Содержание
- 2. 1-1 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Elena Rogova, Professor, erogova@hse.ru 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
- 3. WHAT IS FINANCE? Finance is the study of how and under what terms savings (money) are
- 4. REAL VERSUS FINANCIAL ASSETS 13.09.2021 Real assets are tangible things owned by persons and businesses Residential
- 5. FINANCE EXAMPLES 13.09.2021 Investing personal money in stocks, bonds, or guaranteed investment certificates (GICs) Borrowing money
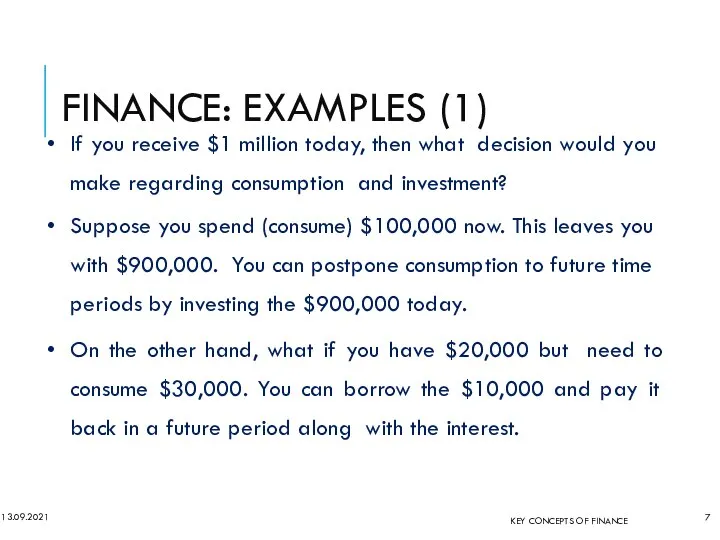
- 6. FINANCE: EXAMPLES (1) 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE If you receive $1 million today, then what
- 7. FINANCE: EXAMPLES (1) 13.09.2021 If you receive $1 million today, then what decision would you make
- 8. FINANCE: EXAMPLES (2) 13.09.2021 A firm must spend $100 million for the required assets if a
- 9. FINANCE: EXAMPLES (3) 13.09.2021 A mutual fund manager that manages a fund with $10 billion portfolio
- 10. GENERAL AREAS OF FINANCE 13.09.2021 Financial Markets and Institutions: banks, insurance companies, savings and loans, and
- 11. FINANCE DISCIPLINES 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Public finance is about the taxing and spending activities
- 12. FINANCE THEORY 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Finance Theory is the study of the behavior of
- 13. BASIC TENET OF FINANCE 13.09.2021 The existence of economic organizations (e.g. firms and governments) facilitates the
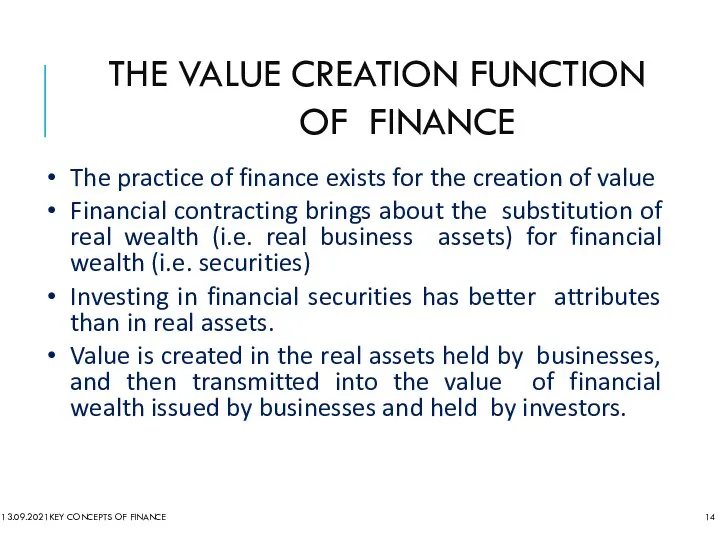
- 14. THE VALUE CREATION FUNCTION OF FINANCE 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE The practice of finance exists
- 15. BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Risk and Return Time value of Money
- 16. BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: RISK AND RETURN 13.09.2021 The higher is the risk of investments, the
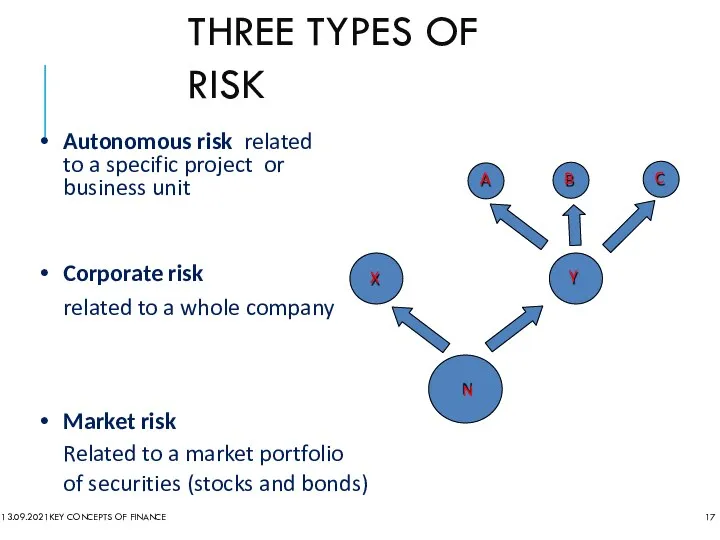
- 17. THREE TYPES OF RISK 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Autonomous risk related to a specific project
- 18. INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (1) 13.09.2021 Risk tolerance – the feature relevant for the decision making about the
