Содержание
- 2. Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae
- 3. Enterobacteriaceae Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous flagella Shigella and Klebsiella
- 4. Ferment glucose Reduce nitrates NO3 to NO2 or all the way to N2 Oxidase negative Distinguishing
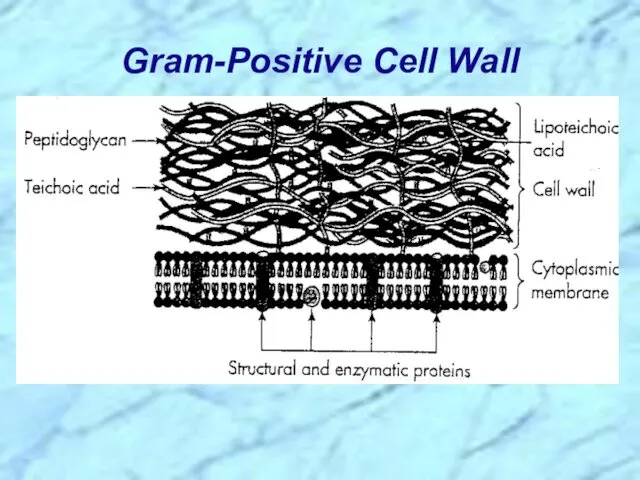
- 5. Gram-Positive Cell Wall
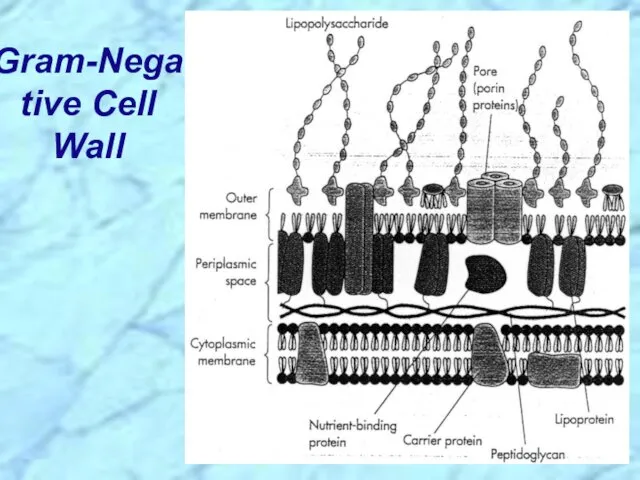
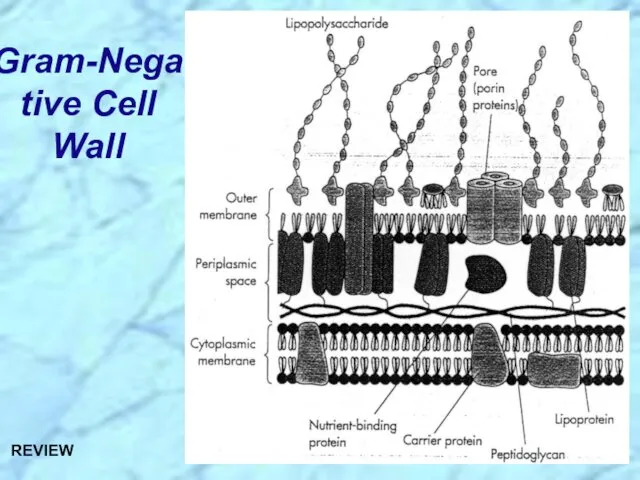
