Содержание
- 2. Forms of business organization Sole (Single) Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Co-operative
- 3. Sole Proprietorships ONE OWNER ALL THE ASSETS AND PROFITS ARE ATTRIBUTED DIRECTLY TO THE OWNER. NO
- 4. SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP ADVANTAGES Easiest and least expensive form of ownership to organize Ease of formation Sole
- 5. SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP ADVANTAGES Sole proprietors receive all income generated by the business to keep or reinvest.
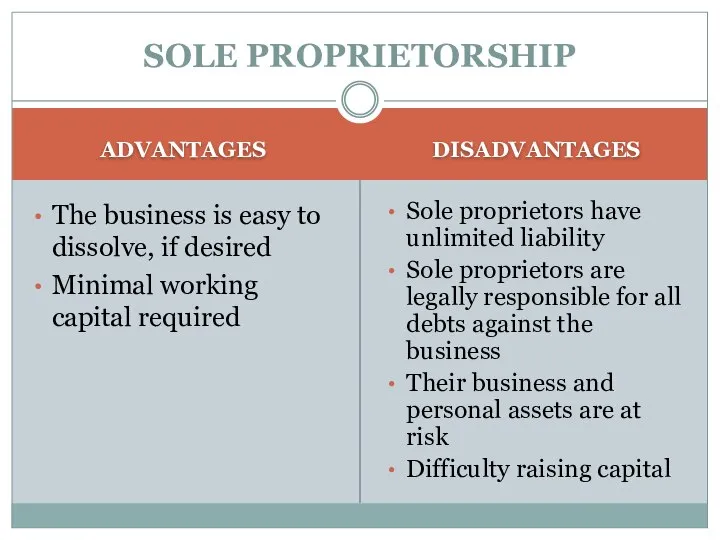
- 6. SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP ADVANTAGES The business is easy to dissolve, if desired Minimal working capital required DISADVANTAGES
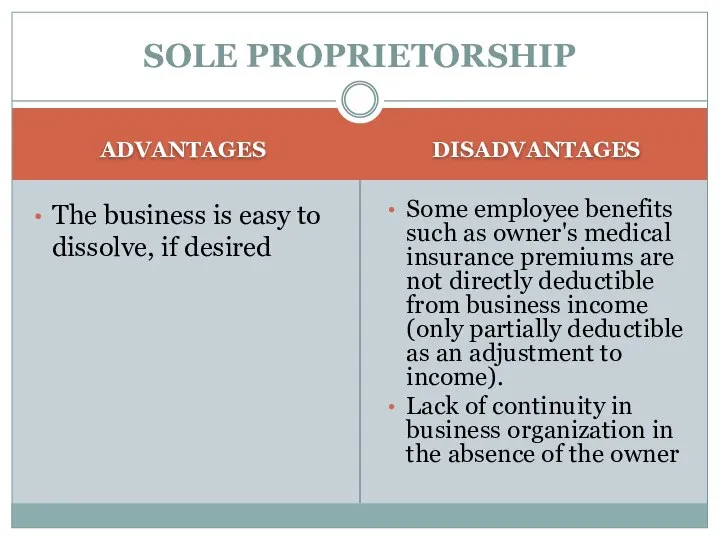
- 7. SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP ADVANTAGES The business is easy to dissolve, if desired DISADVANTAGES Some employee benefits such
- 8. Partnerships TWO OR MORE OWNERS Partnership agreement may be oral or written. PROFITS ARE ATTRIBUTED DIRECTLY
- 9. Partnerships THE PARTNERS MUST DECIDE UP FRONT HOW MUCH TIME AND CAPITAL EACH WILL CONTRIBUTE
- 10. Partnerships ADVANTAGES Partnerships are relatively easy to establish; however time should be invested in developing the
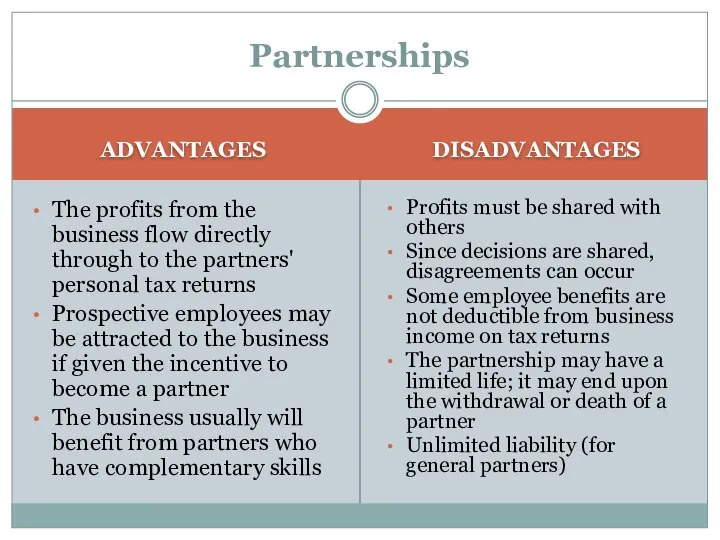
- 11. Partnerships ADVANTAGES The profits from the business flow directly through to the partners' personal tax returns
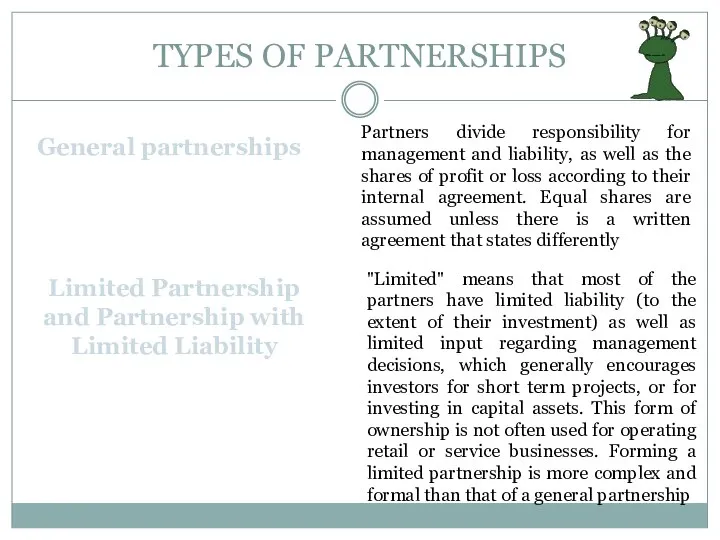
- 12. TYPES OF PARTNERSHIPS General partnerships Partners divide responsibility for management and liability, as well as the
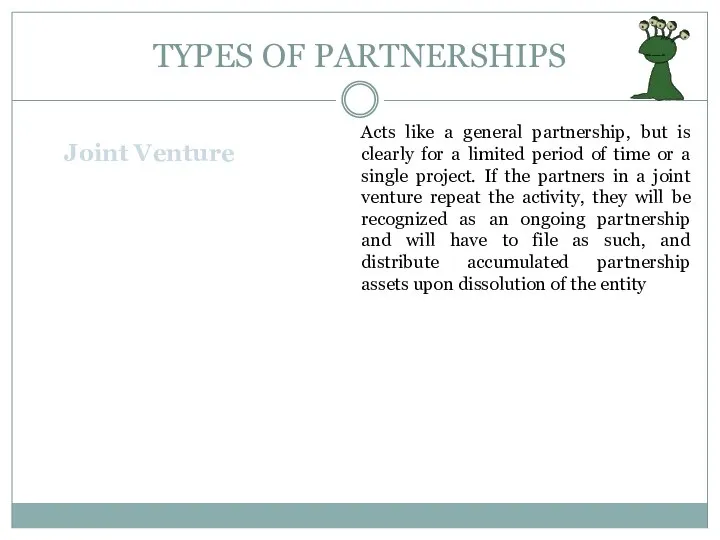
- 13. TYPES OF PARTNERSHIPS Joint Venture Acts like a general partnership, but is clearly for a limited
- 14. Corporations A CORPORATION IS IDENTIFIED BY THE TERMS "LIMITED", "LTD.", "INCORPORATED", "INC.", "CORPORATION", OR "CORP.". WHATEVER
