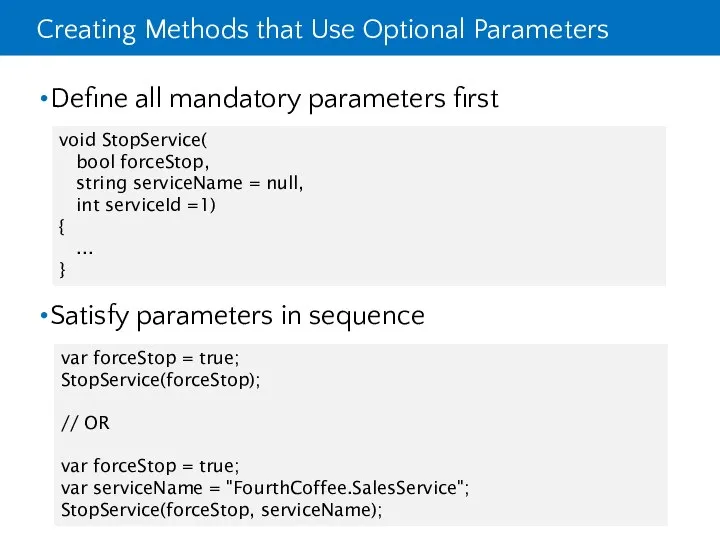
- 12. Creating Methods that Use Optional Parameters Define all mandatory parameters first Satisfy parameters in sequence void
- 13. Calling a Method by Using Named Arguments Specify parameters by name Supply arguments in a sequence
- 14. Creating Methods that Use Output Parameters Use the out keyword to define an output parameter Provide
- 15. Lesson 3: Handling Exceptions What Is an Exception? Handling Exception by Using a Try/Catch Block Using
- 16. What Is an Exception? An exception is an indication of an error or exceptional condition The
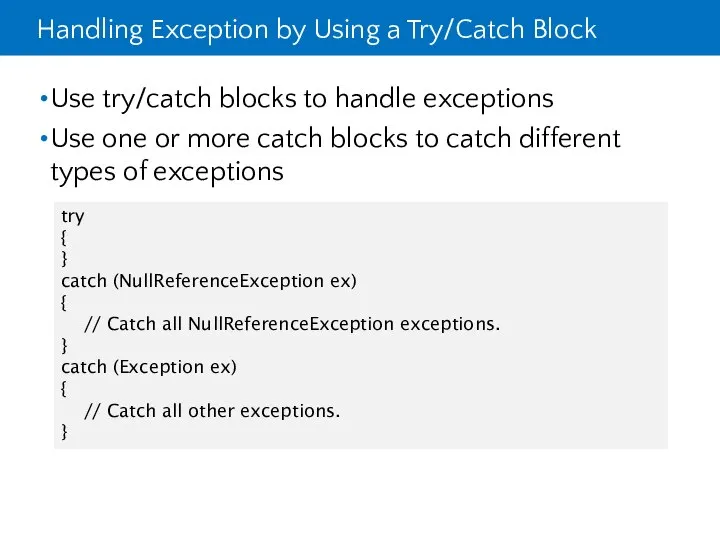
- 17. Handling Exception by Using a Try/Catch Block Use try/catch blocks to handle exceptions Use one or
- 18. Using a Finally Block Use a finally block to run code whether or not an exception
- 19. Throwing Exceptions Use the throw keyword to throw a new exception Use the throw keyword to
- 20. Lesson 4: Monitoring Applications Using Logging and Tracing Using Application Profiling Using Performance Counters Demonstration: Extending
- 21. Using Logging and Tracing Logging provides information to users and administrators Windows event log Text files
- 22. Using Application Profiling Create and run a performance session Analyze the profiling report Revise your code
- 23. Using Performance Counters Create performance counters and categories in code or in Server Explorer Specify: A
- 24. Demonstration: Extending the Class Enrollment Application Functionality Lab In this demonstration, you will learn about the
- 25. Text Continuation
- 26. Lab: Extending the Class Enrollment Application Functionality Exercise 1: Refactoring the Enrollment Code Exercise 2: Validating
- 27. Text Continuation
- 28. Lab Scenario You have been asked to refactor the code that you wrote in the lab
- 29. Module Review and Takeaways Review Question(s)
- 31. Скачать презентацию


























 Методы определения сметной стоимости строительных работ
Методы определения сметной стоимости строительных работ Москва-третий Рим. Выполнил студент группы Э-101 Лапов Артем
Москва-третий Рим. Выполнил студент группы Э-101 Лапов Артем Культурная идентичность
Культурная идентичность Первое родительское собрание Ваш ребёнок идет в школу Муниципальное бюджетное общеобразовательное учреждение средняя общео
Первое родительское собрание Ваш ребёнок идет в школу Муниципальное бюджетное общеобразовательное учреждение средняя общео Содержание функций статистических показателей
Содержание функций статистических показателей Виды ран и общие правила оказания первой медицинской помощи
Виды ран и общие правила оказания первой медицинской помощи Портфолио Графический дизайн и визуальные решения. - презентация
Портфолио Графический дизайн и визуальные решения. - презентация Политическое сознание
Политическое сознание Система смазки и суфлирования
Система смазки и суфлирования Художественное воплощение образов Ф.М. Достоевского в творчестве И.С Глазунова.