- 6. Gram-Negative Cell Wall
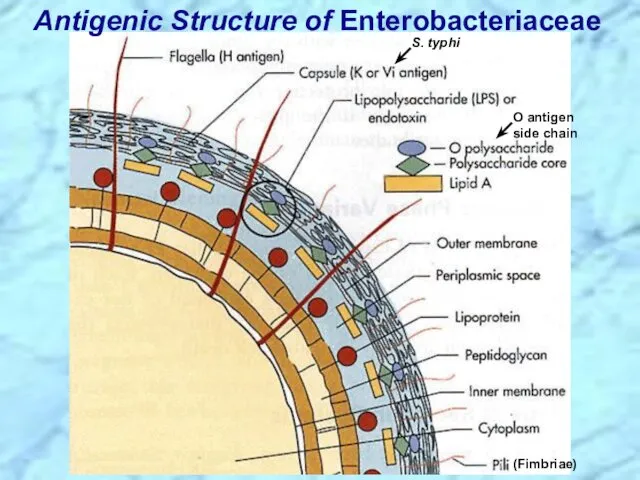
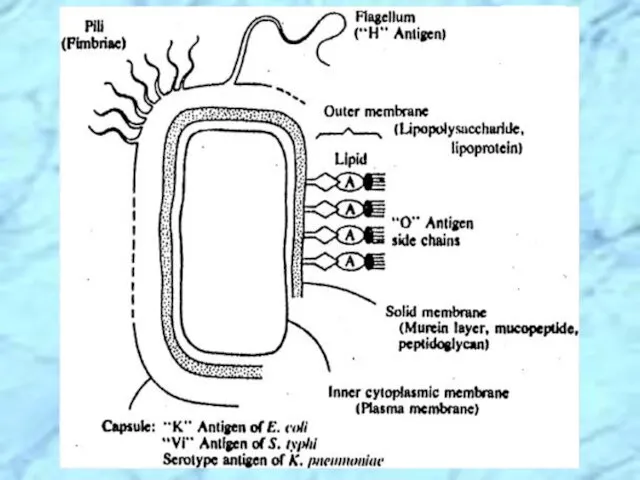
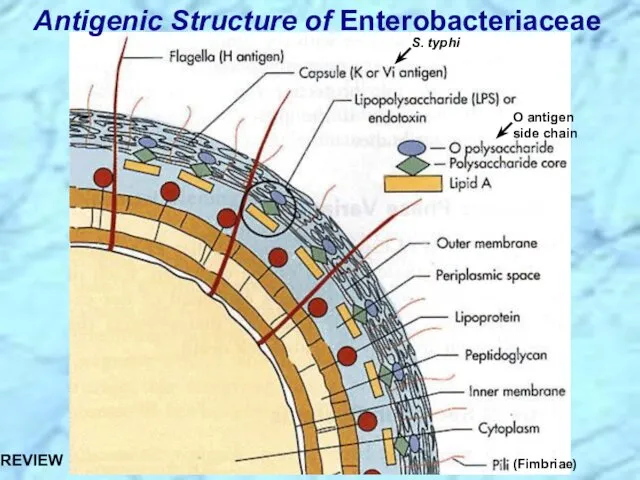
- 7. Antigenic Structure of Enterobacteriaceae S. typhi O antigen side chain (Fimbriae)
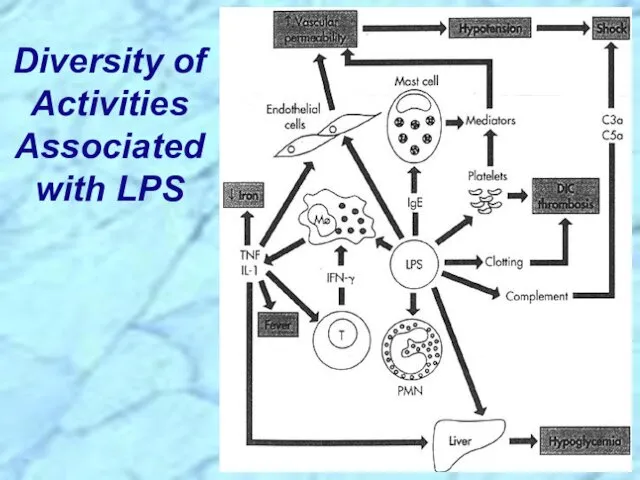
- 9. Diversity of Activities Associated with LPS
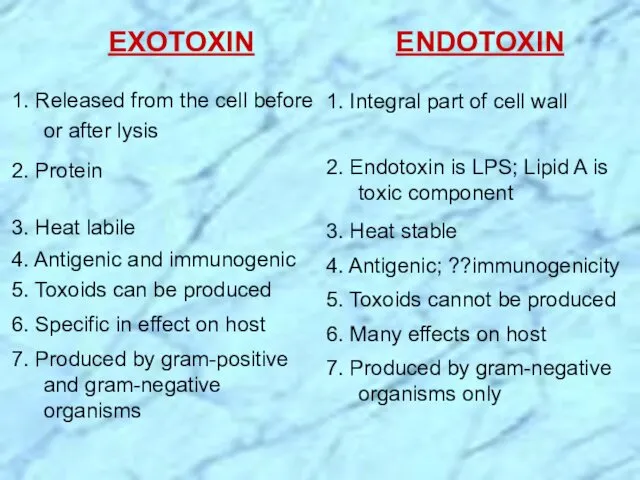
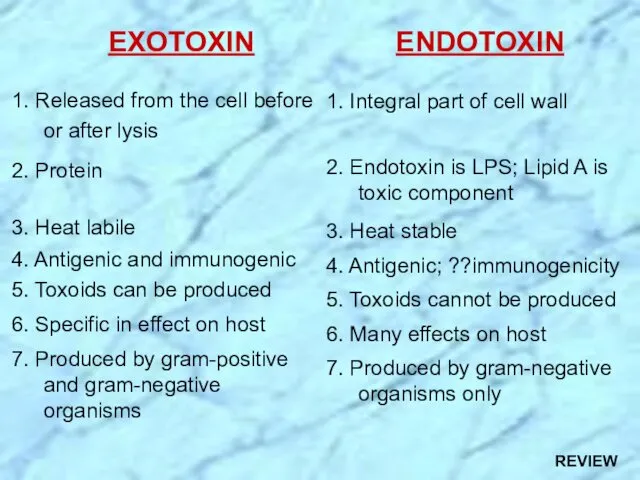