- 19. TEST 1 13.09.2021 You can choose between two games You throw a dice and got $60
- 20. TEST 1 13.09.2021 You can choose between two games You throw a dice and got $60
- 21. RISK TOLERANCE 13.09.2021 If you prefer the first game, you are a RISK- TAKER It you
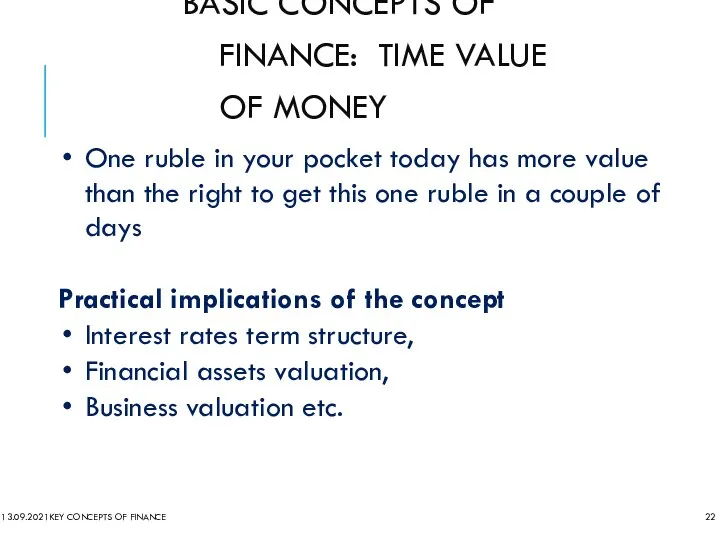
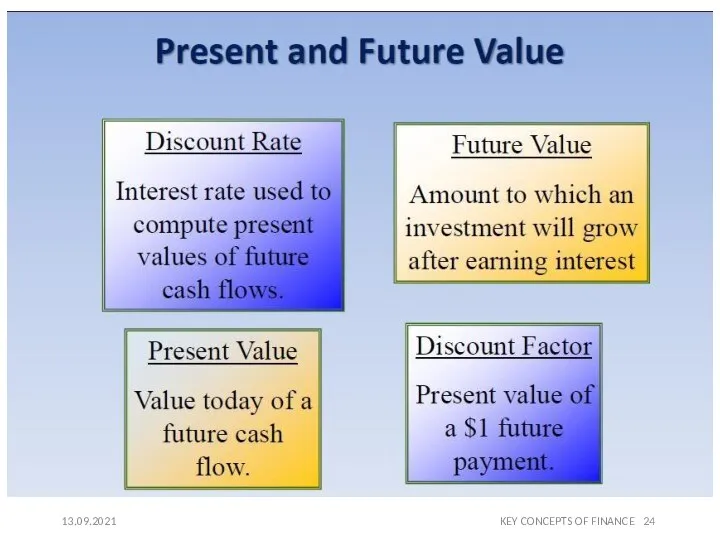
- 22. BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: TIME VALUE OF MONEY 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE One ruble in
- 23. 13.09.2021
- 24. KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE 13.09.2021
- 25. TEST 2 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE You have won in a competition and now can
- 26. TEST 2 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE You have won in a competition and now can
- 27. INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (2) 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Investors’ rationality can be limited by: Asymmetric attitude
- 28. BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: PRIORITY TO CASH FLOWS (CASH IS KING) 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
- 29. INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (3) 13.09.2021 KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE Investors’ rationality is limited by: – The historical
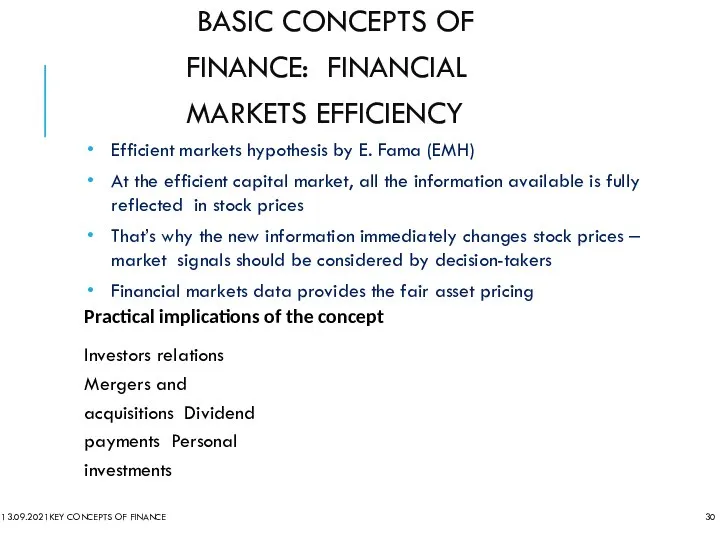
- 30. BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: FINANCIAL MARKETS EFFICIENCY Efficient markets hypothesis by E. Fama (EMH) At the
- 32. Скачать презентацию























 Портфельное инвестрование. Сущность и виды инвестиционного портфеля
Портфельное инвестрование. Сущность и виды инвестиционного портфеля Понятие себестоимости. Роль себестоимости в обеспечении конкурентоспособности продукции предприятия
Понятие себестоимости. Роль себестоимости в обеспечении конкурентоспособности продукции предприятия Источники финансирования инвестиционной деятельности
Источники финансирования инвестиционной деятельности Государственный долг. Долговая политика РФ на современном этапе