- 15. Corporations USUALLY THERE ARE MANY OWNERS. Owners are referred to as shareholders. THE OWNERS HAVE LIMITED
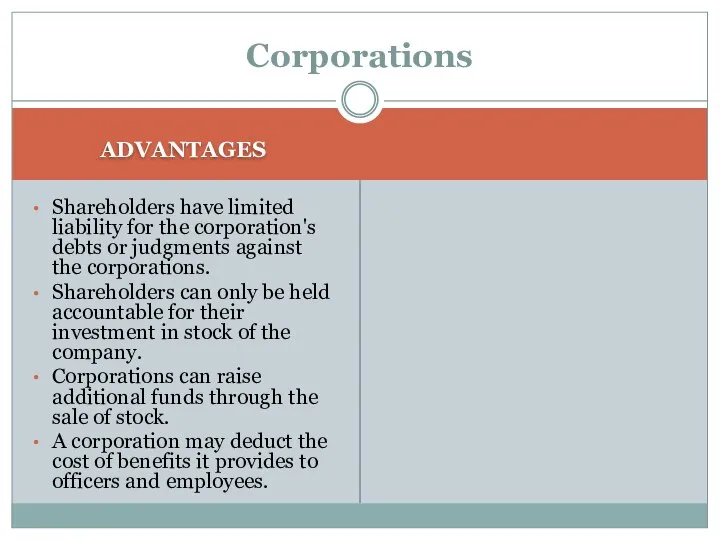
- 16. Corporations ADVANTAGES Shareholders have limited liability for the corporation's debts or judgments against the corporations. Shareholders
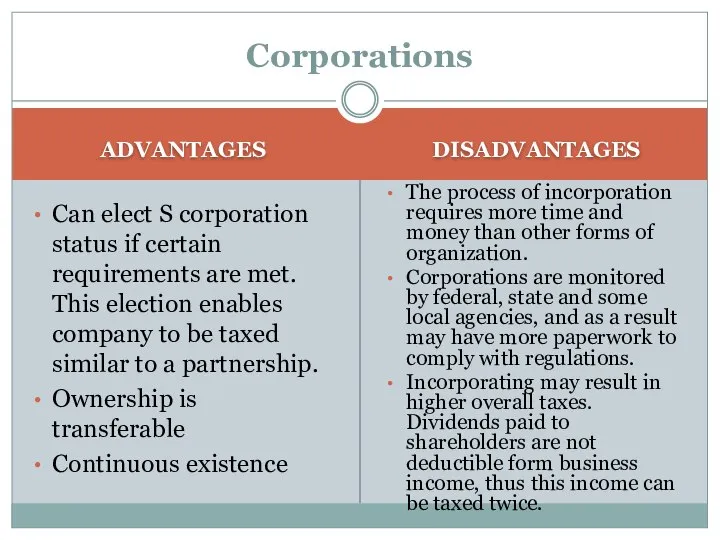
- 17. Corporations ADVANTAGES Can elect S corporation status if certain requirements are met. This election enables company
- 18. TYPES OF CORPORATIONS Subchapter S Corporations A tax election only; this election enables the shareholder to
- 19. TYPES OF CORPORATIONS Private Corporation A private corporation can be formed by one or more people.
- 21. Скачать презентацию











 Презентация к уроку английского языка "A magic island" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "A magic island" - скачать бесплатно I do know both of you! — Я точно знаю вас обоих!
I do know both of you! — Я точно знаю вас обоих! Evolution of Youth Groups in Russia Sokolova Tatyana 10 class
Evolution of Youth Groups in Russia Sokolova Tatyana 10 class  Keep out of
Keep out of Lena River
Lena River  Grammar. Question Words
Grammar. Question Words Презентация к уроку английского языка "Happy easter" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Happy easter" - скачать  Name. Start
Name. Start Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II (к 90-летию со дня рождения) Автор презентации: Антоненко Ирина Григорьевна, учитель английского языка М
Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II (к 90-летию со дня рождения) Автор презентации: Антоненко Ирина Григорьевна, учитель английского языка М Jobs and places. The city and the country. Dwellings
Jobs and places. The city and the country. Dwellings Household chores
Household chores The usage of the Phonetic stylistic devices in Kazakh and English languages