- 10. ENDOTOXIN 1. Integral part of cell wall 2. Endotoxin is LPS; Lipid A is toxic component
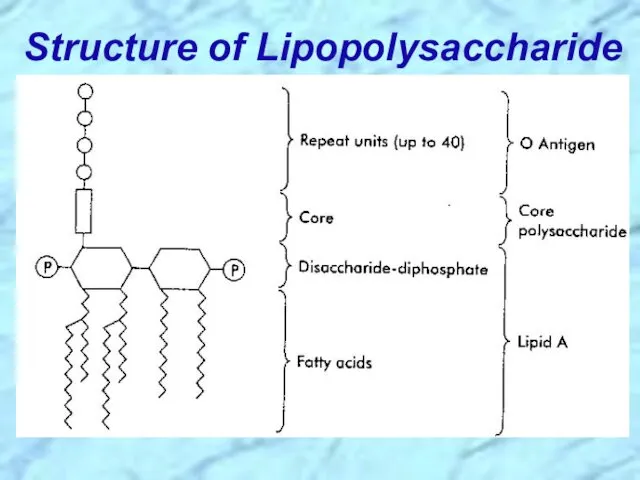
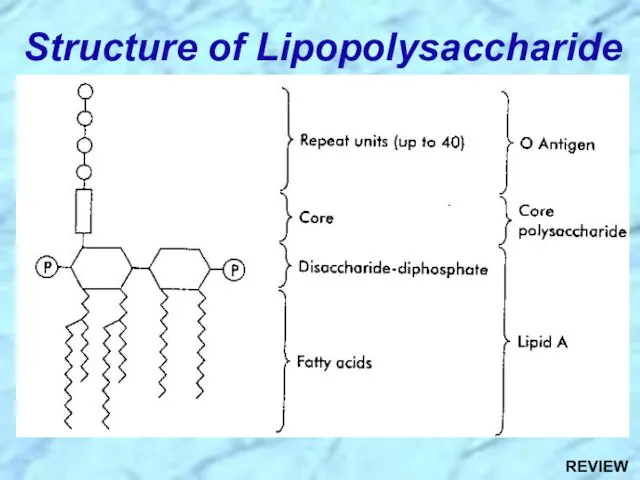
- 11. Structure of Lipopolysaccharide
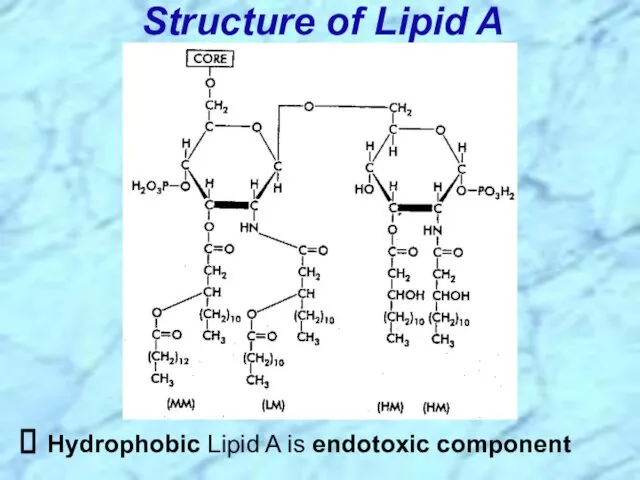
- 12. Structure of Lipid A Hydrophobic Lipid A is endotoxic component
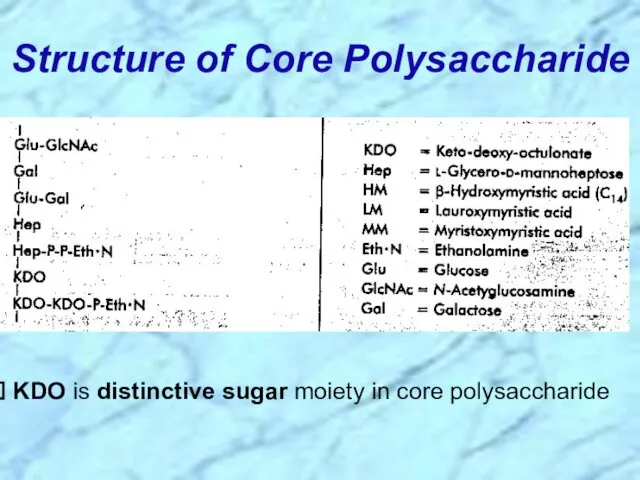
- 13. Structure of Core Polysaccharide KDO is distinctive sugar moiety in core polysaccharide
