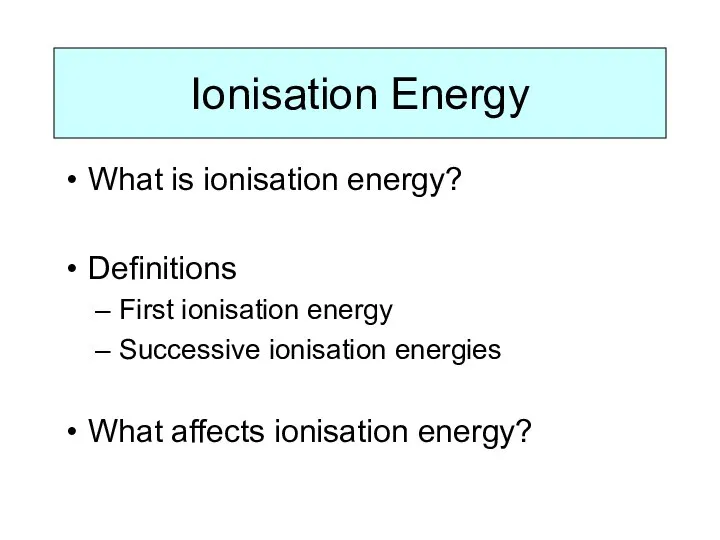
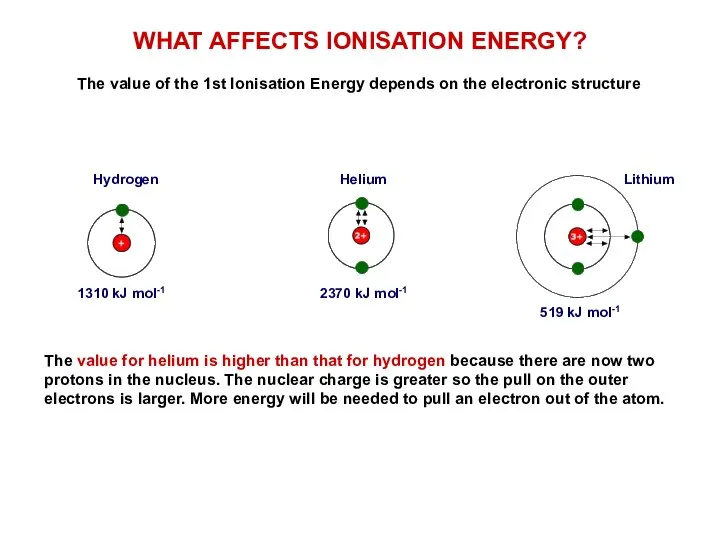
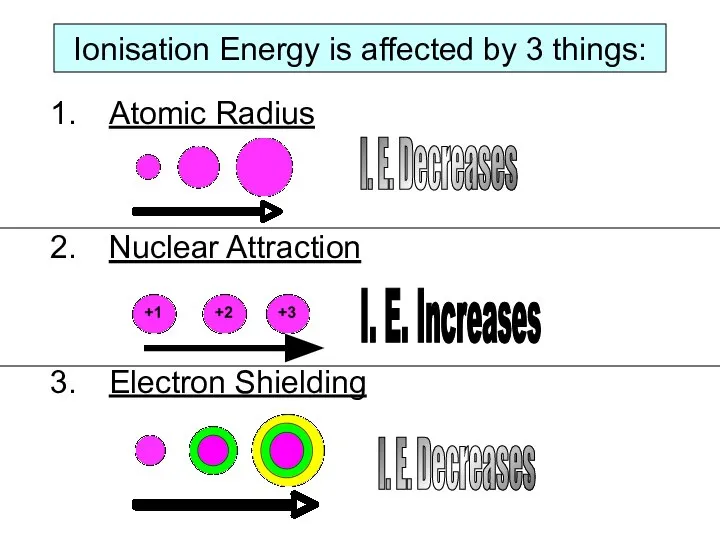
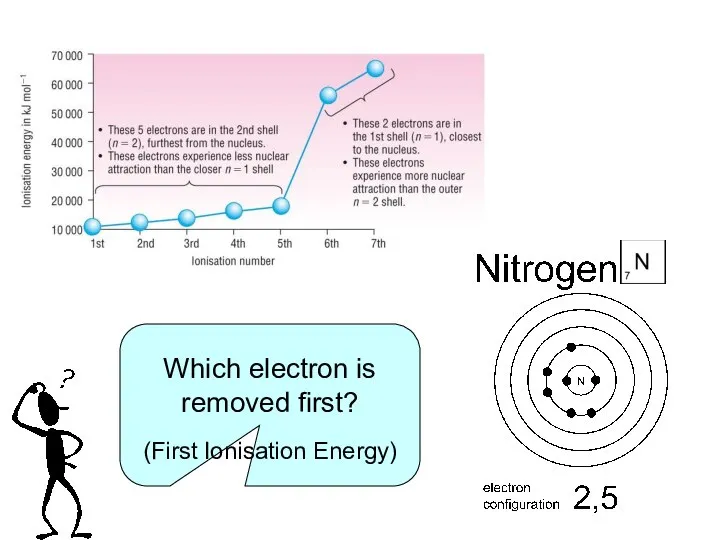
