Содержание
- 2. Topics Covered Ionic Bonds and Compounds Covalent Bonds Lewis Structures Types of Covalent Bonding Geometry and
- 3. Chemical bond The atoms in molecules held together by strong attractive forces called chemical bonds Formed
- 4. Ionic bond Two atoms with large difference in electronegativity reactivity, there is complete electron transfer High
- 5. Ionic bond These two ions are held together by electrostatic forces This force of attraction between
- 6. Nomenclature 1. 2. 3.
- 7. Nomenclature 4. 5.
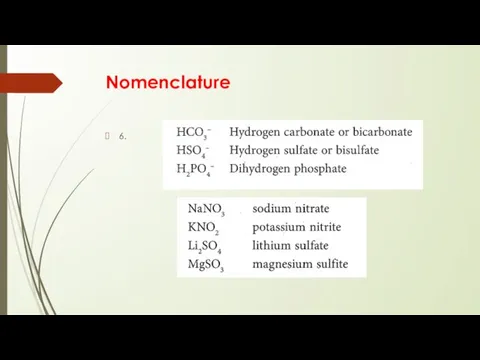
- 8. Nomenclature 6.
- 9. Ionic bond High melting and boiling point – strong electrostatic force Conduct electricity in liquid and
- 10. Covalent Bonds Forms when two elements have similar electronegativities They achieve a noble gas electron configuration
- 11. Covalent bond Bonds length is the average distance between the two nuclei of the atoms involved
- 12. Bonds Primary bonding – covalent and ionic Secondary – hydrogen and Van der Vaals
- 13. Lewis Structures Valence electrons of a covalent bond – bonding electrons Valence electrons not involved in
- 14. Lewis Structures More than one Lewis structure for a molecule – resonance
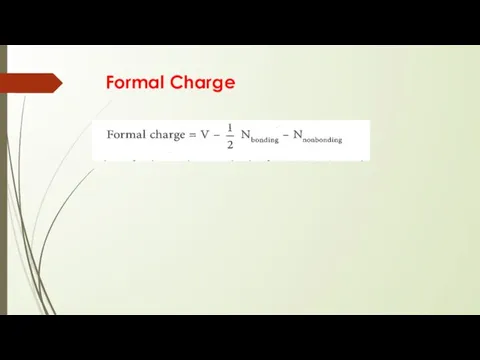
- 15. Formal Charge
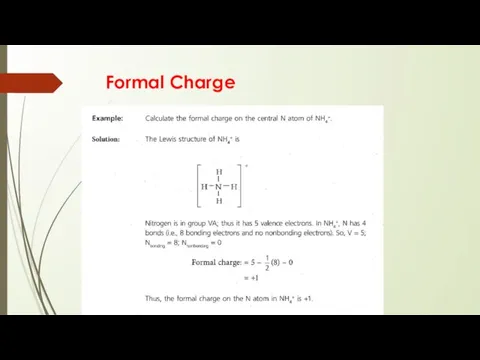
- 16. Formal Charge
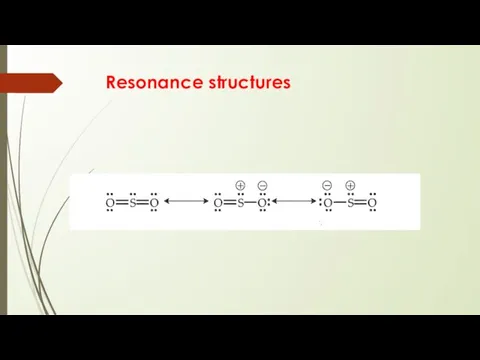
- 17. Resonance structures
- 18. Types of covalent bonds Polar covalent bonds – occurs between atoms with small difference in electronegativity