- 14. Repeat Units of O Antigen Side Chain Heat stable O antigen is often used to serotype
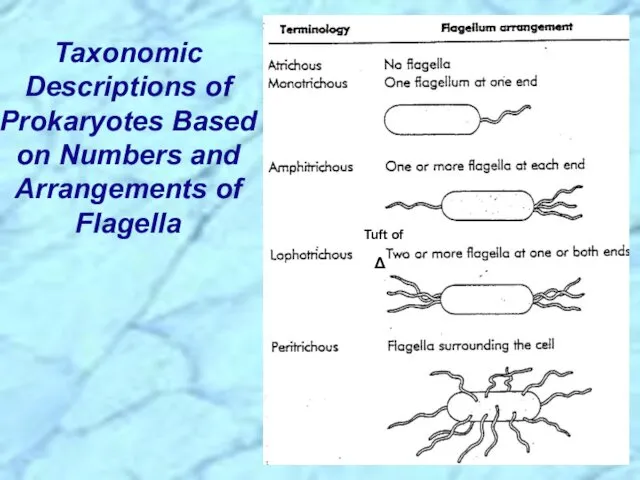
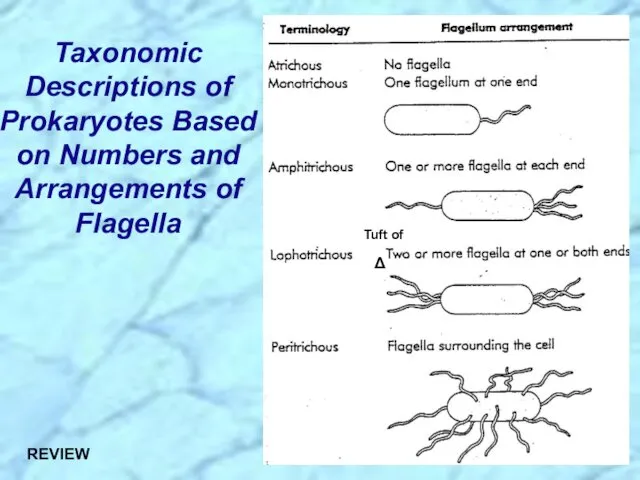
- 15. Taxonomic Descriptions of Prokaryotes Based on Numbers and Arrangements of Flagella
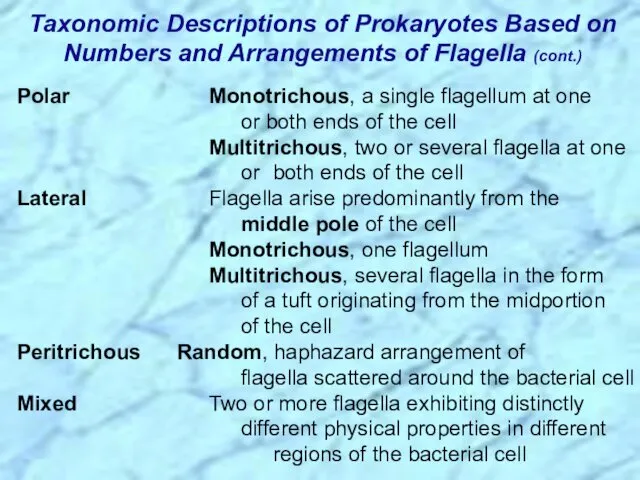
- 16. Polar Monotrichous, a single flagellum at one or both ends of the cell Multitrichous, two or
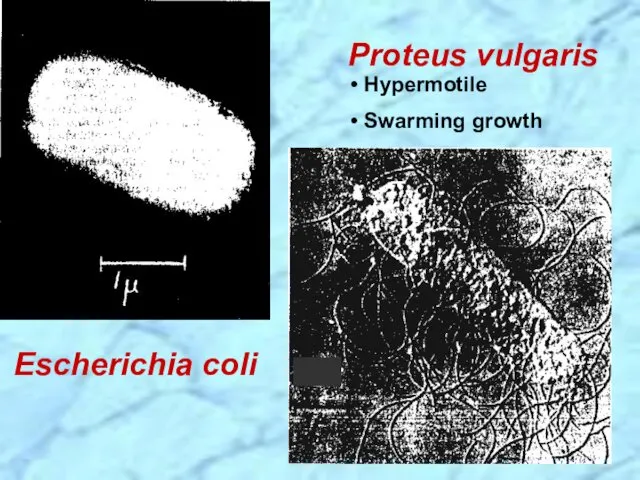
