Содержание
- 2. C H A P T E R 4 Federalism SECTION 1 Federalism: The Division of Power
- 3. Chapter 4, Section 1 S E C T I O N 1 Federalism: The Division of
- 4. The Framers were dedicated to the concept of limited government. They were convinced Why Federalism? (1)
- 5. Federalism Defined Federalism is a system of government in which a written constitution divides the powers
- 6. Powers of the National Government Chapter 4, Section 1 2 3 The National Government is a
- 7. Powers Denied to the National Government Powers are denied to the National Government in three distinct
- 8. The States Powers Reserved to the States The 10th Amendment declares that the States are governments
- 9. The Exclusive and Concurrent Powers Exclusive Powers Powers that can be exercised by the National Government
- 10. The Federal System and Local Governments There are more than 87,000 units of local government in
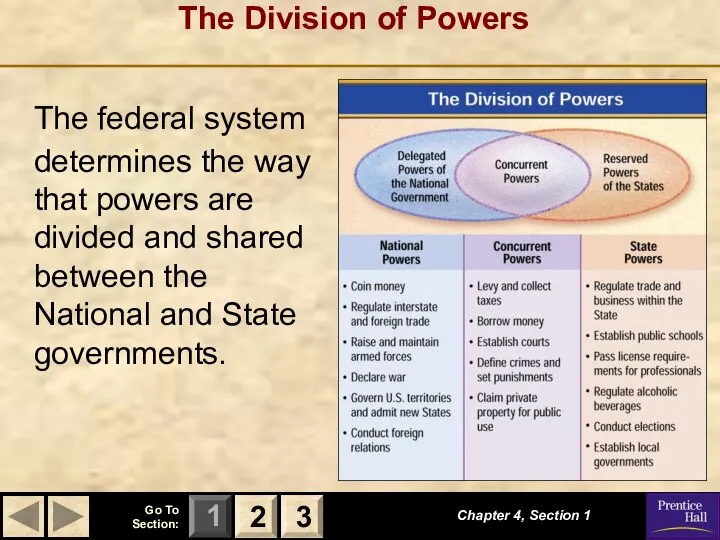
- 11. The Division of Powers The federal system determines the way that powers are divided and shared
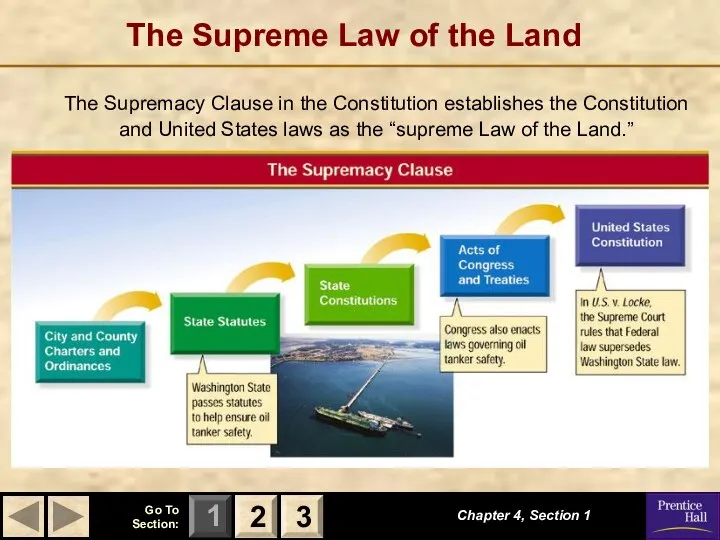
- 12. The Supreme Law of the Land The Supremacy Clause in the Constitution establishes the Constitution and
- 13. Section 1 Review 1. The expressed powers granted to the National Government are found (a) in
- 14. S E C T I O N 2 The National Government and the 50 States What
- 15. Chapter 4, Section 2 3 1 The Nation’s Obligations to the States Republican Form of Government
- 16. The Major Disaster Process Chapter 4, Section 2 3 1
- 17. Admitting New States Chapter 4, Section 2 3 1 Only Congress has the power to admit
- 18. Cooperative Federalism Chapter 4, Section 2 3 1 Federal Grants-in-Aid Grants-in-aid programs are grants of federal
- 19. Federal Grants Chapter 4, Section 2 3 1 Categorical Grants Categorical grants are made for some
- 20. Section 2 Review 1. The Constitution requires the National Government to provide all of the following
- 21. Chapter 4, Section 3 S E C T I O N 3 Interstate Relations Why do
- 22. Interstate Compacts No State may enter into any treaty, alliance, or confederation. Chapter 4, Section 3
- 23. Chapter 4, Section 3 2 1 Full Faith and Credit The Full Faith and Credit Clause
- 24. Extradition Chapter 4, Section 3 2 1 Extradition is the legal process by which a fugitive
- 25. Privileges and Immunities The Privileges and Immunities Clause provides that no State can draw unreasonable distinctions
- 27. Скачать презентацию






















 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Методика обучения иностранным языкам" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Методика обучения иностранным языкам" - скачать бесплатно Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа элективного курса Деловое письмо
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа элективного курса Деловое письмо Education in Britain
Education in Britain Аттестационная работа. Рабочая программа элективного курса Проектная деятельность на уроках английского языка
Аттестационная работа. Рабочая программа элективного курса Проектная деятельность на уроках английского языка Test Yourself
Test Yourself  is washed by is washed by the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico
is washed by is washed by the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico  Yung Lean is a swedish rap artist
Yung Lean is a swedish rap artist English vocabulary. Lesson 4
English vocabulary. Lesson 4 Present perfect
Present perfect History of Halloween
History of Halloween Аттестационная работа. Проектная и исследовательская деятельность в рамках нашей гимназии
Аттестационная работа. Проектная и исследовательская деятельность в рамках нашей гимназии What is Hot with the Young Generation? Subculture
What is Hot with the Young Generation? Subculture Презентация к уроку английского языка "Deep Purple Legend of rock" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Deep Purple Legend of rock" - скачать  Life is a mirace
Life is a mirace The Articles a / an
The Articles a / an Past Simple
Past Simple Claude Monet
Claude Monet  Lecture clause and sentence
Lecture clause and sentence 11 класс, УМК О.Л.Гроза «Новый миллениум» Дождикова А.И., учитель английского языка МОУ ОСОШ №2, пос.Орловский Урок №1
11 класс, УМК О.Л.Гроза «Новый миллениум» Дождикова А.И., учитель английского языка МОУ ОСОШ №2, пос.Орловский Урок №1 Present Simple
Present Simple Презентация к уроку английского языка "ЗА СТОЛОМ" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "ЗА СТОЛОМ" - скачать бесплатно Education in Great Britain
Education in Great Britain  Осторожно - животные Выполнила ученица 3А класса МОУ СОШ №85 Васильева Ксения
Осторожно - животные Выполнила ученица 3А класса МОУ СОШ №85 Васильева Ксения Have got, has got
Have got, has got Countries Game 5
Countries Game 5 Picture dictionary
Picture dictionary Презентация к уроку английского языка "English Sandwiches and English Tea" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "English Sandwiches and English Tea" - скачать  Игра-викторина I like English
Игра-викторина I like English