Государственный долг. Долговая политика РФ на современном этапе VentureMeet_МИК_общая_18-08-22-1 (3)
VentureMeet_МИК_общая_18-08-22-1 (3) Деньги. Кредит. Банки
Деньги. Кредит. Банки Налоги и налогообложение. Теоретические основы налогообложения. Налоговая система РФ
Налоги и налогообложение. Теоретические основы налогообложения. Налоговая система РФ Информация по выписке счет-фактуры за наличный расчет ТОО Газпром нефть-Казахстан
Информация по выписке счет-фактуры за наличный расчет ТОО Газпром нефть-Казахстан Stock Market
Stock Market Расчетная работа ОАО Мечел. Аналитический баланс, вертикальный и горизонтальный анализ
Расчетная работа ОАО Мечел. Аналитический баланс, вертикальный и горизонтальный анализ Содержание и принципы межбюджетных отношений
Содержание и принципы межбюджетных отношений Типовой вариант экзамена
Типовой вариант экзамена Конвенция Юнситрал о международных переводных векселях и международных простых векселях
Конвенция Юнситрал о международных переводных векселях и международных простых векселях Кредитные карты. Кредит Европа Банк
Кредитные карты. Кредит Европа Банк Программа смешанного страхования жизни Гармония жизни
Программа смешанного страхования жизни Гармония жизни Своя игра. Налогообложение
Своя игра. Налогообложение Ценообразование на мировом рынке товаров и услуг
Ценообразование на мировом рынке товаров и услуг Концепция консолидированного бюджета Белгородской области
Концепция консолидированного бюджета Белгородской области Доходный подход
Доходный подход Аудит кредиторской задолженности
Аудит кредиторской задолженности История развития страхования в 21 веке в Германии
История развития страхования в 21 веке в Германии Учёт расчётных операций
Учёт расчётных операций Дебетовые карты
Дебетовые карты Презентация Болдинова
Презентация Болдинова Основи фінансової діяльності підприємства. Тема 6
Основи фінансової діяльності підприємства. Тема 6 Программа страхования имущества при оплате коммунальных платежей
Программа страхования имущества при оплате коммунальных платежей Финансовый ликбез
Финансовый ликбез Управление дебиторской задолженностью и денежными активами предприятия
Управление дебиторской задолженностью и денежными активами предприятия