- 17. Escherichia coli Hypermotile Swarming growth Proteus vulgaris
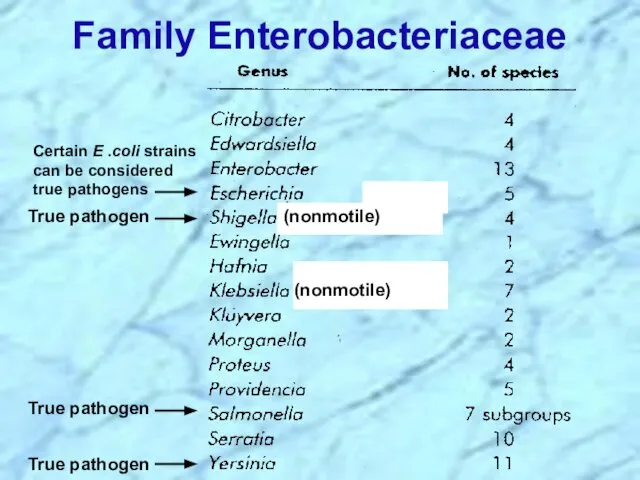
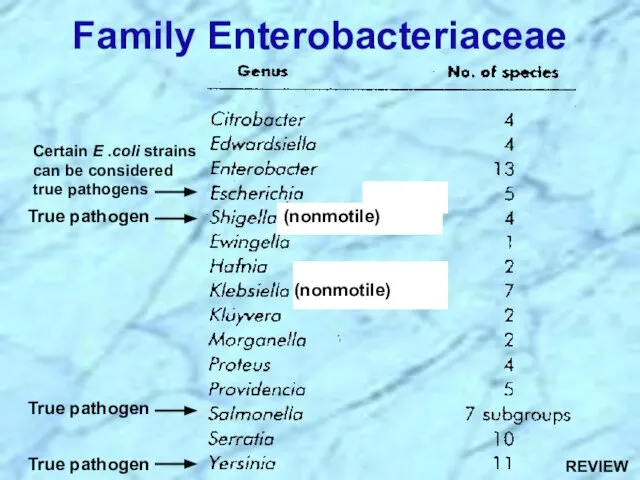
- 18. Family Enterobacteriaceae (nonmotile) (nonmotile) True pathogen True pathogen True pathogen Certain E .coli strains can be
- 19. Citrobacter species Enterobacter spp. Escherichia spp. Klebsiella spp. Morganella spp. Proteus spp. Salmonella spp. Serratia spp.