Художественное воплощение образов Ф.М. Достоевского в творчестве И.С Глазунова.  Солнечные опреснительные установки
Солнечные опреснительные установки  Презентация на тему "СПИД" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "СПИД" - скачать презентации по Медицине Новые технологии голосования & права человека
Новые технологии голосования & права человека Минутка «психиатрии»
Минутка «психиатрии» Знание (информация) по своей сути является возобновляемым ресурсом. Вы, я и миллион других людей можем воспользоваться одним и тем
Знание (информация) по своей сути является возобновляемым ресурсом. Вы, я и миллион других людей можем воспользоваться одним и тем  Западноевропейское искусство
Западноевропейское искусство Страйкбол. История страйкбола
Страйкбол. История страйкбола Прерафаэлиты для Кристины
Прерафаэлиты для Кристины I.От знания учебного предмета II.От знакомства с процедурой проведения экзамена III.От стратегии подготовки к экзамену IV.От психологи
I.От знания учебного предмета II.От знакомства с процедурой проведения экзамена III.От стратегии подготовки к экзамену IV.От психологи Презентация ИСТОРИЯ КОСТЮМА
Презентация ИСТОРИЯ КОСТЮМА  Этические требования к критике
Этические требования к критике Подача шампанского, сервировка
Подача шампанского, сервировка Человеческий капитал и персональные компетенции современного коммуникатора
Человеческий капитал и персональные компетенции современного коммуникатора Прогрессио – движение вперед! Проект подготовлен учителем математики МОУ – СОШ № 13 г. Балаково Склеминой Галиной Александровной
Прогрессио – движение вперед! Проект подготовлен учителем математики МОУ – СОШ № 13 г. Балаково Склеминой Галиной Александровной Тайна имени
Тайна имени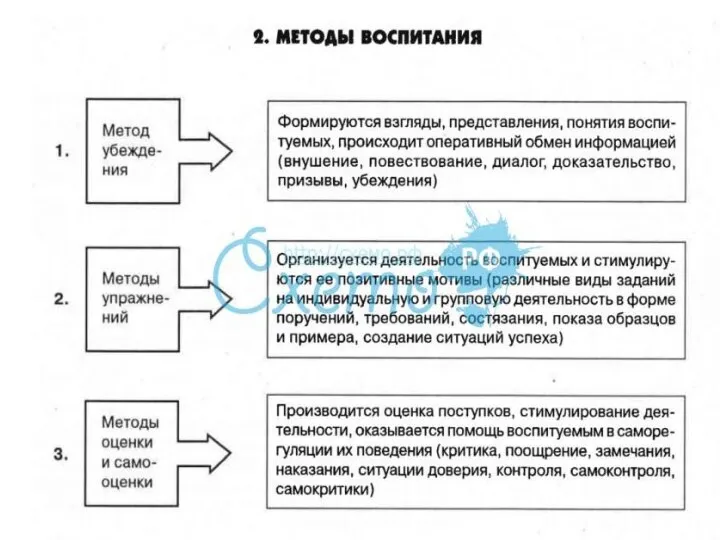 Методы воспитания
Методы воспитания Индуктивные измерительные устройства
Индуктивные измерительные устройства Примерная основная образовательная программа - основа образовательной программы образовательного учреждения
Примерная основная образовательная программа - основа образовательной программы образовательного учреждения