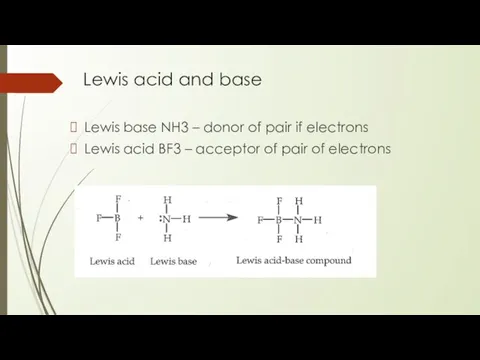
- 19. Lewis acid and base Lewis base NH3 – donor of pair if electrons Lewis acid BF3
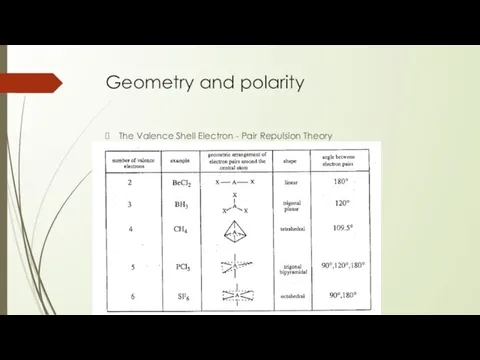
- 20. Geometry and polarity The Valence Shell Electron - Pair Repulsion Theory
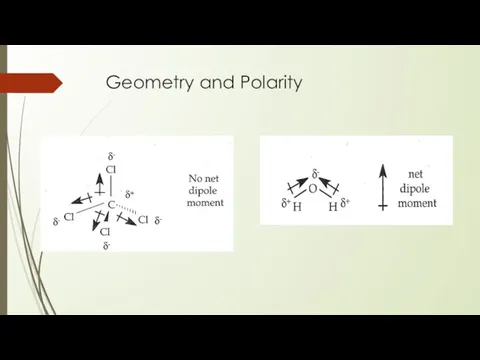
- 21. Geometry and Polarity
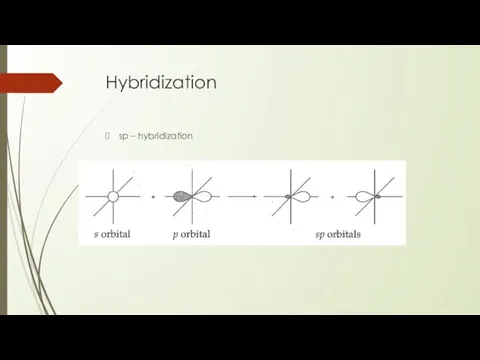
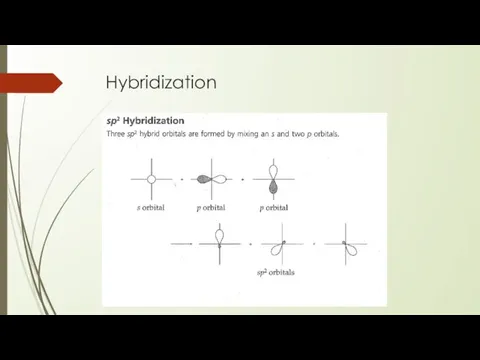
- 22. Hybridization sp – hybridization
- 23. Hybridization
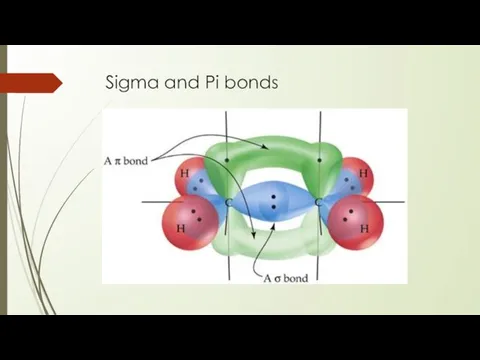
- 24. Sigma and Pi bonds
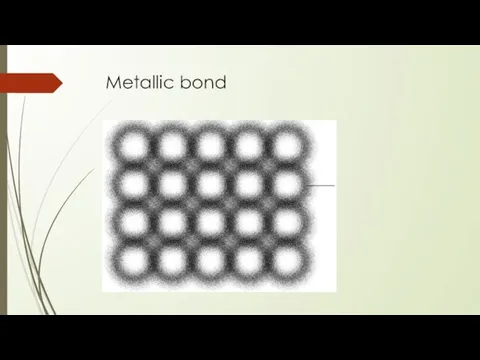
- 25. Metallic bond
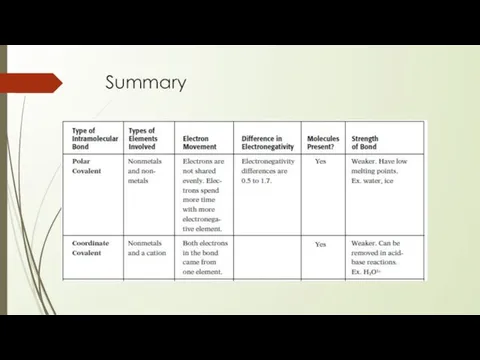
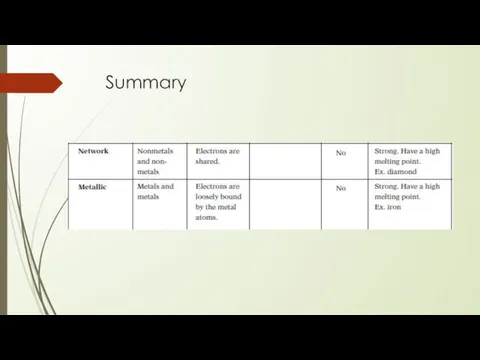
- 26. Summary
- 27. Summary
- 28. Summary
- 30. Скачать презентацию














 Пластмаси, синтетичні каучуки Підготували учениці 11-б класу Оренбургська Марина та Козаренко Таїсія
Пластмаси, синтетичні каучуки Підготували учениці 11-б класу Оренбургська Марина та Козаренко Таїсія  Общая фармакология
Общая фармакология Углерод и его соединения
Углерод и его соединения Обобщающий урок по теме: «Основные классы неорганических соединений. Генетическая связь между классами неорганических соединени
Обобщающий урок по теме: «Основные классы неорганических соединений. Генетическая связь между классами неорганических соединени Урок розв’язування задач
Урок розв’язування задач Ароматичні аміни
Ароматичні аміни Фосфор
Фосфор Углеводы