The usage of the Phonetic stylistic devices in Kazakh and English languages Грамматическая сказка Остров сокровищ
Грамматическая сказка Остров сокровищ Theodore Dreiser
Theodore Dreiser Collective noun. Game
Collective noun. Game Презентация подготовлена учителем английского языка МКОУ «СОШ№15» п.Рефтинский Авдеевой Татьяной Викторовной
Презентация подготовлена учителем английского языка МКОУ «СОШ№15» п.Рефтинский Авдеевой Татьяной Викторовной  УКАЗАТЕЛЬНЫЕ МЕСТОИМЕНИЯ Учитель английского языка ГБОУ школа № 83 г. Санкт-Петербург Корчагина Виктория Евгеньевна
УКАЗАТЕЛЬНЫЕ МЕСТОИМЕНИЯ Учитель английского языка ГБОУ школа № 83 г. Санкт-Петербург Корчагина Виктория Евгеньевна The English language In my daily life
The English language In my daily life IELTS: Last Moment Tips
IELTS: Last Moment Tips Презентация к уроку английского языка "The problems of youth" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "The problems of youth" - скачать  Let's learn some prefixes
Let's learn some prefixes Animals. Внеклассное мероприятие для 4 класса
Animals. Внеклассное мероприятие для 4 класса ОГЭ - Электронное письмо
ОГЭ - Электронное письмо Ancient Greec-Roman philosophy. (Lecture 3)
Ancient Greec-Roman philosophy. (Lecture 3) Happy New Year! Учитель английского языка МОУ СОШ № 10 г. Жуковский Куликова Анастасия Александровна
Happy New Year! Учитель английского языка МОУ СОШ № 10 г. Жуковский Куликова Анастасия Александровна  Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811-1896)
Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811-1896)  TENSES IN ENGLISH Подготовила преподаватель английского языка ГУО «Пинковичской средней школы им.Якуба коласа» Пинского района, брес
TENSES IN ENGLISH Подготовила преподаватель английского языка ГУО «Пинковичской средней школы им.Якуба коласа» Пинского района, брес Phrasal verbs
Phrasal verbs