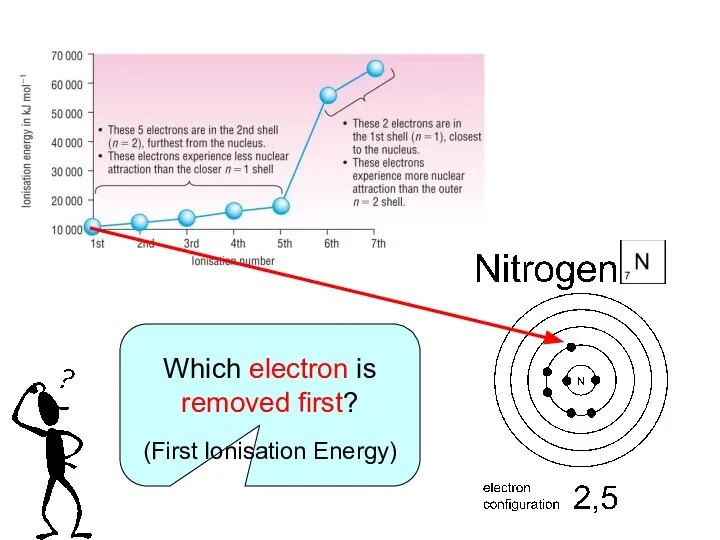
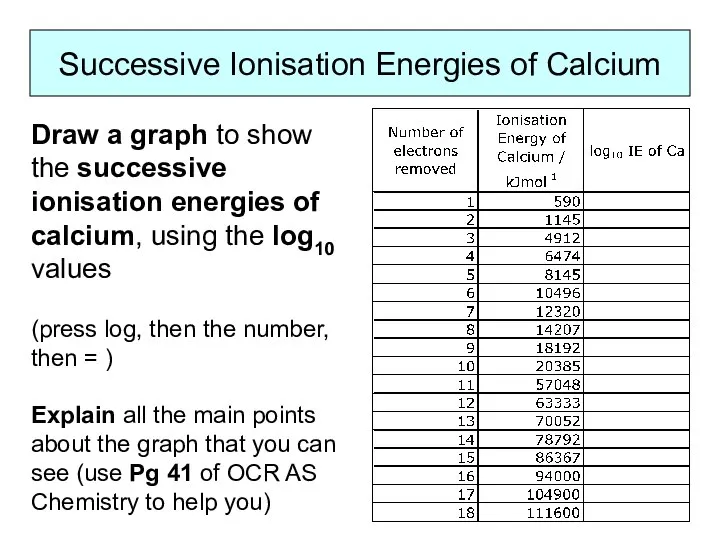
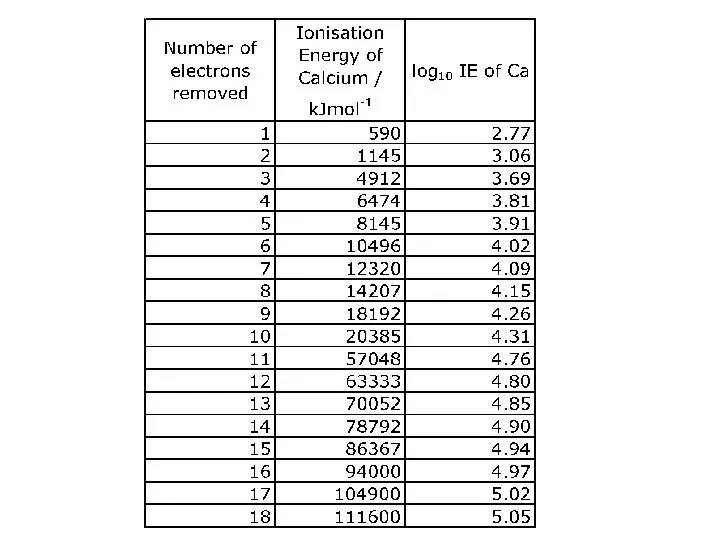
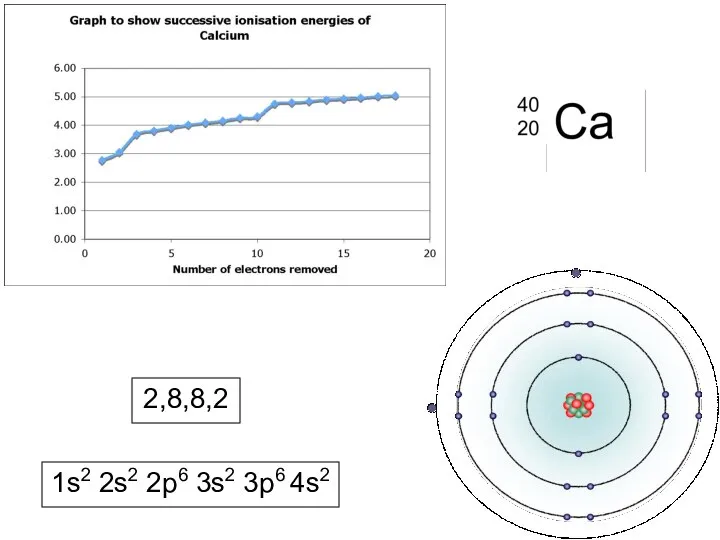
WHAT IS IONISATION ENERGY?