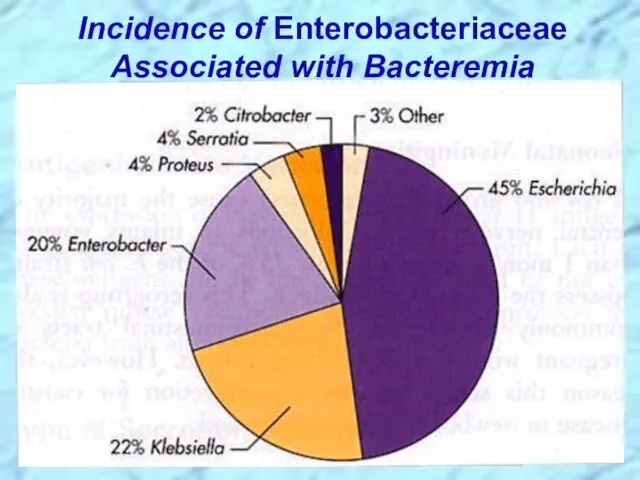
- 20. Incidence of Enterobacteriaceae Associated with Bacteremia
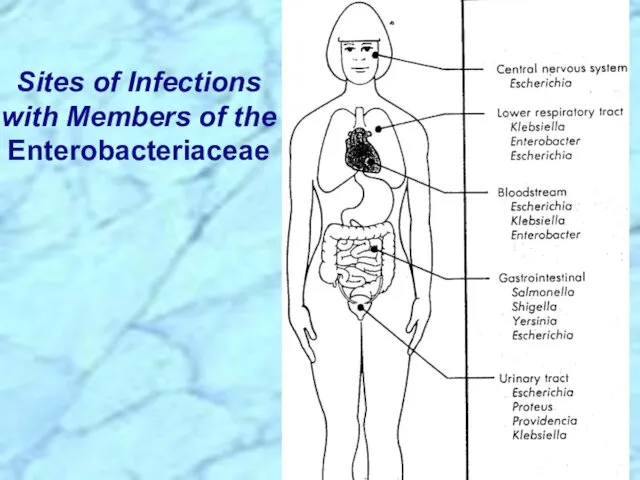
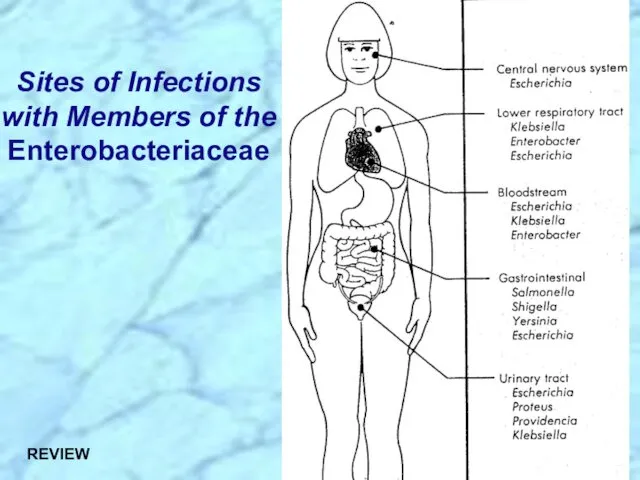
- 21. Sites of Infections with Members of the Enterobacteriaceae
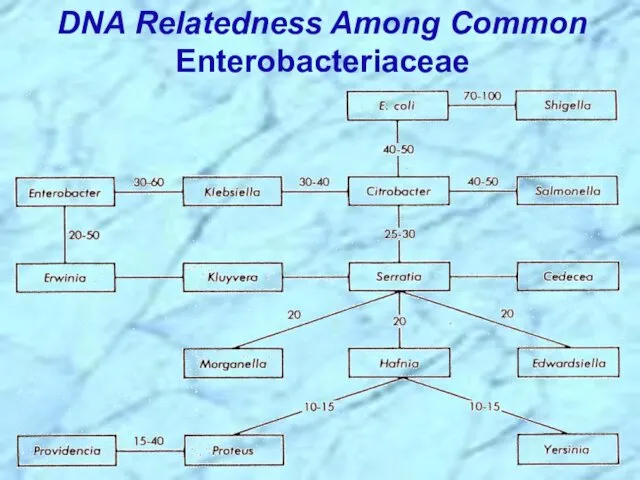
- 22. DNA Relatedness Among Common Enterobacteriaceae
- 24. REVIEW
- 25. Ferment glucose Reduce nitrates NO3 to NO2 or all the way to N2 Oxidase negative Distinguishing
- 26. Gram-Negative Cell Wall REVIEW
- 27. Antigenic Structure of Enterobacteriaceae S. typhi O antigen side chain (Fimbriae) REVIEW
- 28. ENDOTOXIN 1. Integral part of cell wall 2. Endotoxin is LPS; Lipid A is toxic component
- 29. Structure of Lipopolysaccharide REVIEW
- 30. Taxonomic Descriptions of Prokaryotes Based on Numbers and Arrangements of Flagella REVIEW
- 31. Family Enterobacteriaceae (nonmotile) (nonmotile) True pathogen True pathogen True pathogen Certain E .coli strains can be
- 32. Sites of Infections with Members of the Enterobacteriaceae REVIEW
- 34. Скачать презентацию








 Биосинтез белка
Биосинтез белка Виды дельфинов
Виды дельфинов Самоочищение водоемов
Самоочищение водоемов Підготувала: учениця 7-А Щигельська В.