Углеводы Химическая связь
Химическая связь Мило. Синтетичні миючі засоби.
Мило. Синтетичні миючі засоби.  11 хб
11 хб  Нефелиновые сиениты. Щелочные породы
Нефелиновые сиениты. Щелочные породы Презентация по Химии "Фосфорные удобрения" - скачать смотреть
Презентация по Химии "Фосфорные удобрения" - скачать смотреть  Алкины
Алкины Метаболизм источников энергии
Метаболизм источников энергии Химические волокна
Химические волокна Конструкционные полимеры: классификация, достижения и проблемы
Конструкционные полимеры: классификация, достижения и проблемы Дезодоранты. Выполнили: Ученицы 11-В класса МОУ «Лицей №3» Доровских Алёна Чучуменко Анастасия
Дезодоранты. Выполнили: Ученицы 11-В класса МОУ «Лицей №3» Доровских Алёна Чучуменко Анастасия Поліетелен. Застосування поліетилену
Поліетелен. Застосування поліетилену Аммиак
Аммиак Тотығу-тотықсыздану реакциялары Атырау ХББ НЗМ Косанов Р.П. Химия пәні мұғалімі
Тотығу-тотықсыздану реакциялары Атырау ХББ НЗМ Косанов Р.П. Химия пәні мұғалімі Мило. Мийні засоби
Мило. Мийні засоби Виды присадок к моторным топливам. Керосин
Виды присадок к моторным топливам. Керосин Обобщение и систематизация знаний по теме Химическая связь и строение атома
Обобщение и систематизация знаний по теме Химическая связь и строение атома Химическая промышленность
Химическая промышленность Регуляция обмена веществ
Регуляция обмена веществ Протеины: плюсы и минусы
Протеины: плюсы и минусы Биохимия печени
Биохимия печени