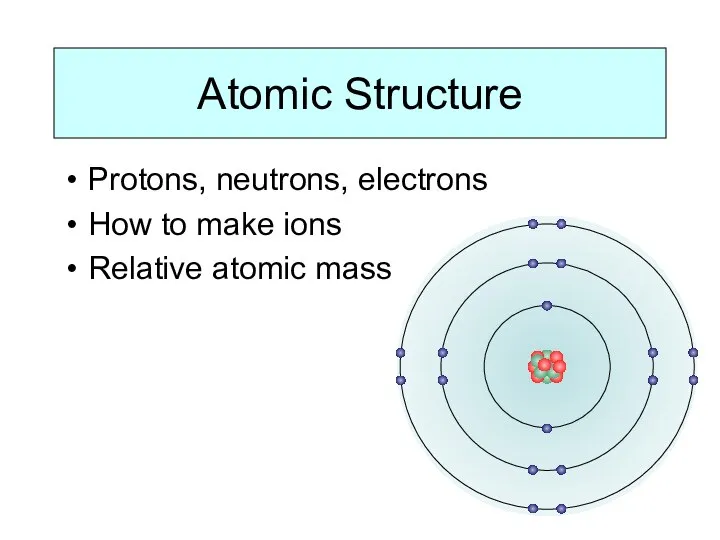
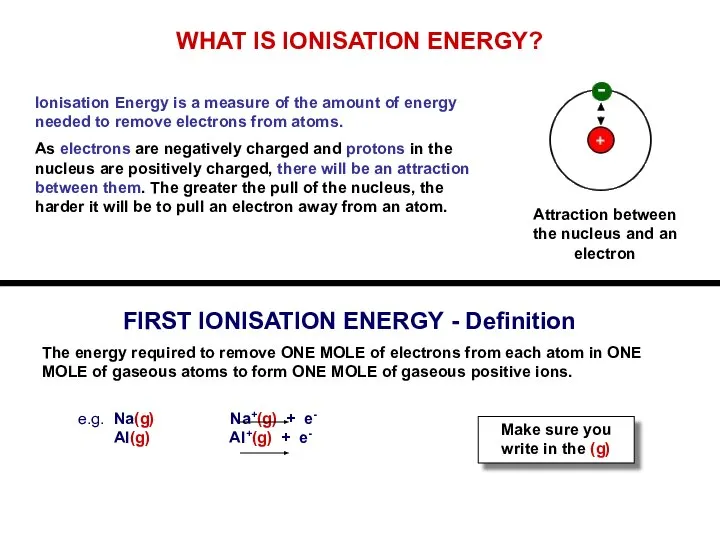
Ionisation Energy is a measure of the amount
of energy needed to remove electrons from atoms.
