Содержание
- 2. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Electron transfer reactions are called oxidation-reduction or redox reactions. Charges of elements are zero.
- 3. Chapter 6 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Na → Na+1 + 1e- oxidation Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl-1 reduction
- 4. Chapter 6 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Example 1 Mg and O2 react to form MgO. What are the
- 5. Chapter 6 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation States Oxidation states of the elements must be known to balance
- 6. Chapter 6 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Example 2 Find the oxidation state of metals in the following species.
- 8. Скачать презентацию





 Законы химической термодинамики. Часть 1. Физическая и коллоидная химия
Законы химической термодинамики. Часть 1. Физическая и коллоидная химия Презентация по Химии "мінеральні добрива." - скачать смотреть бесплатно_
Презентация по Химии "мінеральні добрива." - скачать смотреть бесплатно_ Образование дипептида
Образование дипептида Лекція № 2 Білкові системи: характеристика, використання фізико-хімічних властивостей у виробництві харчових продуктів
Лекція № 2 Білкові системи: характеристика, використання фізико-хімічних властивостей у виробництві харчових продуктів Карбоновые кислоты. Строение
Карбоновые кислоты. Строение Химический элемент. Неон
Химический элемент. Неон Физические свойства спиртов
Физические свойства спиртов Компьютерные программы для оценки устойчивости, биоконцентрирования и токсичности химических веществ
Компьютерные программы для оценки устойчивости, биоконцентрирования и токсичности химических веществ Chemical bonds
Chemical bonds Органічні розчинники
Органічні розчинники Спирты и фенолы
Спирты и фенолы Аммиак. Соли аммония. Методы получения. Химические свойства аммиака и солей аммония
Аммиак. Соли аммония. Методы получения. Химические свойства аммиака и солей аммония  Презентация Изомерия
Презентация Изомерия  Посуда, ее виды и использование. Работу выполнила Гливинская Анастасия ученица 9 класса МБОУ «СОШ №11»
Посуда, ее виды и использование. Работу выполнила Гливинская Анастасия ученица 9 класса МБОУ «СОШ №11»  Термические превращения алкенов
Термические превращения алкенов Липиды. Элементарный химический состав, содержание, строение, разнообразие, функции
Липиды. Элементарный химический состав, содержание, строение, разнообразие, функции Презентация по Химии "Великие учёные, внёсшие значительный вклад в развитие химии." - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Великие учёные, внёсшие значительный вклад в развитие химии." - скачать смотреть бесплатно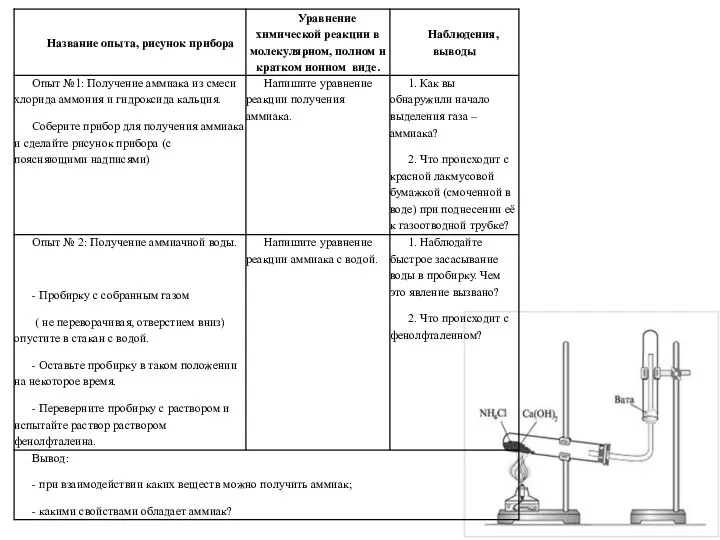 Получение аммиака и изучение его свойств
Получение аммиака и изучение его свойств Характеристика промышленных аэрозолей аллергического и раздражающего действия. Характеристика отдельных нозологических форм
Характеристика промышленных аэрозолей аллергического и раздражающего действия. Характеристика отдельных нозологических форм Химический элемент МЫШЬЯК
Химический элемент МЫШЬЯК Оксиды и кислородсодержащие кислоты неметаллов
Оксиды и кислородсодержащие кислоты неметаллов Аттестационная работа. Рабочая программа по курсу внеурочной деятельности для обучающихся 7 класса Химия в профессиях
Аттестационная работа. Рабочая программа по курсу внеурочной деятельности для обучающихся 7 класса Химия в профессиях Ознайомлення із зразками простих речовин-неметалів
Ознайомлення із зразками простих речовин-неметалів Растворение. Растворимость веществ в воде
Растворение. Растворимость веществ в воде Основные понятия химии
Основные понятия химии Твердоконтактные электрохимические платформы для потенциометрических измерений
Твердоконтактные электрохимические платформы для потенциометрических измерений Коррозия металлов
Коррозия металлов Именные реакции в органической химии. Органический синтез. Механизмы химических процессов
Именные реакции в органической химии. Органический синтез. Механизмы химических процессов