Підготувала: учениця 7-А Щигельська В. Зоологическая азбука
Зоологическая азбука Презентация на тему Семя
Презентация на тему Семя Первая помощь при укусах животных.
Первая помощь при укусах животных. Презентация на тему Биогеоценозы. Экосистемы. Строение и свойства.
Презентация на тему Биогеоценозы. Экосистемы. Строение и свойства. Особенности высшей нервной деятельности общие для человека и животных
Особенности высшей нервной деятельности общие для человека и животных Презентация по биологии Изменчивость. Мутации.
Презентация по биологии Изменчивость. Мутации.  Комнатные растения - друзья человека
Комнатные растения - друзья человека Регуляция активности ферментов
Регуляция активности ферментов Основы анатомии и физиологии человекаа
Основы анатомии и физиологии человекаа Хімічні елементи, які входять до складу живих організмів
Хімічні елементи, які входять до складу живих організмів Презентация на тему "Нейроцитология" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Нейроцитология" - скачать презентации по Биологии Движение крови в организме
Движение крови в организме Презентация на тему "Древние животные" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Древние животные" - скачать презентации по Биологии Органогенні елементи. Хімія в організмах
Органогенні елементи. Хімія в організмах Балансирующий отбор
Балансирующий отбор Умей сказать нет Мельникова Галина Викторовна МОУ Янгельская СОШ Им. Филатова А.К.
Умей сказать нет Мельникова Галина Викторовна МОУ Янгельская СОШ Им. Филатова А.К. ПУТЕШЕСТВИЕ В “ЗЕЛЕНУЮ АПТЕКУ”
ПУТЕШЕСТВИЕ В “ЗЕЛЕНУЮ АПТЕКУ”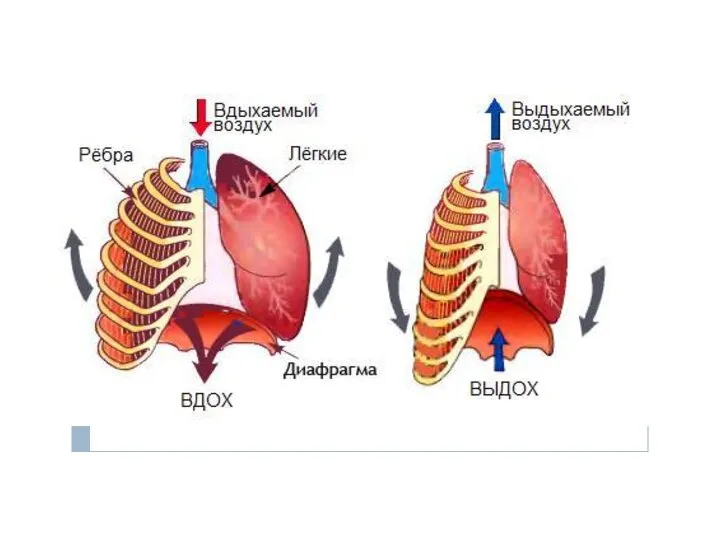 Речевое дыхание
Речевое дыхание Гипотезы происхождения жизни на Земле
Гипотезы происхождения жизни на Земле Органы кровообращения животных
Органы кровообращения животных Птицы
Птицы Особенности внешнего строения птиц, связанные с полетом
Особенности внешнего строения птиц, связанные с полетом Растения - индикаторы почвы
Растения - индикаторы почвы Грибы и ягоды
Грибы и ягоды