As electrons are negatively charged and protons in the nucleus are positively charged, there will be an attraction between them. The greater the pull of the nucleus, the harder it will be to pull an electron away from an atom.
FIRST IONISATION ENERGY - Definition
The energy required to remove ONE MOLE of electrons from each atom in ONE MOLE of gaseous atoms to form ONE MOLE of gaseous positive ions.
e.g. Na(g) Na+(g) + e-
Al(g) Al+(g) + e-
Make sure you write in the (g)
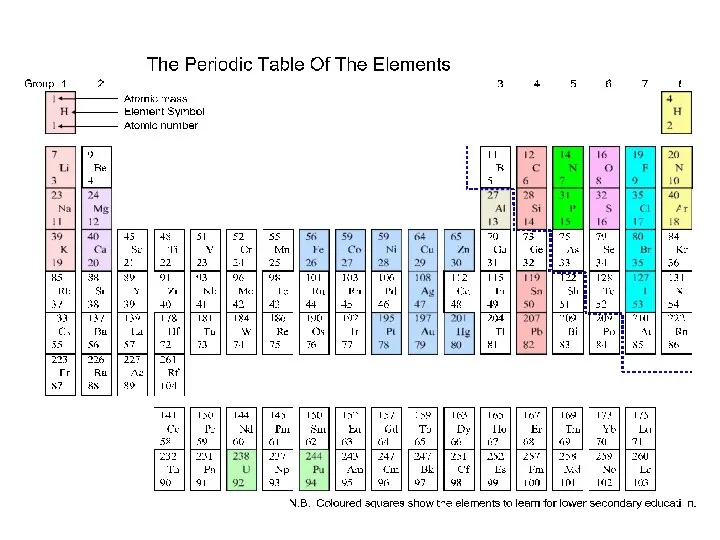
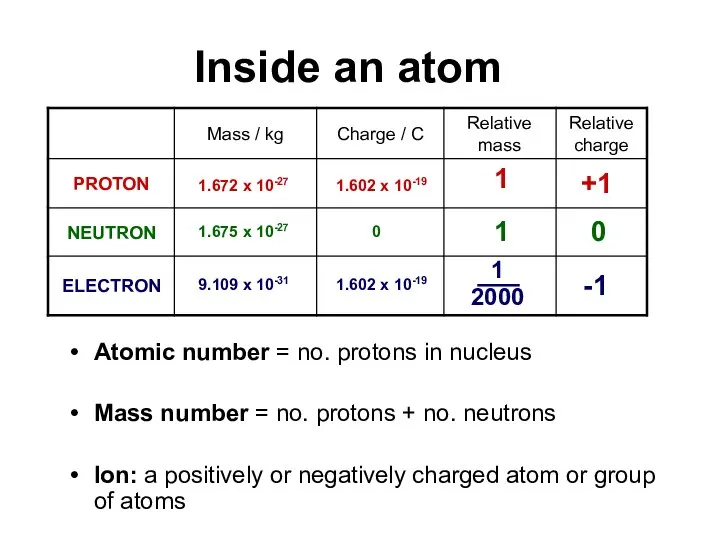


 Классификация химических, физических и механических свойств порошка
Классификация химических, физических и механических свойств порошка Нуклеиновые кислоты
Нуклеиновые кислоты Вредные вещества
Вредные вещества Технологии создания и обработки кристаллических материалов
Технологии создания и обработки кристаллических материалов Номенклатура органических соединений
Номенклатура органических соединений Неметаллы
Неметаллы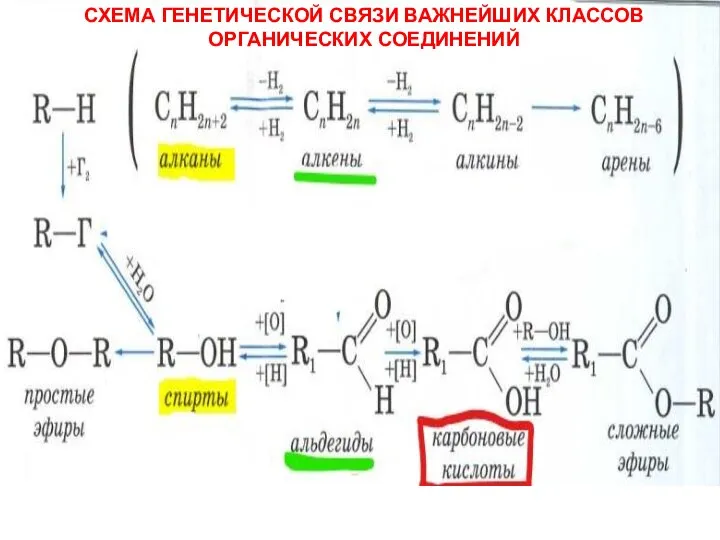 Схема генетической связи важнейших классов органических соединений
Схема генетической связи важнейших классов органических соединений Технология получения гидропероксида изопропилбензола
Технология получения гидропероксида изопропилбензола Iodine
Iodine Коллигативные свойства растворов. Осмос. Осмотическое давление. (Лекция 4)
Коллигативные свойства растворов. Осмос. Осмотическое давление. (Лекция 4) Презентация по Химии "Дисперсные системы" - скачать смотреть
Презентация по Химии "Дисперсные системы" - скачать смотреть  Морфология палочковидных и извитых бактерий. Краски используемые в микробиологии. Приготовление бакпрепаратов. Методы окраски
Морфология палочковидных и извитых бактерий. Краски используемые в микробиологии. Приготовление бакпрепаратов. Методы окраски Классификация, номенклатура углеводородов
Классификация, номенклатура углеводородов Химиялық қауіптілер. Нитраттар
Химиялық қауіптілер. Нитраттар Химическая связь в твердых телах. Классификация твердых тел по типу химической связи
Химическая связь в твердых телах. Классификация твердых тел по типу химической связи Выделение нефтегазоматеринских пород по данным пиролиза. Построение геохимического разреза
Выделение нефтегазоматеринских пород по данным пиролиза. Построение геохимического разреза Методы защиты от коррозии
Методы защиты от коррозии Реакции подлинности лекарственных веществ
Реакции подлинности лекарственных веществ Презентация по Химии "Синтетические моющие средства или химия в ванной" - скачать смотреть _
Презентация по Химии "Синтетические моющие средства или химия в ванной" - скачать смотреть _ Материаловедение. Влияние нагрева на структуру деформированного металла. (Тема 5)
Материаловедение. Влияние нагрева на структуру деформированного металла. (Тема 5) Применение синтетических полимеров в вооружении
Применение синтетических полимеров в вооружении Витамины. Классификация витаминов
Витамины. Классификация витаминов Реакции ионного обмена
Реакции ионного обмена Геохимия природных процессов. Редкие элементы, как индикаторы геодинамических обстановок формирования комплексов. (Лекция 5)
Геохимия природных процессов. Редкие элементы, как индикаторы геодинамических обстановок формирования комплексов. (Лекция 5) Химия атмосферы
Химия атмосферы Электронная конфигурация атома
Электронная конфигурация атома Сера и ее соединения
Сера и ее соединения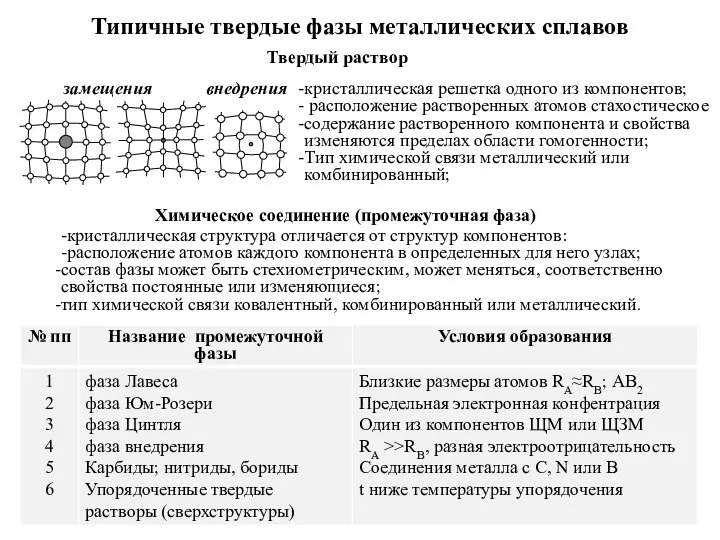 Типичные твердые фазы металлических сплавов
Типичные твердые фазы металлических сплавов